Advanced level competency demonstrates your expertise and ability to perform complex tasks efficiently, showcasing mastery in your field. This high degree of skill often leads to greater job responsibilities, leadership opportunities, and professional growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to achieve and leverage advanced level competency in your career.
Table of Comparison
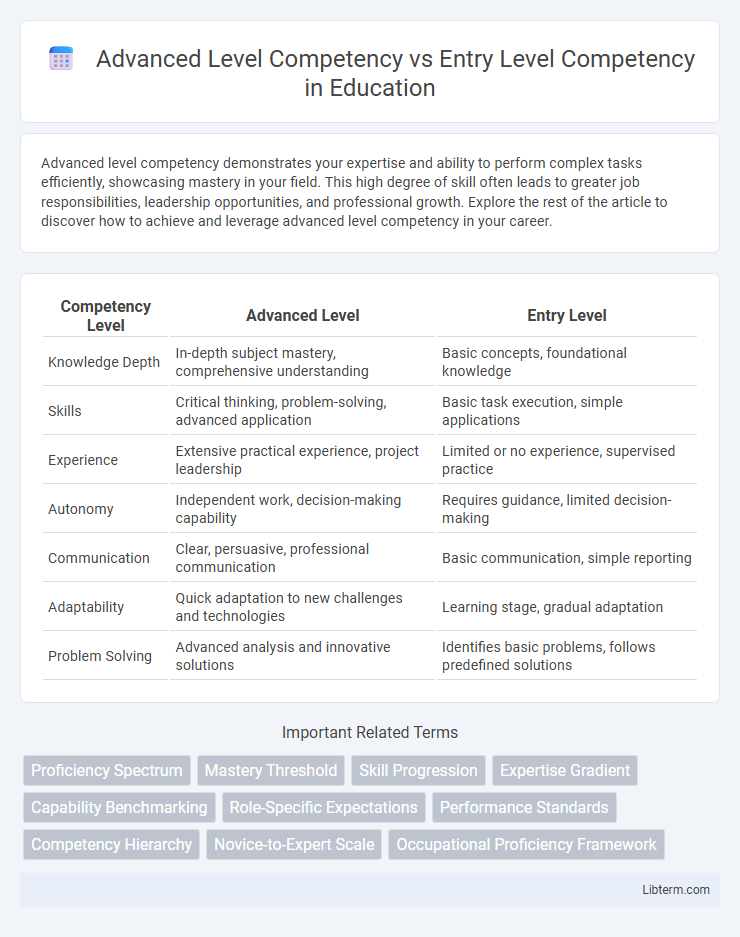
| Competency Level | Advanced Level | Entry Level |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Depth | In-depth subject mastery, comprehensive understanding | Basic concepts, foundational knowledge |
| Skills | Critical thinking, problem-solving, advanced application | Basic task execution, simple applications |
| Experience | Extensive practical experience, project leadership | Limited or no experience, supervised practice |
| Autonomy | Independent work, decision-making capability | Requires guidance, limited decision-making |
| Communication | Clear, persuasive, professional communication | Basic communication, simple reporting |
| Adaptability | Quick adaptation to new challenges and technologies | Learning stage, gradual adaptation |
| Problem Solving | Advanced analysis and innovative solutions | Identifies basic problems, follows predefined solutions |
Defining Entry Level Competency
Entry Level Competency refers to the foundational skills and knowledge required for a newcomer to effectively perform basic tasks within a role, often characterized by limited experience and a need for supervision. It encompasses fundamental problem-solving abilities, understanding of core concepts, and the capacity to follow established procedures. Distinguishing Entry Level from Advanced Level Competency, the latter demands higher analytical skills, independent decision-making, and extensive practical experience in complex scenarios.
Understanding Advanced Level Competency
Advanced Level Competency reflects a deep mastery of skills, integrating complex problem-solving, critical thinking, and strategic decision-making in professional contexts. It requires extensive experience, nuanced understanding, and the ability to adapt knowledge to varied, dynamic situations beyond routine tasks associated with Entry Level Competency. Mastery at this level drives leadership effectiveness, innovation, and contributes significantly to organizational growth and success.
Key Differences Between Entry and Advanced Competencies
Advanced level competency involves a deeper understanding and application of skills, enabling individuals to solve complex problems and lead projects, whereas entry level competency focuses on foundational knowledge and basic task execution. Entry level competency typically requires supervision and guidance, while advanced competency demonstrates autonomy and strategic decision-making capabilities. Key differences include proficiency depth, problem-solving complexity, and leadership responsibilities in advanced competencies compared to the routine and supportive nature of entry level skills.
Skill Sets Required at Entry vs. Advanced Levels
Entry-level competency requires foundational skill sets such as basic problem-solving, effective communication, and familiarity with core tools and concepts within a specific field. Advanced level competency demands specialized skills, including strategic thinking, leadership abilities, and mastery of complex technologies or methodologies. Practical experience and continuous learning are crucial to transition from entry-level tasks to advanced professional responsibilities.
Progression Pathways: From Entry to Advanced Competency
Progression pathways from entry level competency to advanced level competency involve targeted skill development, experiential learning, and mastery of complex concepts within a field. Entry level competency typically includes foundational knowledge and basic task execution, while advanced competency demands strategic thinking, problem-solving, and leadership abilities. Structured training programs, mentorship, and continuous professional development accelerate this transition by reinforcing practical application and expertise growth.
Assessing Competency Levels in the Workplace
Assessing competency levels in the workplace involves evaluating employees' skills, knowledge, and behaviors against defined criteria for both entry-level and advanced-level roles. Entry-level competency focuses on foundational abilities and basic understanding required to perform routine tasks, while advanced-level competency includes specialized expertise, problem-solving skills, and leadership capabilities. Accurate assessment methods such as performance appraisals, skill tests, and behavioral interviews help organizations identify development needs and optimize workforce productivity.
Impact of Competency Levels on Career Growth
Advanced level competency equips professionals with specialized skills and in-depth knowledge, significantly accelerating career growth through leadership roles and higher salary opportunities. Entry level competency provides foundational abilities essential for job entry but limits immediate career advancement and earning potential. Higher competency levels correlate with increased workplace responsibility, influence, and long-term professional development.
Training and Development Strategies
Advanced level competency requires targeted training and development strategies such as customized workshops, mentorship programs, and real-world simulations that deepen expertise and decision-making skills. Entry level competency development focuses on foundational training, including structured onboarding, basic skill-building modules, and frequent feedback cycles to ensure understanding and confidence. Effective training programs blend both approaches by progressively escalating complexity and practical application to bridge entry-level skills to advanced proficiency.
Challenges in Achieving Advanced Competency
Achieving advanced level competency requires overcoming significant challenges such as mastering complex concepts, integrating interdisciplinary knowledge, and consistently applying skills in high-stakes environments. Entry level competency typically involves foundational skills and basic understanding, which do not demand the same depth of critical thinking or problem-solving capabilities. Professional development, sustained practice, and access to expert feedback are crucial factors in bridging the gap between entry and advanced competency levels.
Future Trends in Competency Standards
Advanced level competency integrates complex problem-solving abilities and adaptive learning skills shaped by AI and automation trends, while entry level competency emphasizes foundational knowledge and basic technical skills essential for initial workforce integration. Future competency standards prioritize digital literacy, emotional intelligence, and continuous upskilling to meet evolving industry demands in sectors like technology, healthcare, and finance. Organizations are increasingly adopting competency frameworks that align with emerging technologies, fostering agile and innovative talent capable of driving sustainable growth.
Advanced Level Competency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com