Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and content to meet the diverse learning needs and strengths of each student, enhancing engagement and comprehension. By incorporating varied instructional strategies, educators can support diverse learners, including those with different abilities, interests, and learning styles. Explore the full article to discover practical tips and benefits for implementing differentiated instruction in your classroom.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Differentiated Instruction | Homogeneous Grouping |
|---|---|---|
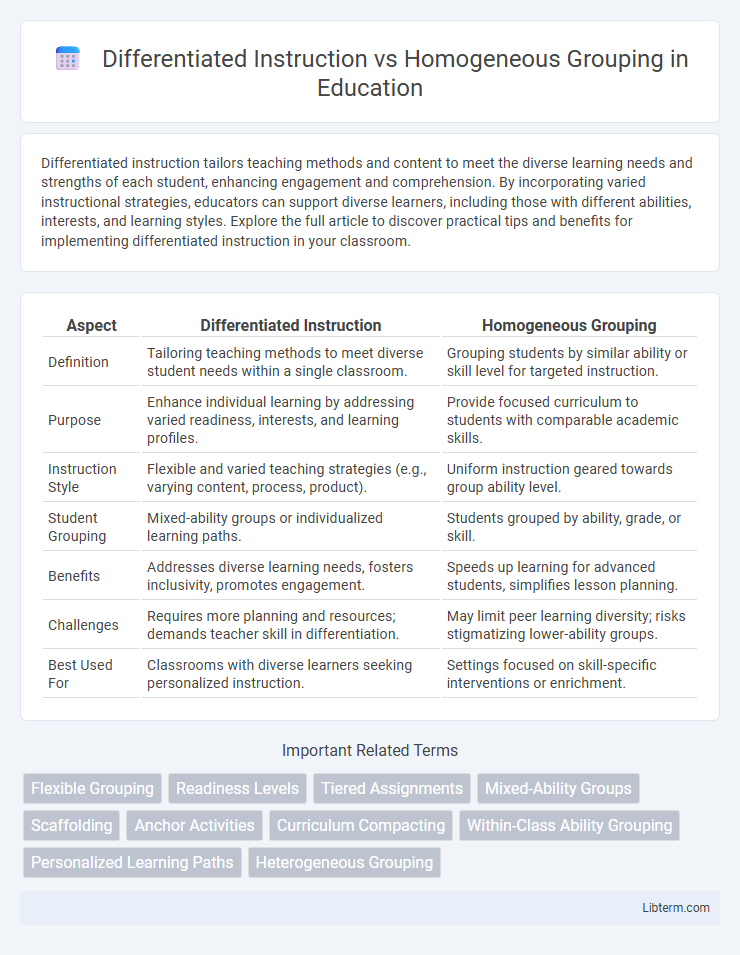
| Definition | Tailoring teaching methods to meet diverse student needs within a single classroom. | Grouping students by similar ability or skill level for targeted instruction. |
| Purpose | Enhance individual learning by addressing varied readiness, interests, and learning profiles. | Provide focused curriculum to students with comparable academic skills. |
| Instruction Style | Flexible and varied teaching strategies (e.g., varying content, process, product). | Uniform instruction geared towards group ability level. |
| Student Grouping | Mixed-ability groups or individualized learning paths. | Students grouped by ability, grade, or skill. |
| Benefits | Addresses diverse learning needs, fosters inclusivity, promotes engagement. | Speeds up learning for advanced students, simplifies lesson planning. |
| Challenges | Requires more planning and resources; demands teacher skill in differentiation. | May limit peer learning diversity; risks stigmatizing lower-ability groups. |
| Best Used For | Classrooms with diverse learners seeking personalized instruction. | Settings focused on skill-specific interventions or enrichment. |
Introduction to Differentiated Instruction and Homogeneous Grouping
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and materials to accommodate diverse student abilities, learning styles, and interests within a single classroom setting, promoting personalized learning experiences. Homogeneous grouping organizes students by similar skill levels or abilities, enabling targeted instruction and peer collaboration among learners with comparable proficiency. Both approaches aim to optimize student engagement and achievement but differ fundamentally in grouping strategies and instructional flexibility.
Defining Differentiated Instruction: Key Concepts
Differentiated instruction involves tailoring teaching methods, content, and assessments to address the diverse learning needs, readiness levels, interests, and learning profiles of individual students. It emphasizes flexible grouping, varied instructional strategies, and ongoing assessment to promote student engagement and achievement. Key concepts include scaffolding, tiered assignments, and formative feedback for personalized learning experiences.
Understanding Homogeneous Grouping in Education
Homogeneous grouping in education involves organizing students based on similar abilities, skill levels, or learning needs to tailor instruction more precisely. This approach allows teachers to focus lessons and activities that match the group's specific strengths or challenges, potentially increasing engagement and efficiency. Research indicates that while homogeneous grouping can enhance targeted instruction, it may also limit peer learning opportunities and diversity of thought within the classroom.
Core Principles of Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated Instruction centers on tailoring teaching methods, content, and assessments to meet diverse student needs, abilities, and interests within a heterogeneous classroom. It emphasizes flexible grouping, ongoing assessment, and student-centered learning to promote engagement and mastery of core competencies. This approach contrasts with homogeneous grouping, which organizes students by similar ability levels but may limit personalized learning opportunities and adaptive instructional strategies.
Advantages of Differentiated Instruction for Diverse Learners
Differentiated instruction enhances learning by tailoring teaching methods and materials to meet the varied needs, abilities, and interests of diverse learners, promoting engagement and academic growth. It supports individualized pacing and multiple learning styles, allowing students to grasp concepts more effectively compared to homogeneous grouping, which may neglect unique learner differences. Research shows differentiated instruction improves student motivation, self-efficacy, and achievement across heterogeneous classrooms.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Homogeneous Grouping
Homogeneous grouping allows teachers to tailor instruction to students with similar skill levels, promoting efficient lesson pacing and targeted skill development. However, this approach may limit exposure to diverse perspectives and hinder social skill growth, potentially reinforcing achievement gaps. The lack of heterogeneous interaction can decrease motivation for some learners and reduce opportunities for peer mentorship.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Differentiated instruction enhances student engagement by tailoring content, process, and product to individual learning styles and readiness levels, fostering personalized learning experiences that boost achievement. Homogeneous grouping clusters students by similar ability, which can streamline instruction and promote peer collaboration but may limit exposure to diverse perspectives, potentially affecting long-term engagement and growth. Research indicates that differentiated instruction generally leads to higher academic gains and motivation across diverse classrooms compared to homogeneous grouping strategies.
Classroom Management Strategies for Both Approaches
Differentiated instruction employs flexible classroom management strategies such as varied learning stations and personalized pacing, enabling teachers to address diverse student needs while maintaining engagement and organization. In contrast, homogeneous grouping streamlines classroom management by allowing teachers to deliver targeted instruction to groups with similar abilities, reducing behavior disruptions and simplifying lesson planning. Both approaches require strategic classroom layout and clear behavioral expectations to optimize learning environments based on student grouping methods.
Research Findings: Differentiated Instruction vs. Homogeneous Grouping
Research findings indicate that differentiated instruction enhances student engagement and achievement by tailoring teaching methods to individual learning styles, whereas homogeneous grouping primarily benefits students with similar abilities but may limit peer learning opportunities. Studies show differentiated instruction fosters higher academic growth and motivation across diverse classrooms, while homogeneous grouping can reinforce skill gaps and reduce cognitive challenge for advanced learners. Effective classrooms often integrate differentiated instruction within flexible groupings to optimize educational outcomes for varied student needs.
Best Practices and Recommendations for Educators
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching strategies to diverse learner needs by varying content, process, and product within mixed-ability classrooms, enhancing student engagement and achievement according to research by the ASCD. Homogeneous grouping clusters students by similar ability level, allowing for targeted instruction but potentially limiting social interaction and growth opportunities in diverse settings. Best practices recommend combining differentiated instruction with flexible grouping, regularly assessing student progress, and fostering an inclusive environment to maximize learning outcomes and address individual strengths and challenges effectively.
Differentiated Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com