Cooperative learning enhances student engagement and improves retention by encouraging group collaboration and shared responsibility in the learning process. This method fosters critical thinking and communication skills, enabling learners to benefit from diverse perspectives. Dive deeper into how cooperative learning strategies can transform Your educational experience by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
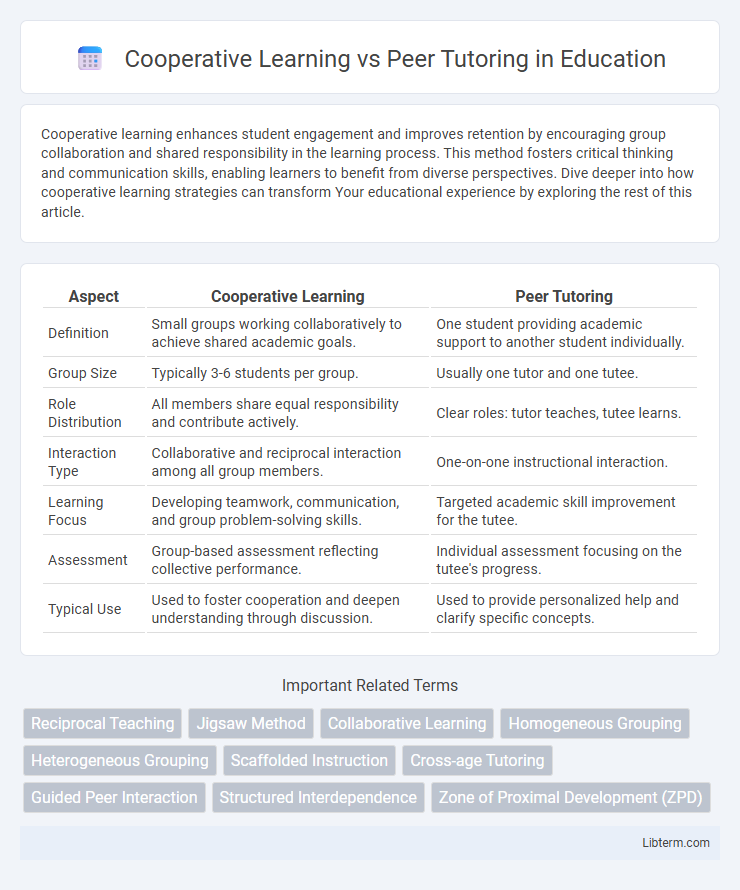
| Aspect | Cooperative Learning | Peer Tutoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small groups working collaboratively to achieve shared academic goals. | One student providing academic support to another student individually. |
| Group Size | Typically 3-6 students per group. | Usually one tutor and one tutee. |
| Role Distribution | All members share equal responsibility and contribute actively. | Clear roles: tutor teaches, tutee learns. |
| Interaction Type | Collaborative and reciprocal interaction among all group members. | One-on-one instructional interaction. |
| Learning Focus | Developing teamwork, communication, and group problem-solving skills. | Targeted academic skill improvement for the tutee. |
| Assessment | Group-based assessment reflecting collective performance. | Individual assessment focusing on the tutee's progress. |
| Typical Use | Used to foster cooperation and deepen understanding through discussion. | Used to provide personalized help and clarify specific concepts. |
Introduction to Cooperative Learning and Peer Tutoring
Cooperative learning involves structured group activities where students work collaboratively to achieve shared learning goals, promoting communication, critical thinking, and social skills. Peer tutoring is a one-on-one or small-group approach where more knowledgeable students provide personalized academic support to their peers, enhancing understanding through explanation and guidance. Both methods foster active engagement and build confidence, but cooperative learning emphasizes teamwork and collective problem-solving while peer tutoring focuses on individualized learning assistance.
Defining Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning is an educational approach where students work together in small groups to achieve shared learning goals, promoting active engagement and the development of social skills. This method emphasizes interdependence, individual accountability, and collaborative problem-solving to enhance understanding and retention of material. Unlike peer tutoring, which typically involves a one-on-one mentoring dynamic, cooperative learning involves equal participation among group members.
Understanding Peer Tutoring
Peer tutoring involves students with varying levels of expertise working one-on-one or in small groups, where a more knowledgeable peer provides personalized guidance and feedback to enhance understanding and skill development. This method promotes active learning, improves communication abilities, and reinforces the tutor's mastery of the subject matter through teaching. Unlike cooperative learning, which emphasizes group collaboration and shared responsibility, peer tutoring focuses more on individualized support tailored to the tutee's specific learning needs.
Key Differences Between Cooperative Learning and Peer Tutoring
Cooperative learning involves small groups of students working collaboratively on a shared task with mutual accountability, while peer tutoring typically pairs a more knowledgeable student with a less proficient learner for individualized instruction. In cooperative learning, all group members actively contribute and engage in problem-solving, enhancing social and communication skills, whereas peer tutoring emphasizes one-on-one support tailored to the tutee's specific learning needs. Assessment in cooperative learning focuses on group performance and interaction, contrasted with peer tutoring's focus on individual progress and mastery.
Benefits of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging active participation and collaboration among diverse group members. It promotes social interaction, communication, and teamwork, leading to improved academic achievement and higher retention rates. Students develop a deeper understanding of content through shared responsibility and peer support, fostering a positive learning environment.
Advantages of Peer Tutoring
Peer tutoring offers personalized learning experiences that cater to individual student needs, promoting deeper understanding and retention of subject matter. It fosters strong communication skills and builds confidence as tutors reinforce their knowledge by teaching peers. The flexibility and immediacy of feedback in peer tutoring enhance student motivation and academic performance more effectively compared to cooperative learning in larger group settings.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Cooperative learning often faces challenges such as uneven participation, social loafing, and difficulty in balancing group dynamics, which can hinder individual accountability and learning outcomes. Peer tutoring may be limited by the tutor's knowledge gaps, inconsistent tutoring quality, and the potential for reinforcing misconceptions without proper oversight. Both approaches require structured guidance and monitoring to maximize effectiveness and address issues related to student motivation, skill disparities, and group cohesion.
Classroom Implementation Strategies
Classroom implementation of cooperative learning involves structuring students into small, diverse groups where each member is assigned specific roles to promote collaboration and accountability, enhancing problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Peer tutoring emphasizes one-on-one or small group interactions, with trained student tutors guiding peers through targeted instruction to address individual learning needs and reinforce content mastery. Effective strategies for both methods include establishing clear objectives, providing training and scaffolding for participants, and using continuous formative assessments to monitor progress and adjust instruction.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Selecting the appropriate instructional strategy between cooperative learning and peer tutoring depends on the classroom dynamics and learning objectives. Cooperative learning fosters group collaboration and critical thinking through structured tasks, ideal for enhancing communication and problem-solving skills. Peer tutoring offers personalized support, making it suitable for addressing individual academic needs and promoting mastery in specific subjects.
Conclusion: Maximizing Student Engagement and Success
Cooperative learning fosters collective problem-solving and communication skills through structured group activities, enhancing student engagement and critical thinking. Peer tutoring provides individualized support, allowing tutors to reinforce their knowledge while tutees receive personalized guidance, improving academic achievement. Combining both strategies maximizes student success by balancing collaborative learning dynamics with tailored instructional support.
Cooperative Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com