Cognitive skills encompass the mental capabilities required for learning, problem-solving, and decision-making, including memory, attention, and reasoning. Developing these skills enhances your ability to process information efficiently and adapt to new challenges. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective strategies for strengthening your cognitive abilities.
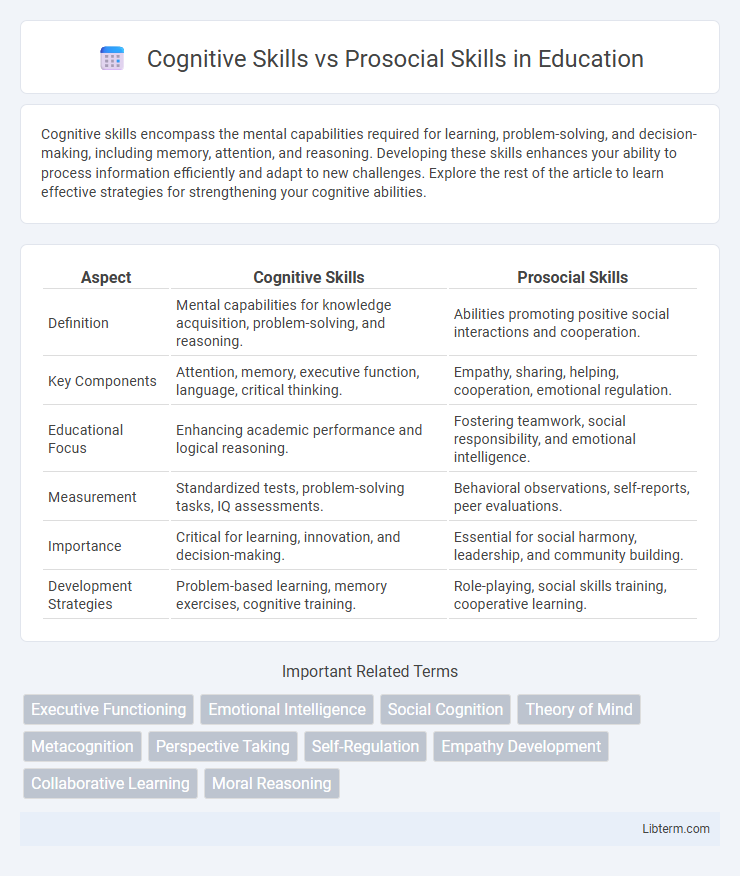
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cognitive Skills | Prosocial Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mental capabilities for knowledge acquisition, problem-solving, and reasoning. | Abilities promoting positive social interactions and cooperation. |
| Key Components | Attention, memory, executive function, language, critical thinking. | Empathy, sharing, helping, cooperation, emotional regulation. |
| Educational Focus | Enhancing academic performance and logical reasoning. | Fostering teamwork, social responsibility, and emotional intelligence. |
| Measurement | Standardized tests, problem-solving tasks, IQ assessments. | Behavioral observations, self-reports, peer evaluations. |
| Importance | Critical for learning, innovation, and decision-making. | Essential for social harmony, leadership, and community building. |
| Development Strategies | Problem-based learning, memory exercises, cognitive training. | Role-playing, social skills training, cooperative learning. |
Understanding Cognitive Skills: Definition and Importance
Cognitive skills refer to mental capabilities such as attention, memory, reasoning, and problem-solving that enable individuals to process information effectively and adapt to new situations. These skills are fundamental for learning, decision-making, and goal-directed behavior, forming the foundation for academic achievement and everyday functioning. Understanding cognitive skills is crucial because they influence how people acquire knowledge, solve problems, and navigate complex environments, distinguishing them from prosocial skills that primarily involve social interactions and empathy.
Prosocial Skills: What They Are and Why They Matter
Prosocial skills encompass behaviors such as empathy, cooperation, and effective communication that promote positive social interactions and relationships. These skills play a crucial role in fostering teamwork, reducing conflicts, and enhancing emotional intelligence, which are essential for personal and professional success. Developing prosocial skills contributes to a supportive community environment and improves overall mental health by encouraging understanding and collaboration.
Key Differences Between Cognitive and Prosocial Skills
Cognitive skills involve the mental processes required for acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and senses, such as attention, memory, problem-solving, and reasoning. Prosocial skills refer to behaviors that promote positive social interactions and relationships, including empathy, cooperation, communication, and conflict resolution. The key difference lies in cognitive skills being primarily focused on intellectual functions and information processing, whereas prosocial skills are centered around social awareness and interpersonal effectiveness.
The Role of Cognitive Skills in Academic Success
Cognitive skills such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and critical thinking play a crucial role in academic success by enabling students to process information efficiently and apply knowledge effectively. These skills facilitate comprehension, reasoning, and the ability to tackle complex tasks across subjects like mathematics, reading, and science. Enhancing cognitive abilities through targeted exercises directly correlates with improved academic performance, making them foundational for learning and intellectual development.
How Prosocial Skills Influence Social Development
Prosocial skills, such as empathy, cooperation, and effective communication, play a critical role in enhancing social development by fostering positive interactions and building strong relationships. These skills contribute to emotional intelligence, enabling individuals to navigate social environments, resolve conflicts, and collaborate efficiently within groups. The development of prosocial behaviors supports community engagement and promotes a sense of belonging, which are essential for healthy social growth.
Cognitive Skills and Emotional Intelligence Connection
Cognitive skills encompass mental processes such as attention, memory, and problem-solving, which are fundamental for developing emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence relies on these cognitive abilities to perceive, understand, and regulate emotions effectively in oneself and others. Strengthening cognitive skills enhances emotional awareness and empathy, fostering better interpersonal relationships and prosocial behavior.
Prosocial Skills in Building Positive Relationships
Prosocial skills, such as empathy, active listening, and cooperation, play a crucial role in building positive relationships by fostering trust and mutual understanding. These skills enable individuals to respond compassionately to others' needs and emotions, creating a supportive social environment. Developing prosocial behaviors enhances social cohesion, reduces conflicts, and promotes collaboration in personal and professional settings.
Enhancing Cognitive Skills: Effective Strategies
Enhancing cognitive skills involves targeted strategies such as problem-solving exercises, memory training, and critical thinking activities designed to improve mental processes like attention, reasoning, and decision-making. Incorporating cognitive challenges through puzzles, strategic games, and educational technology promotes neuroplasticity and strengthens executive functions. Structured learning environments and consistent practice enable measurable improvements in processing speed, working memory, and cognitive flexibility essential for academic and professional success.
Developing Prosocial Skills in Children and Adults
Developing prosocial skills in children and adults fosters empathy, cooperation, and effective communication, which are essential for building strong social relationships. Techniques such as modeling positive behavior, encouraging perspective-taking, and practicing active listening enhance emotional intelligence and social understanding. Structured group activities and real-life social interactions also promote the development of sharing, helping, and conflict resolution abilities, contributing to overall social competence.
Integrating Cognitive and Prosocial Skills for Holistic Growth
Integrating cognitive skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making with prosocial skills like empathy, cooperation, and communication fosters holistic growth in individuals. This combination enhances emotional intelligence, supports effective collaboration, and promotes adaptive learning in diverse social environments. Research indicates that educational programs targeting both skill sets lead to improved academic performance and stronger social relationships.
Cognitive Skills Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com