Summative assessment evaluates student learning by measuring knowledge or skills at the end of an instructional period, often through tests, projects, or final exams. It provides valuable feedback on overall achievement and helps educators determine if learning objectives have been met. Explore the rest of the article to learn how summative assessment can optimize your educational outcomes.
Table of Comparison
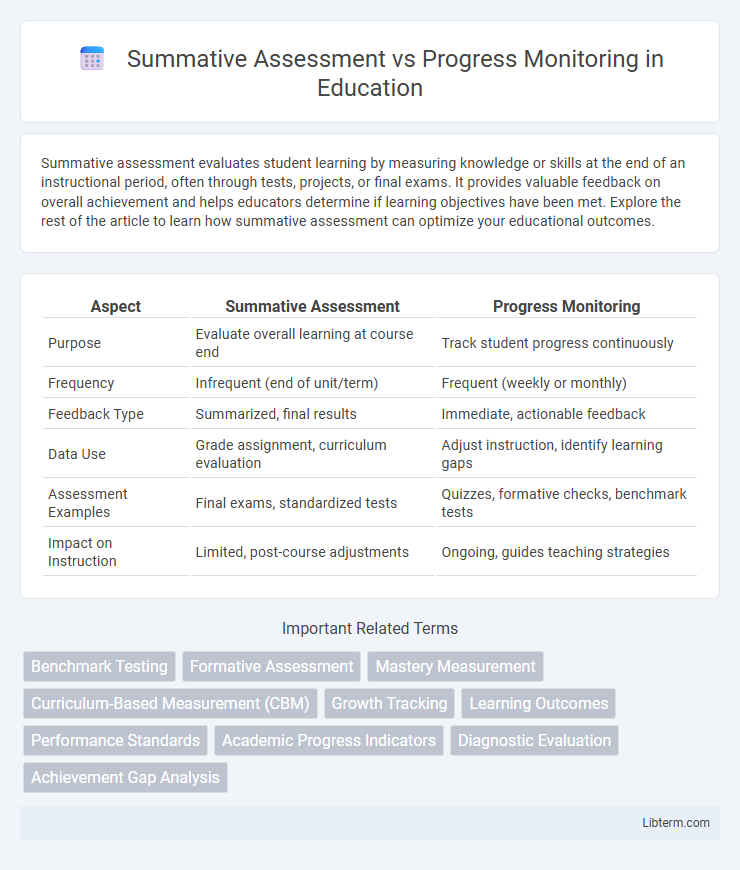
| Aspect | Summative Assessment | Progress Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate overall learning at course end | Track student progress continuously |
| Frequency | Infrequent (end of unit/term) | Frequent (weekly or monthly) |
| Feedback Type | Summarized, final results | Immediate, actionable feedback |
| Data Use | Grade assignment, curriculum evaluation | Adjust instruction, identify learning gaps |
| Assessment Examples | Final exams, standardized tests | Quizzes, formative checks, benchmark tests |
| Impact on Instruction | Limited, post-course adjustments | Ongoing, guides teaching strategies |
Understanding Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring mastery of curriculum standards through exams, final projects, or standardized tests. It provides comprehensive data on academic achievement and informs stakeholders about overall educational effectiveness. This type of assessment contrasts with progress monitoring, which involves frequent, formative checks to guide ongoing instruction.
Defining Progress Monitoring
Progress monitoring is a systematic process used to track students' academic performance and growth over time through frequent, curriculum-based assessments. It provides real-time data to inform instruction and identify students needing additional support. Unlike summative assessment, which evaluates overall learning outcomes at the end of an instructional period, progress monitoring emphasizes ongoing evaluation to guide instructional adjustments.
Key Differences Between Summative Assessment and Progress Monitoring
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing a comprehensive measure of achievement against standardized criteria. Progress monitoring occurs regularly throughout the learning process, offering real-time data to inform instructional adjustments and track student growth. Key differences include timing, purpose, and frequency, with summative assessments being episodic and evaluative, while progress monitoring is ongoing and diagnostic.
Purposes of Summative Assessment
Summative assessment primarily aims to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring mastery of curriculum standards and overall academic achievement. It provides critical data for determining final grades, informing educational decisions, and assessing the effectiveness of instructional programs. These assessments include standardized tests, final exams, and end-of-term projects that summarize cumulative knowledge and skills.
Purposes of Progress Monitoring
Progress monitoring serves to frequently assess student learning and performance to guide instructional decisions and interventions in real-time. It helps educators identify students' strengths and weaknesses, monitor progress toward specific academic goals, and adjust teaching strategies to improve outcomes. Unlike summative assessments, which evaluate overall achievement at the end of a period, progress monitoring emphasizes ongoing measurement to support continuous growth.
Timing and Frequency of Assessments
Summative assessments are typically conducted at the end of an instructional period, such as a semester or academic year, to evaluate overall student learning and achievement. Progress monitoring occurs regularly and frequently throughout the learning process, often weekly or biweekly, to track student performance and inform instructional adjustments. The timing and frequency differences ensure summative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation, while progress monitoring offers ongoing data for timely interventions.
Data Collection Methods Compared
Summative assessment typically utilizes standardized tests, final projects, or end-of-unit exams to collect quantitative data reflecting overall student achievement and mastery of content. Progress monitoring relies on frequent, formative data collection methods such as quizzes, observational checklists, or curriculum-based measurements to track student learning growth over time. The contrast lies in summative assessments providing a comprehensive evaluation at a single point, while progress monitoring captures ongoing performance to inform instructional adjustments.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Summative assessment provides a comprehensive evaluation of student learning at the end of an instructional period, offering valuable data to measure overall achievement and inform curriculum adjustments. Progress monitoring delivers real-time feedback by frequently assessing student performance, enabling timely interventions to address learning gaps and support individualized instruction. Combining summative assessment with ongoing progress monitoring maximizes the potential for improved student learning outcomes by aligning instructional strategies with evolving student needs.
Choosing the Right Assessment Strategy
Selecting the right assessment strategy involves understanding that summative assessments primarily evaluate overall learning outcomes at the end of an instructional period, providing comprehensive data on student achievement. Progress monitoring, however, offers frequent, real-time insights into student performance, allowing educators to adjust instruction and interventions promptly. Effective educational planning integrates both methods to balance outcome measurement with ongoing learning support.
Integrating Both Approaches for Effective Education
Integrating summative assessment and progress monitoring creates a balanced educational approach that supports student growth and accountability. Summative assessments provide comprehensive evaluations of learning outcomes, while progress monitoring offers ongoing feedback to inform instructional adjustments. Combining both methods ensures data-driven decision-making that enhances teaching effectiveness and fosters continuous student improvement.
Summative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com