Expulsion is the formal removal of a student from an educational institution, often due to serious misconduct or repeated violations of school policies. This process can significantly impact a student's academic record and future opportunities, emphasizing the importance of understanding school rules and procedures. Discover how expulsion works, its consequences, and ways to navigate the challenges in the full article.
Table of Comparison
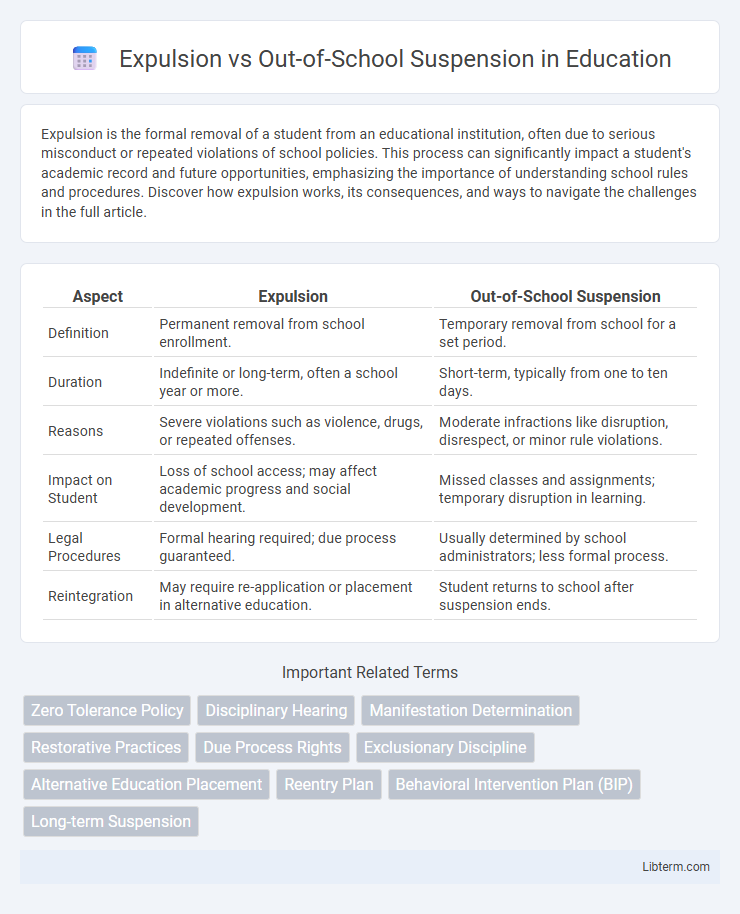
| Aspect | Expulsion | Out-of-School Suspension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent removal from school enrollment. | Temporary removal from school for a set period. |
| Duration | Indefinite or long-term, often a school year or more. | Short-term, typically from one to ten days. |
| Reasons | Severe violations such as violence, drugs, or repeated offenses. | Moderate infractions like disruption, disrespect, or minor rule violations. |
| Impact on Student | Loss of school access; may affect academic progress and social development. | Missed classes and assignments; temporary disruption in learning. |
| Legal Procedures | Formal hearing required; due process guaranteed. | Usually determined by school administrators; less formal process. |
| Reintegration | May require re-application or placement in alternative education. | Student returns to school after suspension ends. |
Understanding Expulsion and Out-of-School Suspension
Expulsion is a formal removal of a student from school for a prolonged period, typically for severe or repeated violations of school rules, often requiring a formal hearing and documentation. Out-of-school suspension (OSS) is a temporary removal from school for days or weeks as a disciplinary action, allowing students to return after the suspension period ends. Both disciplinary measures aim to address behavioral issues, but expulsion is more permanent and carries more significant consequences for the student's educational trajectory.
Key Differences Between Expulsion and Suspension
Expulsion involves the complete removal of a student from school for a prolonged period, often until re-admitted by authorities, whereas out-of-school suspension is a temporary exclusion lasting a few days to weeks. Expulsion typically requires a formal hearing and is reserved for more serious or repeated infractions, while suspension addresses less severe misconduct with shorter disciplinary measures. The legal procedures and documentation for expulsion are more rigorous, ensuring due process rights compared to the relatively administrative approach in suspension cases.
Legal Definitions and Educational Policies
Expulsion is a formal, long-term removal of a student from a school district, often requiring a hearing and documented legal procedures under state education codes, whereas out-of-school suspension (OSS) is a temporary exclusion ranging from one to several days without immediate removal from the district. Educational policies mandate explicit due process rights for expulsions, including written notice and the opportunity for appeal, while suspensions typically involve shorter notices and limited procedural safeguards. Legal definitions vary by state statutes but consistently emphasize the permanency of expulsion compared to the transient nature of OSS, impacting student enrollment status and eligibility for educational services.
Grounds for Expulsion vs Suspension
Expulsion is typically reserved for severe infractions such as violent behavior, possession of weapons, or repeated serious misconduct, reflecting a permanent removal from the school environment. Out-of-school suspension applies to less severe but still significant violations like disruptive behavior, insubordination, or minor drug possession, resulting in temporary exclusion. The grounds for expulsion emphasize long-term safety and behavioral concerns, while suspension addresses short-term disciplinary measures to correct student conduct.
Duration and Long-Term Impact on Students
Expulsion typically involves removal from school for an extended period, often the remainder of the academic year or longer, resulting in a significant disruption to a student's educational trajectory. Out-of-school suspension (OSS) generally lasts from one to ten days, causing a shorter break but still interrupting learning and social development. Long-term impacts of expulsion include increased dropout rates and reduced access to educational resources, while OSS may contribute to behavioral issues and academic decline, though effects are less severe compared to expulsion.
Procedural Steps: Expulsion vs Suspension Process
Expulsion requires a formal hearing where evidence is presented, and the student has a right to legal representation and to appeal the decision, often involving school board review. Out-of-school suspension typically involves a disciplinary meeting with school administrators, notification to parents, and a shorter duration without a formal hearing or appeal process. Both procedures mandate documentation and adherence to state-specific education codes, but expulsion procedures are more stringent due to the severity of removing a student from the school system for an extended period.
Rights of Students and Parents
Students facing expulsion have the right to a formal hearing and legal representation, ensuring due process under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) when applicable. Parents must receive timely written notices detailing the reasons for expulsion or out-of-school suspension, along with the opportunity to appeal decisions and participate in disciplinary hearings. Out-of-school suspension rights typically include access to continued educational services and communication with school officials, safeguarding students' right to education during temporary removal.
Academic and Social Consequences
Expulsion removes students from the school environment for an extended period, often leading to significant academic setbacks such as loss of instructional time and limited access to curriculum resources. Out-of-school suspension temporarily excludes students but maintains the possibility of reintegration, though it still disrupts learning continuity and can result in social isolation. Both disciplinary actions can harm peer relationships, increase dropout rates, and exacerbate behavioral issues, negatively impacting long-term academic achievement and social development.
Alternatives to Expulsion and Suspension
Alternatives to expulsion and out-of-school suspension include restorative justice practices, which emphasize conflict resolution and accountability through mediated dialogue and community service. Positive behavioral interventions and supports (PBIS) promote proactive strategies to improve student behavior and create a supportive school climate, reducing the need for exclusionary discipline. Implementing in-school suspension programs and tailored counseling services helps address underlying issues while keeping students engaged in their education.
School District Responsibilities and Support Systems
School districts must ensure due process and equitable treatment during both expulsions and out-of-school suspensions, complying with state laws and maintaining clear documentation. They are responsible for providing educational continuity through alternative instruction methods or placement in specialized programs to prevent academic disruption. Support systems including counseling, behavioral interventions, and family engagement are essential to address underlying issues and facilitate student reintegration.
Expulsion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com