Top-down policies are strategic decisions made by senior leadership that cascade down through an organization or government, shaping operations and behaviors at every level. These policies often provide clear directives and objectives, ensuring alignment across departments and fostering efficient implementation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how top-down policies impact your organization and drive effective governance.
Table of Comparison
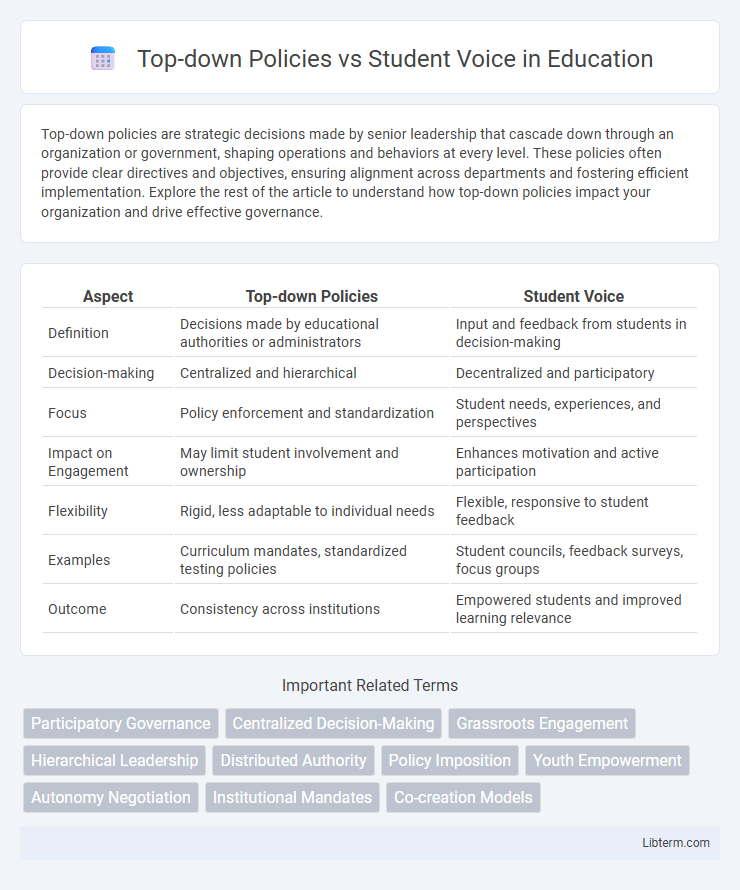
| Aspect | Top-down Policies | Student Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decisions made by educational authorities or administrators | Input and feedback from students in decision-making |
| Decision-making | Centralized and hierarchical | Decentralized and participatory |
| Focus | Policy enforcement and standardization | Student needs, experiences, and perspectives |
| Impact on Engagement | May limit student involvement and ownership | Enhances motivation and active participation |
| Flexibility | Rigid, less adaptable to individual needs | Flexible, responsive to student feedback |
| Examples | Curriculum mandates, standardized testing policies | Student councils, feedback surveys, focus groups |
| Outcome | Consistency across institutions | Empowered students and improved learning relevance |
Understanding Top-Down Educational Policies
Top-down educational policies are directives issued by central authorities, focusing on standardized curricula and assessment frameworks that aim to create uniformity across schools. These policies often prioritize compliance and efficiency, potentially overlooking the unique needs and input of students within the learning environment. Understanding the impact of top-down approaches reveals challenges such as reduced student engagement and limited opportunities for student voice in shaping educational experiences.
Defining Student Voice in Education
Student voice in education refers to the active participation and empowerment of students in decision-making processes that affect their learning environment, curriculum, and school policies. Unlike top-down policies, which are imposed by administrators or policymakers without student input, student voice emphasizes collaboration and the acknowledgment of students as key stakeholders. This approach fosters a more inclusive educational experience, promoting critical thinking, engagement, and ownership of learning outcomes.
Historical Context of Educational Decision-Making
Top-down policies in education have historically centralized authority within government bodies and administrative agencies, often marginalizing student input in decision-making processes. This approach gained prominence during the Industrial Revolution, emphasizing standardization and control to meet national economic and social goals. Conversely, advocacy for student voice emerged as educators recognized the importance of including learners' perspectives to create more responsive and equitable educational environments.
Benefits of Top-Down Policy Approaches
Top-down policy approaches in education ensure a unified and consistent implementation of standards across schools, enhancing accountability and streamlined decision-making processes. These policies facilitate efficient resource allocation and clear directives, enabling school leaders to align goals with district or national objectives. The structured framework supports measurable outcomes, fostering systemic improvements and reducing disparities in educational quality.
Advantages of Empowering Student Voice
Empowering student voice fosters increased engagement and ownership in learning, leading to higher academic achievement and motivation. It promotes critical thinking and collaboration by encouraging diverse perspectives, which enhances school culture and inclusivity. Schools with strong student voice initiatives report improved communication between students and administrators, resulting in policies that better address student needs and well-being.
Challenges of Implementing Top-Down Policies
Top-down policies in education often face resistance due to limited stakeholder engagement and a lack of alignment with students' diverse needs, which undermines effective implementation. These policies can result in rigid structures that stifle student voice, reducing motivation and critical input from learners. The challenge lies in balancing centralized decision-making with inclusive practices that recognize student perspectives to foster meaningful educational outcomes.
Obstacles to Integrating Student Perspectives
Top-down policies often face obstacles in integrating student voice due to rigid administrative structures that limit flexibility and responsiveness to student input. Institutional resistance and lack of effective communication channels hinder authentic participation, causing student perspectives to be overlooked or marginalized. These barriers reduce the potential for policies that truly reflect student needs and experiences, impacting educational outcomes and engagement.
Impact of Policy Approaches on Student Outcomes
Top-down policies in education often lead to standardized outcomes but may limit student engagement and intrinsic motivation, affecting academic performance and well-being. Emphasizing student voice encourages participatory decision-making, fostering empowerment and higher retention rates, which positively influence achievement and social-emotional development. Research indicates that schools integrating student perspectives within policy frameworks see improved attendance, collaboration, and critical thinking skills among students.
Balancing Authority and Student Participation
Balancing authority and student participation in education requires integrating top-down policies with authentic student voice to foster inclusive decision-making that respects institutional frameworks while empowering learners. Effective implementation hinges on creating dialogue channels where policy mandates are adapted through student input, enhancing ownership and engagement. This synergy promotes a dynamic learning environment that supports both strategic objectives and individual agency.
Future Directions: Towards Collaborative Policy-Making
Future directions in education underscore the shift from top-down policies to integrating student voice, fostering collaborative policy-making that aligns administrative goals with learners' needs. Research highlights participatory frameworks where students actively contribute to decision-making, enhancing policy relevance, engagement, and effectiveness. Embracing co-creation models in policy formulation promises adaptive, inclusive educational environments that respond dynamically to diverse student perspectives.
Top-down Policies Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com