Transdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge from various disciplines to address complex problems beyond traditional boundaries. This methodology fosters innovative solutions by synthesizing diverse perspectives and expertise. Explore the full article to understand how you can apply transdisciplinary strategies to enhance your projects.
Table of Comparison
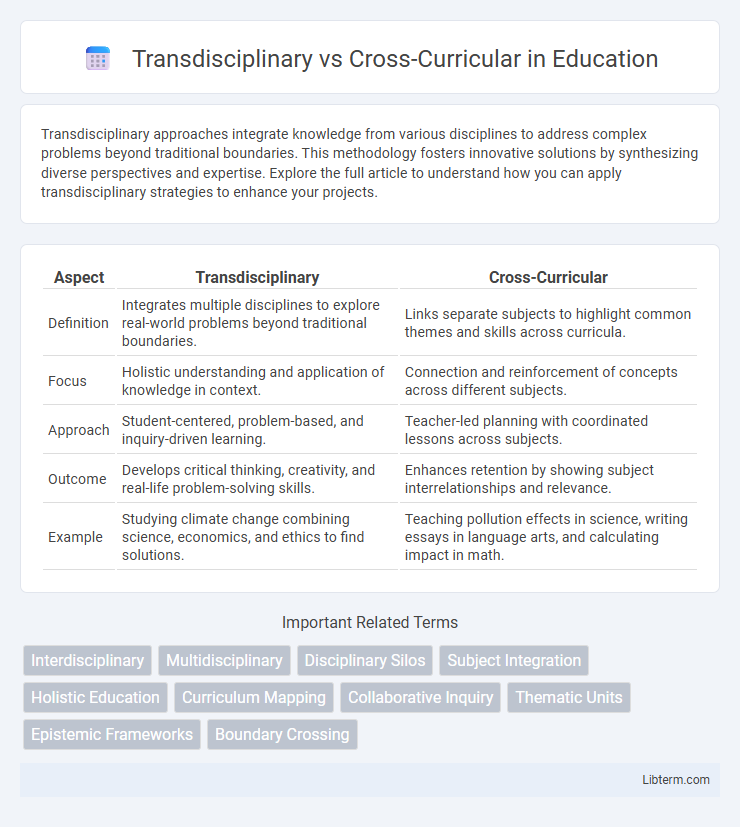
| Aspect | Transdisciplinary | Cross-Curricular |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates multiple disciplines to explore real-world problems beyond traditional boundaries. | Links separate subjects to highlight common themes and skills across curricula. |
| Focus | Holistic understanding and application of knowledge in context. | Connection and reinforcement of concepts across different subjects. |
| Approach | Student-centered, problem-based, and inquiry-driven learning. | Teacher-led planning with coordinated lessons across subjects. |
| Outcome | Develops critical thinking, creativity, and real-life problem-solving skills. | Enhances retention by showing subject interrelationships and relevance. |
| Example | Studying climate change combining science, economics, and ethics to find solutions. | Teaching pollution effects in science, writing essays in language arts, and calculating impact in math. |
Introduction to Educational Integration Approaches
Transdisciplinary approaches in educational integration emphasize addressing real-world problems by transcending traditional subject boundaries to create holistic learning experiences. Cross-curricular strategies coordinate content from multiple subjects while maintaining their distinct disciplinary perspectives, promoting connections that enhance comprehension. Understanding these differences is crucial for designing effective curricula that foster critical thinking and collaboration across various disciplines.
Defining Transdisciplinary Learning
Transdisciplinary learning integrates knowledge and skills from multiple disciplines to address complex real-world problems, promoting holistic understanding beyond traditional subject boundaries. It focuses on developing critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving by connecting thematic inquiry to authentic contexts. Unlike cross-curricular approaches that link subjects through common themes, transdisciplinary learning dissolves these boundaries entirely to create a unified learning experience.
Understanding Cross-Curricular Teaching
Cross-curricular teaching integrates content and skills from multiple disciplines to enhance learning connections and real-world application. This approach emphasizes collaborative planning where subject boundaries remain distinct but are linked through thematic units or projects. Understanding cross-curricular teaching involves recognizing its role in promoting critical thinking and problem-solving by bridging knowledge across traditional academic areas.
Key Differences: Transdisciplinary vs Cross-Curricular
Transdisciplinary learning integrates multiple disciplines into a unified approach, focusing on real-world themes that transcend traditional subject boundaries, fostering deep critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Cross-curricular learning connects related concepts across different subjects but maintains the distinct methods and objectives of each discipline. The key difference lies in transdisciplinary's holistic, theme-driven approach versus cross-curricular's thematic links that preserve disciplinary separateness.
Benefits of Transdisciplinary Approaches
Transdisciplinary approaches enhance student engagement by integrating real-world problems across multiple disciplines, fostering deeper critical thinking and collaboration skills. This method promotes holistic learning by breaking down traditional subject barriers, allowing students to apply knowledge in diverse contexts, which improves retention and relevance. Educators report that transdisciplinary projects increase creativity and adaptability, essential competencies in the 21st-century workforce.
Advantages of Cross-Curricular Instruction
Cross-curricular instruction enhances student engagement by integrating multiple subjects through common themes, promoting deeper understanding and real-world application. It facilitates critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging learners to make connections across disciplines. This approach also supports differentiated learning, catering to diverse student needs and fostering collaboration and communication among peers.
Challenges in Implementing Transdisciplinary Models
Implementing transdisciplinary models faces significant challenges such as integrating diverse disciplinary perspectives, which often requires extensive collaboration and flexibility among educators. The complexity of designing curriculum that transcends traditional subject boundaries can create resistance from teachers accustomed to siloed instruction and standardized testing frameworks. Limited professional development and assessment tools tailored to transdisciplinary approaches further hinder effective implementation in educational settings.
Practical Examples in the Classroom
Transdisciplinary learning integrates multiple disciplines to address real-world problems, such as students designing a community garden combining science, math, and social studies concepts. Cross-curricular approaches connect related subjects through thematic units, like reading historical novels in literature while studying the corresponding historical period in social studies. Both methods enhance critical thinking and collaboration by encouraging students to apply knowledge across different academic areas in practical, hands-on projects.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Curriculum
Choosing between transdisciplinary and cross-curricular approaches depends on curriculum goals and student needs. Transdisciplinary learning integrates subjects around real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and collaboration. Cross-curricular methods link related topics across disciplines, enhancing content retention and reinforcing skills through multiple perspectives.
Future Trends in Integrated Education
Future trends in integrated education emphasize the shift from cross-curricular approaches, which connect subjects around a common theme, to transdisciplinary models that dissolve traditional boundaries for holistic problem-solving. Transdisciplinary education fosters critical thinking and real-world application by blending knowledge from multiple disciplines, enhancing student engagement and innovation. Emerging technologies and global challenges are driving educators to adopt transdisciplinary frameworks to better prepare learners for complex future scenarios.
Transdisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com