Traditional classrooms provide a structured learning environment with face-to-face interaction between teachers and students, fostering immediate feedback and collaboration. This setting supports discipline, routine, and direct engagement, which can enhance understanding and retention of material. Explore the rest of the article to discover how traditional classrooms compare to modern educational methods and what might suit Your learning style best.
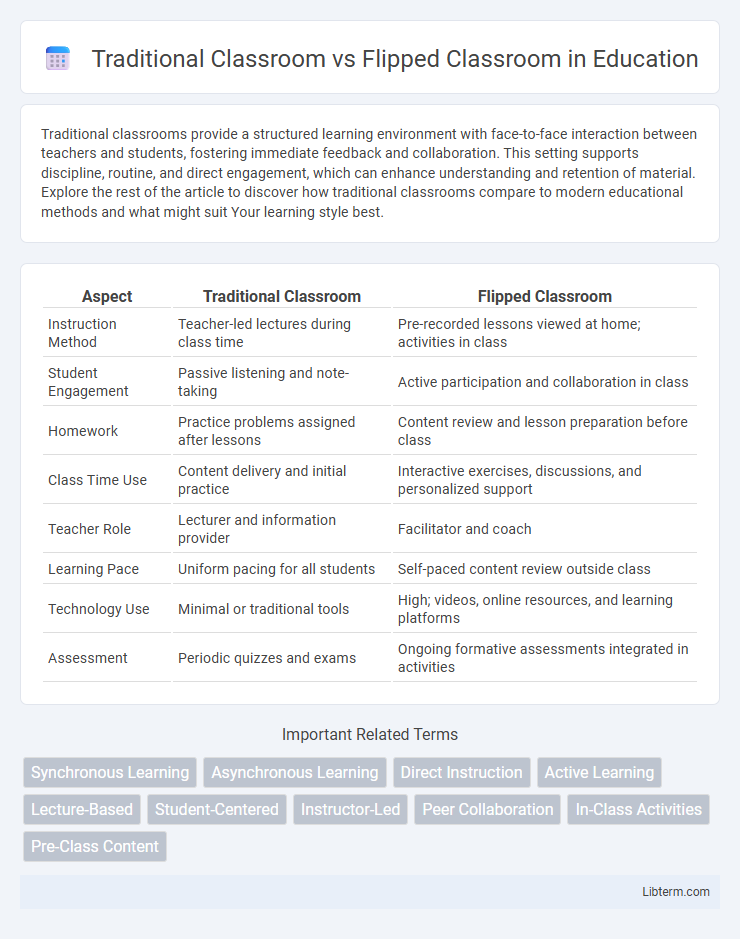
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Classroom | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Instruction Method | Teacher-led lectures during class time | Pre-recorded lessons viewed at home; activities in class |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening and note-taking | Active participation and collaboration in class |
| Homework | Practice problems assigned after lessons | Content review and lesson preparation before class |
| Class Time Use | Content delivery and initial practice | Interactive exercises, discussions, and personalized support |
| Teacher Role | Lecturer and information provider | Facilitator and coach |
| Learning Pace | Uniform pacing for all students | Self-paced content review outside class |
| Technology Use | Minimal or traditional tools | High; videos, online resources, and learning platforms |
| Assessment | Periodic quizzes and exams | Ongoing formative assessments integrated in activities |
Introduction to Traditional and Flipped Classrooms
Traditional classrooms follow a teacher-centered approach where instructors deliver lectures and students listen passively, emphasizing direct instruction during scheduled class time. Flipped classrooms invert this model by assigning pre-class learning materials such as videos and readings, allowing in-class time to focus on interactive activities, problem-solving, and personalized guidance. This pedagogical shift aims to enhance student engagement and improve learning outcomes by fostering active participation and self-directed study.
Core Principles of Traditional Classroom Instruction
Traditional classroom instruction centers on direct teacher-led lessons where educators deliver content through lectures and structured activities. This approach emphasizes standardized curriculum pacing, classroom management, and face-to-face interactions to facilitate immediate feedback. Core principles include teacher authority, sequential learning, and in-class knowledge transmission.
Understanding the Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, while in-class time is dedicated to interactive activities and personalized support. This approach enhances student engagement, encourages active learning, and enables educators to address individual learning needs more effectively. Research shows that flipped classrooms improve comprehension and retention compared to conventional lecture-based instruction.
Student Engagement: Comparing Both Approaches
Traditional classrooms often rely on passive learning, where students listen to lectures and complete homework individually, resulting in lower student engagement. Flipped classrooms promote active participation by having students review instructional content at home and engage in collaborative, hands-on activities during class, leading to higher motivation and deeper understanding. Research indicates that flipped classrooms enhance student engagement by fostering interactive learning environments and immediate feedback.
Teacher’s Role: Direct Instruction vs Facilitation
In a traditional classroom, the teacher predominantly acts as the direct instructor, delivering content through lectures and controlling the pace of learning. In contrast, the flipped classroom positions the teacher as a facilitator who guides students through active, collaborative learning during class time, having assigned content for students to explore independently beforehand. This shift empowers students to engage critically, while teachers provide personalized support and encourage deeper understanding.
Classroom Dynamics and Learning Environment
Traditional classrooms emphasize teacher-centered instruction with direct lectures, promoting passive student participation and structured learning environments. Flipped classrooms invert this model by encouraging active student engagement through pre-class content review and collaborative, problem-solving activities during class time. This approach fosters dynamic interaction, personalized learning experiences, and deeper comprehension within a more flexible and student-centered environment.
Technological Integration in Flipped Classrooms
Flipped classrooms leverage advanced technological integration by utilizing digital platforms for pre-class video lectures, interactive quizzes, and collaborative online tools, enhancing student engagement and personalized learning. This approach contrasts with traditional classrooms where technology use is often limited to in-person instruction and minimal digital resources. The integration of learning management systems (LMS), multimedia content, and real-time analytics in flipped classrooms facilitates data-driven insights and active student participation.
Assessment Methods: Traditional vs Flipped
Traditional classroom assessment methods typically rely on standardized tests, quizzes, and periodic exams that measure students' ability to recall and apply information under timed conditions. Flipped classroom assessments emphasize formative evaluation techniques such as project-based learning, peer reviews, and real-time feedback that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This shift enhances personalized learning and continuous assessment, aligning with active student engagement and mastery of complex concepts.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Model
Traditional classrooms provide structured, face-to-face instruction with direct teacher supervision, fostering immediate feedback and a controlled learning environment. Challenges include limited flexibility and passive student engagement, which can hinder personalized learning. Flipped classrooms encourage active learning through pre-class content review and in-class collaboration, enhancing critical thinking and student accountability but require reliable technology access and strong self-motivation to prevent students from falling behind.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Choosing the right approach for diverse learners requires understanding the strengths of both traditional and flipped classrooms. Traditional classrooms offer structured, teacher-led instruction ideal for learners who benefit from direct guidance and clear timelines. Flipped classrooms promote active, self-paced learning that supports students with varying learning speeds and encourages deeper engagement through interactive, technology-driven content.
Traditional Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com