Game-based learning enhances engagement and motivation by integrating educational content with interactive gameplay. It promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and collaboration through immersive experiences that adapt to different learning styles. Discover how game-based learning can transform your educational approach by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
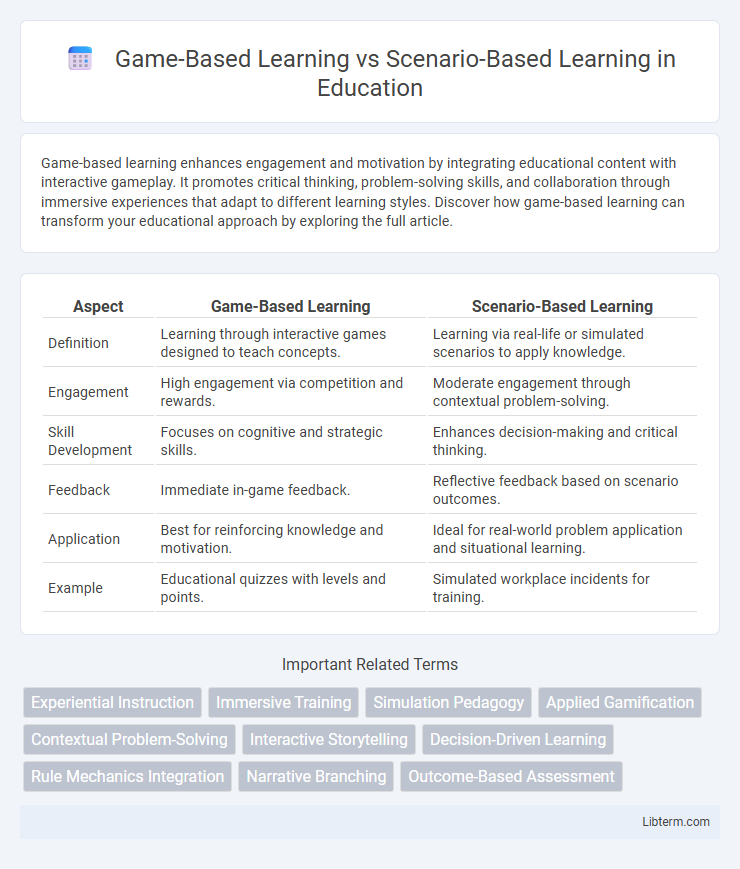
| Aspect | Game-Based Learning | Scenario-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through interactive games designed to teach concepts. | Learning via real-life or simulated scenarios to apply knowledge. |
| Engagement | High engagement via competition and rewards. | Moderate engagement through contextual problem-solving. |
| Skill Development | Focuses on cognitive and strategic skills. | Enhances decision-making and critical thinking. |
| Feedback | Immediate in-game feedback. | Reflective feedback based on scenario outcomes. |
| Application | Best for reinforcing knowledge and motivation. | Ideal for real-world problem application and situational learning. |
| Example | Educational quizzes with levels and points. | Simulated workplace incidents for training. |
Introduction to Game-Based Learning and Scenario-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning utilizes interactive games to enhance engagement and retention by embedding educational content within gameplay mechanics, fostering an immersive learning environment. Scenario-Based Learning presents learners with realistic, contextual challenges that encourage critical thinking and problem-solving through decision-making processes in simulated situations. Both methods prioritize active participation and experiential learning, but Game-Based Learning emphasizes motivation through play, whereas Scenario-Based Learning focuses on practical application in relevant contexts.
Defining Game-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning is an instructional approach that uses video games or gamified elements to engage learners, enhance motivation, and reinforce knowledge through interactive, rule-based challenges. It incorporates game mechanics such as point scoring, competition, and feedback loops to promote active participation and skill acquisition. This method leverages digital or physical games to create immersive experiences that foster problem-solving and critical thinking within educational contexts.
Defining Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-Based Learning (SBL) immerses learners in realistic, context-driven situations aimed at developing critical thinking and decision-making skills. Unlike Game-Based Learning, which often emphasizes engagement through game mechanics and rewards, SBL focuses on narrative and problem-solving within authentic scenarios to deepen understanding. This method enhances practical application of knowledge by simulating real-world challenges.
Key Differences Between Game-Based and Scenario-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning emphasizes interactive gameplay and challenges to foster engagement and motivation, leveraging points, levels, and rewards to drive progress. Scenario-Based Learning centers on realistic, context-driven situations that develop critical thinking and decision-making by simulating real-world complexities. The key difference lies in Game-Based Learning's focus on entertainment and skill acquisition through play, while Scenario-Based Learning prioritizes practical application of knowledge in lifelike scenarios.
Benefits of Game-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning enhances engagement through interactive gameplay that motivates learners and improves knowledge retention by providing immediate feedback and rewards. It fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills in a dynamic environment, promoting active learning and collaboration. Studies show game-based approaches can increase motivation and adaptability, leading to higher academic performance compared to traditional methods.
Benefits of Scenario-Based Learning
Scenario-based learning enhances critical thinking and decision-making skills by immersing learners in realistic situations that require problem-solving and application of knowledge. This method fosters deeper understanding and long-term retention through contextual engagement, promoting active learning and immediate feedback. It also supports soft skills development, such as communication and teamwork, which are essential in real-world professional environments.
Challenges in Implementing Game-Based Learning
Game-based learning faces challenges such as high development costs, technological requirements, and difficulties aligning game mechanics with educational objectives. Limited teacher training and resistance to adopting new digital tools also hinder effective implementation. Ensuring engagement while maintaining curriculum relevance requires continuous evaluation and adaptation of game content.
Challenges in Implementing Scenario-Based Learning
Implementing scenario-based learning presents challenges such as the need for realistic, context-rich content that requires significant time and expertise to develop effectively. Educators often face difficulties in designing scenarios that balance complexity with learner engagement while ensuring alignment with instructional goals. Furthermore, technological limitations and the requirement for learner facilitation can hinder seamless integration into diverse educational environments.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between game-based learning and scenario-based learning depends on factors such as learner engagement, educational goals, and content complexity. Game-based learning excels in motivating learners through interactive challenges and rewards, making it ideal for skill acquisition and retention. Scenario-based learning supports decision-making and critical thinking by immersing learners in realistic contexts, which is effective for developing problem-solving abilities and applying knowledge in real-world situations.
Future Trends in Learning Methodologies
Game-based learning integrates interactive gameplay mechanics to enhance engagement and motivation, showing significant growth with advancements in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies. Scenario-based learning emphasizes immersive, real-world problem solving through carefully designed narratives, increasingly incorporating AI-driven adaptive feedback to personalize learner experiences. Future trends indicate a convergence of these methodologies, leveraging data analytics and machine learning to create hybrid models that optimize skill retention and critical thinking in diverse educational contexts.
Game-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com