Analysis involves examining data or information methodically to uncover patterns, trends, or insights that drive informed decision-making. Effective analysis uses various tools and techniques to interpret complex data accurately and predict outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to enhance your analytical skills and apply them effectively in your work.
Table of Comparison
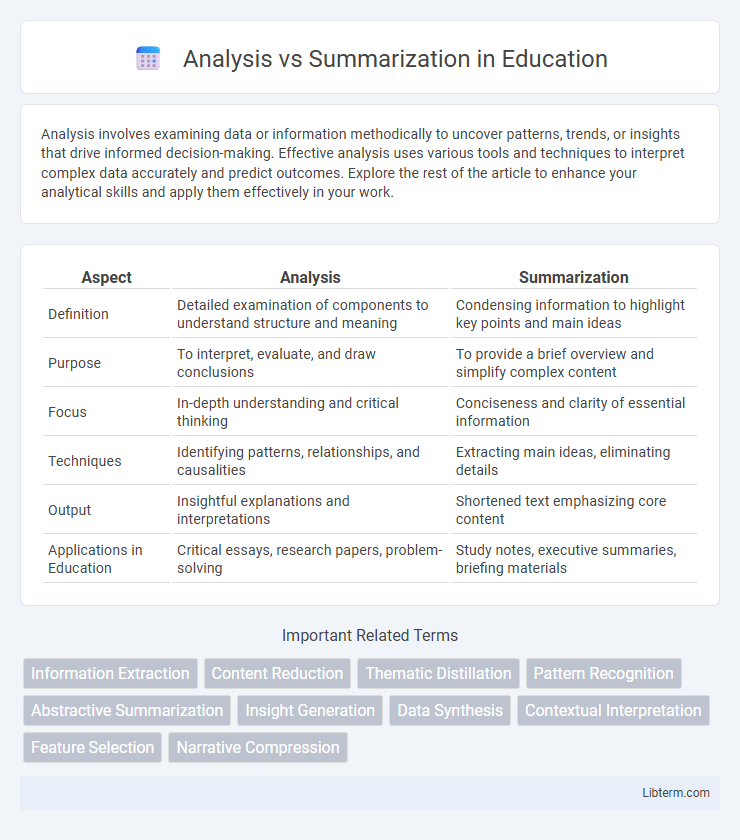
| Aspect | Analysis | Summarization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Detailed examination of components to understand structure and meaning | Condensing information to highlight key points and main ideas |
| Purpose | To interpret, evaluate, and draw conclusions | To provide a brief overview and simplify complex content |
| Focus | In-depth understanding and critical thinking | Conciseness and clarity of essential information |
| Techniques | Identifying patterns, relationships, and causalities | Extracting main ideas, eliminating details |
| Output | Insightful explanations and interpretations | Shortened text emphasizing core content |
| Applications in Education | Critical essays, research papers, problem-solving | Study notes, executive summaries, briefing materials |
Introduction to Analysis and Summarization
Analysis involves examining and interpreting data or information to uncover patterns, relationships, and deeper insights, enabling a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Summarization condenses information by highlighting key points and main ideas, providing a concise overview without detailed interpretation or evaluation. Both techniques serve distinct purposes in processing information, with analysis offering depth and critical thinking, while summarization emphasizes brevity and clarity.
Defining Analysis
Analysis involves examining information methodically to understand underlying patterns, relationships, and meanings within data or text. It requires breaking down complex material into smaller components for critical evaluation, interpretation, and insight generation. Unlike summarization, which condenses content, analysis emphasizes depth and detailed understanding to support conclusions or recommendations.
Defining Summarization
Summarization condenses extensive content into concise versions, preserving essential information while omitting details. It captures the core message, main ideas, and key facts from texts or data without interpreting or evaluating the material. This process enhances information accessibility by producing brief overviews ideal for quick understanding and decision-making.
Key Differences Between Analysis and Summarization
Analysis involves examining information critically to uncover underlying meanings, patterns, and relationships, whereas summarization condenses content by highlighting main points without interpretation. Analysis requires evaluating context and drawing conclusions, while summarization focuses on presenting a concise, objective overview. Key differences include depth of understanding, purpose, and the level of detail involved in processing the original information.
Purpose and Goals of Analysis
Analysis aims to examine and interpret data or information to uncover patterns, causes, and underlying meanings, enabling informed decision-making and problem-solving. Its purpose is to break down complex topics into detailed components for deeper understanding and insight generation. Unlike summarization, which condenses content to its main points, analysis involves critical evaluation and synthesis to support strategic objectives.
Purpose and Goals of Summarization
Summarization aims to condense large volumes of information into concise, easily digestible content that highlights key points and essential details. Its primary goal is to enhance comprehension and facilitate quick decision-making by presenting a clear overview without the need to review the entire source. In contrast, analysis involves deeper examination and interpretation of data to uncover patterns, relationships, and insights beyond surface-level understanding.
Techniques Used in Analysis
Techniques used in analysis involve breaking down complex data into components to understand underlying patterns, often employing methods such as statistical modeling, thematic coding, and machine learning algorithms. These approaches enable the extraction of meaningful insights, identification of trends, and prediction of outcomes, surpassing the surface-level content condensation typical in summarization. Data visualization and sentiment analysis further enhance interpretability, providing multidimensional perspectives essential for informed decision-making.
Techniques Used in Summarization
Summarization techniques primarily include extractive and abstractive methods; extractive summarization identifies and selects key sentences or phrases directly from the source text based on statistical features like term frequency and sentence position. Abstractive summarization generates new sentences by understanding the context, employing advanced deep learning models such as transformers and sequence-to-sequence architectures with attention mechanisms. These techniques optimize information retention while reducing text length, ensuring semantic coherence and relevance in the summarized output.
When to Use Analysis vs Summarization
Use analysis when you need to interpret data, uncover patterns, or evaluate underlying meanings to make informed decisions or provide insights. Summarization is appropriate for condensing information into a concise overview, highlighting key points without detailed interpretation. Choose analysis for critical thinking and problem-solving, while summarization suits quick reference and information recall.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the appropriate method between analysis and summarization hinges on the objective: analysis provides a deeper understanding by examining underlying themes and implications, while summarization offers a concise overview of the main points. For academic and decision-making contexts, analysis delivers critical insights that inform conclusions and strategies. Summarization suits scenarios requiring quick comprehension or review, making it essential to match the approach to the specific informational needs.
Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com