Authenticity means staying true to your values, beliefs, and identity without pretense or imitation. Embracing authenticity fosters genuine connections, boosts self-confidence, and promotes personal growth in both your personal and professional life. Discover how cultivating authenticity can transform your relationships and success by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
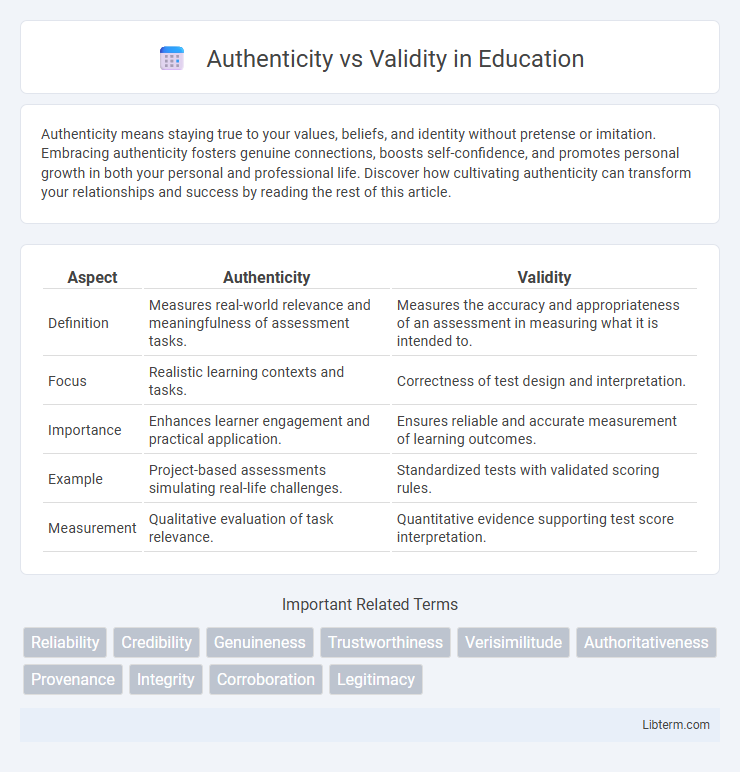
| Aspect | Authenticity | Validity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures real-world relevance and meaningfulness of assessment tasks. | Measures the accuracy and appropriateness of an assessment in measuring what it is intended to. |
| Focus | Realistic learning contexts and tasks. | Correctness of test design and interpretation. |
| Importance | Enhances learner engagement and practical application. | Ensures reliable and accurate measurement of learning outcomes. |
| Example | Project-based assessments simulating real-life challenges. | Standardized tests with validated scoring rules. |
| Measurement | Qualitative evaluation of task relevance. | Quantitative evidence supporting test score interpretation. |
Understanding Authenticity: Core Concepts
Authenticity centers on the genuine expression of identity, emphasizing self-awareness, honesty, and alignment between one's values and actions. It involves recognizing internal motivations and resisting external pressures that may lead to inauthentic behavior. By fostering authenticity, individuals achieve deeper psychological well-being and meaningful interpersonal connections.
Defining Validity in Context
Validity in context refers to the degree to which a measurement or assessment accurately reflects the specific concept or variable it is intended to measure, ensuring that the results are applicable and meaningful within the given framework. It encompasses construct validity, which confirms that the test truly represents the theoretical construct, and criterion validity, which compares outcomes with external benchmarks to verify relevance. Establishing validity is crucial for maintaining the integrity of data interpretation and avoiding misleading conclusions in research or practical applications.
Key Differences: Authenticity vs Validity
Authenticity refers to the genuineness or originality of an object, document, or identity, ensuring it is real and not counterfeit or altered. Validity concerns the correctness or legitimacy of a claim, argument, or test, confirming it meets the required standards and criteria for accuracy or effectiveness. Key differences include authenticity emphasizing origin and trustworthiness, while validity focuses on the logical soundness and appropriateness within a specific context.
The Role of Authenticity in Personal Identity
Authenticity plays a crucial role in personal identity by aligning an individual's actions and beliefs with their true self, fostering a sense of integrity and self-coherence. Unlike validity, which measures the logical or factual correctness of information, authenticity centers on the genuineness of experiences and the congruence between external expressions and internal values. Cultivating authenticity supports psychological well-being and resilience, reinforcing a stable and meaningful personal identity.
Validity in Academic and Professional Settings
Validity in academic and professional settings ensures that assessments, tests, and research accurately measure what they intend to, supporting credible and reliable outcomes. It encompasses content validity, construct validity, and criterion-related validity, which collectively confirm the appropriateness and applicability of evaluation tools. High validity strengthens decision-making processes, enhances the quality of academic research, and validates professional certifications and performance appraisals.
Measuring Authenticity: Tools and Challenges
Measuring authenticity involves evaluating the genuineness and originality of content or identity using tools like biometric verification, blockchain records, and digital watermarking. Challenges in this process include detecting sophisticated forgeries, ensuring privacy during data collection, and establishing standardized metrics across diverse platforms. Advanced AI algorithms and cross-referencing databases enhance accuracy but require constant updating to counter evolving fraudulent techniques.
Assessing Validity: Standards and Criteria
Assessing validity involves applying rigorous standards and criteria to ensure that a measurement or test accurately reflects the concept it intends to measure. Key validity types include content validity, construct validity, and criterion-related validity, each with specific evaluation methods such as expert reviews, correlation analyses, and predictive testing. Adherence to established frameworks like the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing guarantees systematic validation processes that enhance reliability and interpretability of assessment outcomes.
Real-World Applications: Authenticity vs Validity
Authenticity in real-world applications emphasizes genuine representation and alignment with actual context, ensuring that processes or data reflect true conditions or experiences. Validity measures the accuracy and reliability of outcomes, confirming that results or tools effectively fulfill their intended purpose. Balancing authenticity and validity enhances decision-making in fields like education, research, and user experience design by providing trustworthy and relevant insights.
Common Misconceptions Explained
Authenticity and validity are often confused, but authenticity refers to the genuineness of a source or material, while validity concerns the accuracy and credibility of the information or argument presented. A common misconception is assuming that authentic sources are automatically valid without critical evaluation of their content. Understanding this distinction is crucial for proper research and analysis in academic and professional contexts.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Authenticity and Validity
Striking a balance between authenticity and validity in assessments ensures that evaluation methods accurately measure real-world skills while maintaining rigorous standards. Authenticity emphasizes practical, relevant tasks reflecting genuine contexts, whereas validity guarantees that these tasks effectively assess the intended competencies. Integrating both concepts involves designing assessments that are both meaningful and reliable, enhancing the overall quality of educational and professional evaluations.
Authenticity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com