Modeling involves creating accurate representations of real-world objects, systems, or concepts to analyze and predict outcomes efficiently. By utilizing various techniques such as mathematical models, simulations, and 3D designs, you can enhance decision-making and problem-solving processes across different industries. Explore the rest of this article to discover how effective modeling can transform your projects and elevate your results.
Table of Comparison
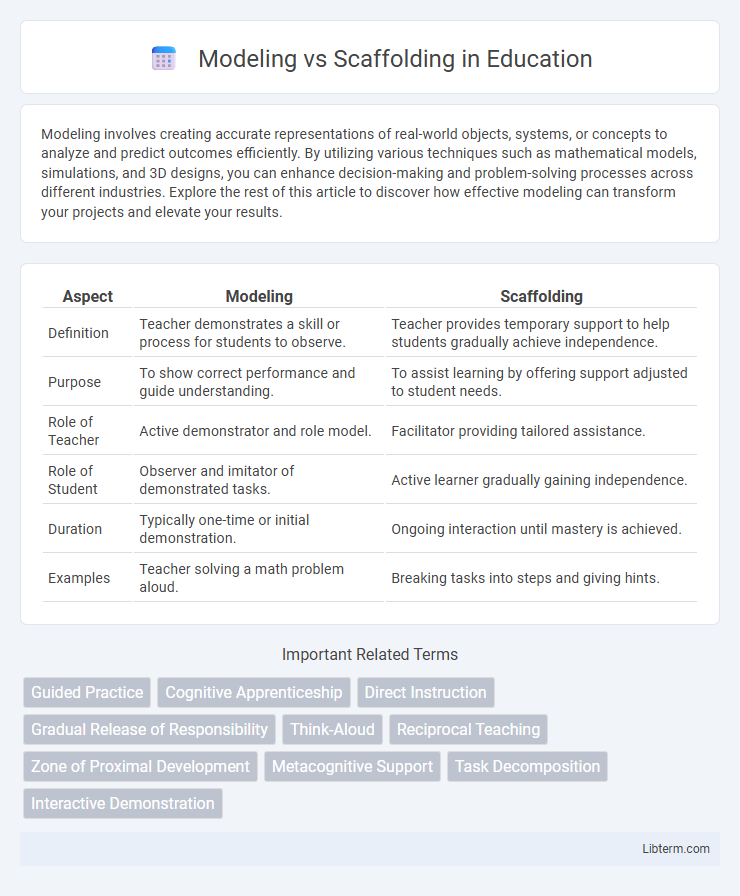
| Aspect | Modeling | Scaffolding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher demonstrates a skill or process for students to observe. | Teacher provides temporary support to help students gradually achieve independence. |
| Purpose | To show correct performance and guide understanding. | To assist learning by offering support adjusted to student needs. |
| Role of Teacher | Active demonstrator and role model. | Facilitator providing tailored assistance. |
| Role of Student | Observer and imitator of demonstrated tasks. | Active learner gradually gaining independence. |
| Duration | Typically one-time or initial demonstration. | Ongoing interaction until mastery is achieved. |
| Examples | Teacher solving a math problem aloud. | Breaking tasks into steps and giving hints. |
Understanding the Concepts: Modeling and Scaffolding
Modeling involves demonstrating a specific skill or behavior to provide a clear example for learners, helping them visualize and internalize the desired outcome. Scaffolding supports learners by breaking tasks into manageable steps and offering guidance tailored to their current level of understanding, progressively removing assistance as competence develops. Both concepts enhance learning by making complex tasks more accessible and encouraging independent mastery through structured support.
Key Differences Between Modeling and Scaffolding
Modeling involves demonstrating a skill or behavior for learners to observe and imitate, whereas scaffolding provides temporary support tailored to the learner's current level, gradually removed as competence increases. Modeling offers a concrete example to internalize, while scaffolding adapts instruction to bridge gaps in understanding, promoting independent problem-solving. The key difference lies in modeling serving as a visual/template guide, whereas scaffolding is an interactive, adjustable aid aligned with learner needs.
The Role of Modeling in Learning
Modeling plays a crucial role in learning by providing clear examples and demonstrating desired behaviors or skills, which helps learners internalize and replicate complex concepts effectively. It activates observational learning mechanisms, allowing students to acquire new knowledge through imitation and guided practice. Unlike scaffolding, which offers temporary support and gradually withdraws it, modeling establishes a foundational understanding that learners can build upon independently.
The Function of Scaffolding in Education
Scaffolding in education functions as a targeted support system that guides learners through complex tasks by breaking down information into manageable steps, thereby enhancing comprehension and skill acquisition. This instructional technique adapts to the learner's current abilities, gradually reducing assistance as mastery develops, which promotes independent problem-solving and critical thinking. Unlike modeling, which demonstrates desired behaviors or outcomes, scaffolding actively involves students in the learning process through personalized, step-by-step support.
Benefits of Modeling in Classroom Instruction
Modeling in classroom instruction provides students with clear examples of expected behaviors and problem-solving processes, enhancing comprehension and skill acquisition. It supports the development of critical thinking by demonstrating strategic approaches to tasks and encourages learner independence by making abstract concepts concrete. This method fosters engagement and retention by allowing students to observe and imitate expert performance within authentic contexts.
Advantages of Scaffolding for Student Engagement
Scaffolding enhances student engagement by providing tailored support that meets learners at their current skill level, fostering confidence and motivation. This approach encourages active participation through guided practice and incremental challenges, which promotes deeper understanding and retention. Unlike modeling, scaffolding adapts dynamically to student needs, creating a more interactive and personalized learning environment.
When to Use Modeling vs Scaffolding
Use modeling when introducing new skills or concepts to provide a clear example for learners to imitate, especially effective in early learning stages or complex tasks. Scaffolding is best applied during guided practice, offering tailored support that gradually fades as learners gain competence and independence. Choosing between modeling and scaffolding depends on learners' prior knowledge, with modeling establishing initial understanding and scaffolding enhancing mastery through incremental assistance.
Practical Strategies for Effective Modeling
Effective modeling involves demonstrating a specific skill or behavior clearly and consistently, allowing learners to observe and internalize desired practices through step-by-step examples. Incorporating verbal explanations along with visual cues enhances comprehension and retention, making the modeled action more accessible for replication. Using real-world contexts relevant to learners' experiences ensures that the modeled behavior is practical and applicable, thereby increasing engagement and facilitating skill acquisition.
Scaffolding Techniques to Support Diverse Learners
Scaffolding techniques support diverse learners by providing tailored instructional strategies such as guided questioning, visual aids, and chunking information to enhance comprehension and retention. These methods adapt to individual student needs, gradually reducing support as learners gain independence and confidence in mastering new concepts. Effective scaffolding fosters an inclusive classroom environment where varied learning styles and abilities are accommodated through differentiated instruction and ongoing formative assessment.
Integrating Modeling and Scaffolding for Optimal Outcomes
Integrating modeling and scaffolding enhances learning by combining explicit demonstration with tailored support, enabling learners to grasp complex tasks effectively. Modeling provides clear examples and processes, while scaffolding offers adaptive guidance that gradually decreases as learners gain proficiency. This synergy fosters deeper understanding, skill retention, and independent problem-solving abilities in educational and training environments.
Modeling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com