Teacher-centered education prioritizes the instructor's role in delivering knowledge, where students are passive recipients of information. This approach often emphasizes memorization, lectures, and standardized testing, which can limit opportunities for critical thinking and creativity. Explore the rest of the article to understand the implications of this method and how it compares to student-centered learning.
Table of Comparison
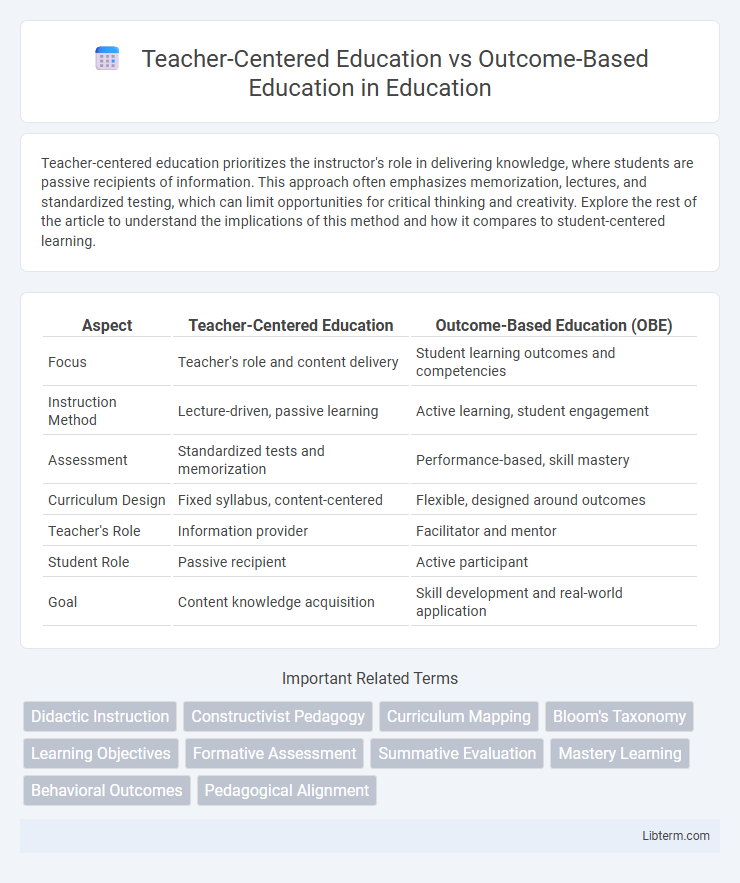
| Aspect | Teacher-Centered Education | Outcome-Based Education (OBE) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Teacher's role and content delivery | Student learning outcomes and competencies |
| Instruction Method | Lecture-driven, passive learning | Active learning, student engagement |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and memorization | Performance-based, skill mastery |
| Curriculum Design | Fixed syllabus, content-centered | Flexible, designed around outcomes |
| Teacher's Role | Information provider | Facilitator and mentor |
| Student Role | Passive recipient | Active participant |
| Goal | Content knowledge acquisition | Skill development and real-world application |
Introduction to Teacher-Centered and Outcome-Based Education
Teacher-Centered Education emphasizes the instructor's role as the primary source of knowledge, focusing on structured lectures and rote memorization to deliver content. Outcome-Based Education prioritizes clearly defined learning outcomes, assessing students by their ability to demonstrate specific skills and competencies after instruction. Both approaches shape curriculum design, assessment methods, and instructional strategies but differ fundamentally in focus--content delivery versus measurable student achievement.
Defining Teacher-Centered Education
Teacher-centered education prioritizes the instructor as the primary source of knowledge, emphasizing direct instruction, structured curriculum, and passive student absorption of content. This approach focuses on standardized testing and uniform assessment methods to measure student performance and mastery. It contrasts sharply with student-driven models by limiting active learning opportunities and critical thinking development.
Core Principles of Outcome-Based Education
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) centers on clearly defined learning outcomes that students must demonstrate upon course completion, emphasizing mastery over the learning process. It prioritizes student-centered instruction, continuous assessment, and flexible teaching strategies to ensure all learners achieve specified competencies. Core principles include alignment of curriculum, instruction, and assessment with outcomes, accountability for results, and a focus on measurable, observable skills and knowledge.
Historical Context and Evolution
Teacher-centered education originated in the 19th century, emphasizing direct instruction and rote memorization, reflecting an industrial-age need for standardized knowledge transmission. Outcome-Based Education (OBE) emerged in the late 20th century as a progressive reform, prioritizing measurable student competencies and skills over traditional seat-time and content coverage. The evolution from teacher-centered models to OBE signifies a shift from authoritative knowledge delivery toward learner-centered accountability and performance standards.
Key Differences Between Teacher-Centered and Outcome-Based Approaches
Teacher-centered education emphasizes the instructor's role in delivering content and controlling the learning environment, focusing on knowledge transmission and standardized assessment. Outcome-based education prioritizes student learning outcomes, ensuring curriculum, teaching methods, and assessments align with specific competencies and skills that students must demonstrate. Key differences include the focus on teaching process versus learning results, with outcome-based education promoting active learner engagement and mastery of measurable objectives.
Impact on Curriculum Design
Teacher-centered education emphasizes a curriculum designed around instructor expertise and content delivery, often leading to rigid, standardized lesson plans focused on knowledge transmission. Outcome-based education shifts the focus to clearly defined learning outcomes, prompting curriculum designers to create flexible, student-centered modules that promote skills mastery and measurable competencies. This approach requires continuous assessment integration to ensure alignment between learning activities and desired educational results, fostering adaptive and dynamic curriculum structures.
Teaching Methods and Student Engagement
Teacher-centered education emphasizes direct instruction where teachers control the learning process, often leading to passive student engagement focused on memorization and repetition. Outcome-based education prioritizes clear learning outcomes, promoting interactive, student-centered teaching methods that foster active participation and critical thinking. This shift enhances student engagement by aligning instructional strategies with measurable competencies and real-world applications.
Assessment and Evaluation Strategies
Teacher-centered education primarily utilizes standardized tests and quizzes to assess student knowledge, focusing on memorization and recall, which often emphasizes summative evaluation. Outcome-based education employs continuous formative assessments, including performance tasks, portfolios, and rubrics, designed to measure specific learning outcomes and competencies. This shift ensures evaluation strategies align with skill mastery and real-world application rather than solely content retention.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Model
Teacher-centered education offers structured, content-rich instruction that ensures mastery of foundational knowledge, fostering discipline and consistency in learning environments; however, it often limits student engagement and critical thinking development. Outcome-based education emphasizes measurable learning results and skills acquisition tailored to real-world applications, promoting student-centered active learning and accountability, yet it can face challenges in standardized assessment reliability and curriculum flexibility. Balancing these models requires integrating clear instructional guidance with outcome-driven goals to optimize educational effectiveness and learner success.
Future Trends in Educational Practices
Teacher-centered education emphasizes structured curriculum delivery by instructors, while outcome-based education focuses on measurable student competencies and skills acquisition. Future trends highlight a shift towards personalized learning technologies, integrating AI-driven analytics to tailor educational experiences that bridge both instructional guidance and outcome achievement. Hybrid models leveraging data-informed assessments promote adaptive learning environments, fostering critical thinking and lifelong skill development aligned with evolving workforce demands.
Teacher-Centered Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com