Teacher absenteeism negatively impacts student learning outcomes and disrupts the overall educational environment. Frequent absences can lead to gaps in curriculum coverage and increased workload for other staff. Discover more about how addressing teacher absenteeism can improve your school's academic success in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
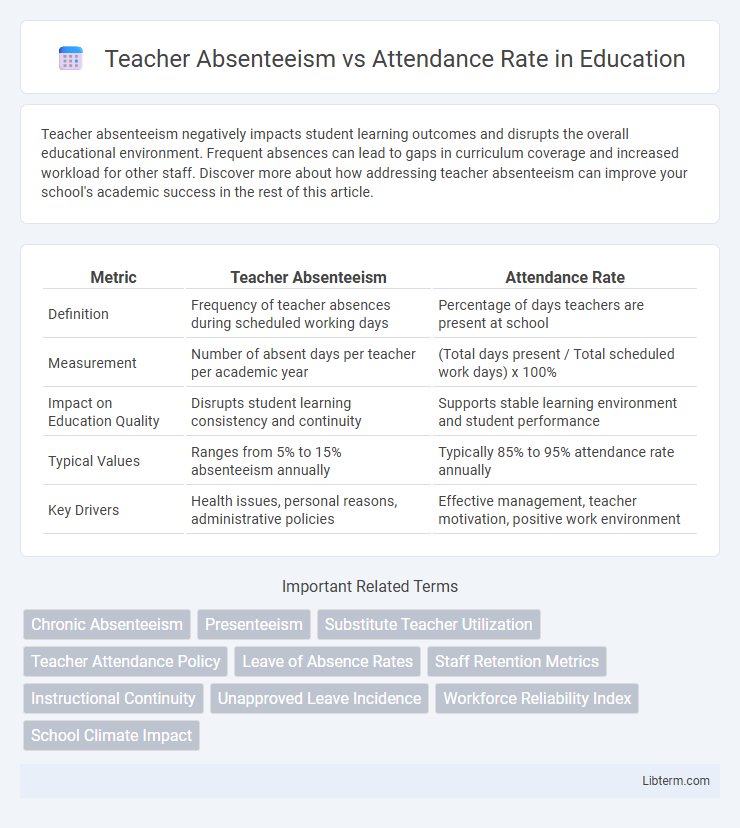
| Metric | Teacher Absenteeism | Attendance Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Frequency of teacher absences during scheduled working days | Percentage of days teachers are present at school |
| Measurement | Number of absent days per teacher per academic year | (Total days present / Total scheduled work days) x 100% |
| Impact on Education Quality | Disrupts student learning consistency and continuity | Supports stable learning environment and student performance |
| Typical Values | Ranges from 5% to 15% absenteeism annually | Typically 85% to 95% attendance rate annually |
| Key Drivers | Health issues, personal reasons, administrative policies | Effective management, teacher motivation, positive work environment |
Introduction to Teacher Absenteeism and Attendance Rate
Teacher absenteeism significantly impacts student learning outcomes by reducing instructional time and hindering curriculum continuity. Attendance rate, expressed as the percentage of teachers present during scheduled working hours, serves as a key metric for assessing school efficiency and educational quality. Understanding the relationship between teacher absenteeism and attendance rates is essential for developing policies aimed at improving teacher reliability and student achievement.
Defining Teacher Absenteeism
Teacher absenteeism refers to the frequency and duration of a teacher's unexplained or unapproved absence from scheduled working days, significantly impacting student learning outcomes and school performance. Attendance rate measures the proportion of days a teacher is present out of the total required working days, serving as a key indicator of teacher reliability and school operational efficiency. High absenteeism rates correlate with lower student achievement, increased workload for present staff, and overall declines in educational quality.
Understanding Attendance Rate in Schools
Attendance rate in schools measures the percentage of days students or teachers are present out of the total school days. High attendance rates correlate positively with improved student performance and overall school effectiveness. Understanding teacher attendance rate helps identify patterns of absenteeism that can impact instructional quality and student outcomes.
Causes of Teacher Absenteeism
Teacher absenteeism is primarily caused by factors such as illness, lack of motivation, inadequate working conditions, and personal or family responsibilities. High stress levels and limited access to professional development also contribute significantly to frequent absences. Understanding these causes helps improve attendance rates by addressing underlying issues within educational institutions.
Impact of Absenteeism on Student Achievement
Teacher absenteeism significantly lowers attendance rates, directly impacting student achievement by disrupting instructional continuity and reducing learning time. Studies reveal that higher rates of teacher absences correlate with lower student test scores and decreased academic performance, particularly in low-income schools. Consistent teacher presence improves classroom stability, fostering better engagement and positive educational outcomes for students.
Factors Influencing Teacher Attendance
Teacher attendance rates are influenced by multiple factors such as job satisfaction, school leadership quality, work environment, and availability of professional development opportunities. High levels of stress, health issues, and inadequate support systems contribute significantly to teacher absenteeism. Effective policies targeting improved working conditions and teacher motivation can enhance attendance rates and reduce absenteeism.
Comparing Absenteeism and Attendance Metrics
Teacher absenteeism directly impacts student learning outcomes and school performance by reducing instructional time, with rates often measured as the percentage of days teachers are absent over a given period. Attendance rate metrics quantify the proportion of days teachers are present, commonly expressed as a percentage, serving as a critical indicator of educational stability and workforce reliability. Comparing absenteeism with attendance rates highlights the inverse relationship between these metrics, providing key insights for school administrators to allocate resources effectively and develop targeted interventions to improve teacher presence.
Strategies to Improve Teacher Attendance
Implementing comprehensive monitoring systems using biometric attendance and real-time data analytics significantly reduces teacher absenteeism by promoting accountability. Professional development programs that emphasize motivation and well-being enhance teacher commitment, directly increasing attendance rates. Incentive schemes, such as performance-based rewards and community recognition, effectively encourage consistent teacher presence in classrooms.
Monitoring and Reporting Attendance Data
Effective monitoring and reporting of teacher attendance data are crucial for addressing teacher absenteeism, which directly impacts student learning outcomes. Utilizing digital attendance systems and real-time data analytics helps schools track patterns, identify chronic absenteeism, and allocate resources for timely interventions. Transparent reporting mechanisms enable education authorities to set accountability standards and improve overall teacher attendance rates, fostering a more reliable and productive educational environment.
Conclusion: Addressing Teacher Absenteeism for Educational Success
Reducing teacher absenteeism directly improves the attendance rate, enhancing student learning outcomes and overall school performance. Implementing effective monitoring systems and offering supportive incentives are critical strategies to maintain consistent teacher presence. Prioritizing teacher attendance fosters a stable educational environment, essential for maximizing student achievement and long-term academic success.
Teacher Absenteeism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com