Assignments play a crucial role in reinforcing your understanding of key concepts by encouraging active engagement with the material. They help develop critical thinking, time management, and research skills essential for academic success. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective strategies for tackling assignments efficiently.
Table of Comparison
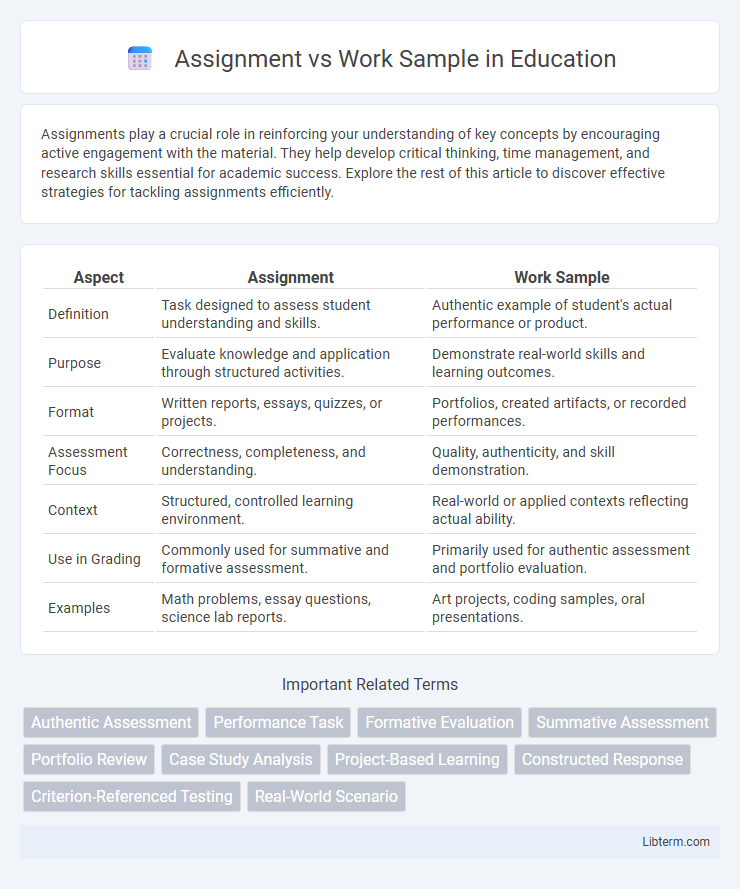
| Aspect | Assignment | Work Sample |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Task designed to assess student understanding and skills. | Authentic example of student's actual performance or product. |
| Purpose | Evaluate knowledge and application through structured activities. | Demonstrate real-world skills and learning outcomes. |
| Format | Written reports, essays, quizzes, or projects. | Portfolios, created artifacts, or recorded performances. |
| Assessment Focus | Correctness, completeness, and understanding. | Quality, authenticity, and skill demonstration. |
| Context | Structured, controlled learning environment. | Real-world or applied contexts reflecting actual ability. |
| Use in Grading | Commonly used for summative and formative assessment. | Primarily used for authentic assessment and portfolio evaluation. |
| Examples | Math problems, essay questions, science lab reports. | Art projects, coding samples, oral presentations. |
Introduction to Assignment and Work Sample
An assignment is a structured task designed to evaluate specific skills or knowledge within an educational or professional context. A work sample, in contrast, provides a practical demonstration of an individual's ability to perform real-world tasks by showcasing actual completed work. Both tools serve assessment purposes but differ in format and application, with assignments often being hypothetical or controlled exercises while work samples reflect authentic job performance.
Defining Assignment and Work Sample
An assignment is a specific task or project given to assess an individual's understanding or skills within a particular subject or job role. A work sample involves the actual output or deliverable produced by an individual, demonstrating practical abilities and proficiency in real-world scenarios. Both tools are essential for evaluating competence but differ in their approach: assignments test theoretical knowledge, while work samples showcase applied expertise.
Purpose and Objectives
Assignments primarily aim to evaluate a student's understanding and application of theoretical concepts through structured tasks, fostering knowledge retention and critical thinking skills. Work samples showcase actual performance by presenting tangible evidence of skills and competencies in real-world or simulated scenarios, helping employers or educators assess practical abilities and quality of output. Both methods serve distinct purposes: assignments focus on learning reinforcement and conceptual clarity, while work samples emphasize demonstration of proficiency and readiness for specific tasks or roles.
Key Differences Between Assignment and Work Sample
Assignments typically refer to tasks or projects assigned to evaluate a learner's understanding of specific concepts, while work samples represent actual pieces of completed work that showcase skills and competencies. Assignments are often time-bound and structured with specific instructions, whereas work samples are more flexible, demonstrating real-world application and quality of work over time. The key difference lies in their purpose: assignments assess knowledge through prescribed tasks, whereas work samples provide tangible evidence of practical ability and experience.
Evaluation Criteria and Assessment Methods
Assignment evaluation criteria emphasize clarity, coherence, relevance to the topic, and the ability to demonstrate understanding through written or creative outputs. Work sample assessments prioritize practical skills, accuracy, application of knowledge, and real-world problem-solving demonstrated through physical or digital products. Assessment methods for assignments typically include rubrics analyzing structure and content quality, while work samples are often evaluated using performance checklists and direct observation.
Advantages of Using Assignments
Assignments provide structured learning experiences that reinforce key concepts through practical application, enhancing students' retention and understanding. They enable personalized feedback, allowing educators to identify areas for improvement and tailor instruction accordingly. This targeted approach supports skill development and academic growth more effectively than work samples alone.
Benefits of Implementing Work Samples
Work samples offer a more accurate assessment of candidates' practical skills by simulating real job tasks, leading to better job performance predictions compared to traditional assignments. Implementing work samples reduces hiring bias and increases the validity of selection processes, ensuring candidates meet the specific requirements of the role. Organizations benefit from higher retention rates and improved employee satisfaction due to more precise talent matching through work sample evaluations.
Use Cases in Academic and Professional Settings
Assignments serve as structured tasks in academic settings to assess students' understanding and mastery of course material, often involving essays, problem sets, or presentations. Work samples, common in professional environments, demonstrate an individual's practical skills and competencies through tangible outputs like portfolios, coding projects, or design prototypes. Both methods provide evaluators with insights into performance, but assignments emphasize theoretical knowledge while work samples highlight applied expertise.
Which to Choose: Assignment or Work Sample?
Choosing between an assignment and a work sample depends on the specific goals of evaluation and the context of the task. Assignments typically assess comprehension and learning progress through structured questions, while work samples demonstrate practical skills and real-world task performance. For accurate skill validation and portfolio enhancement, work samples often provide more compelling evidence than traditional assignments.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Assignment and work sample assessments provide distinct insights into candidate capabilities, with assignments offering scenario-based problem solving and work samples demonstrating actual task execution. Best practices include aligning assessment type with job requirements, ensuring realistic and relevant tasks, and incorporating objective evaluation criteria to enhance predictive validity. Leveraging both methods together can optimize talent selection by combining theoretical understanding with practical proficiency.
Assignment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com