Traditional lecture-based learning relies on instructor-centered delivery where students passively receive information, often leading to limited engagement and retention. This method emphasizes rote memorization over critical thinking and practical application, which can hinder deeper understanding and skill development. Explore the rest of the article to discover how modern educational approaches can enhance your learning experience beyond traditional lectures.
Table of Comparison
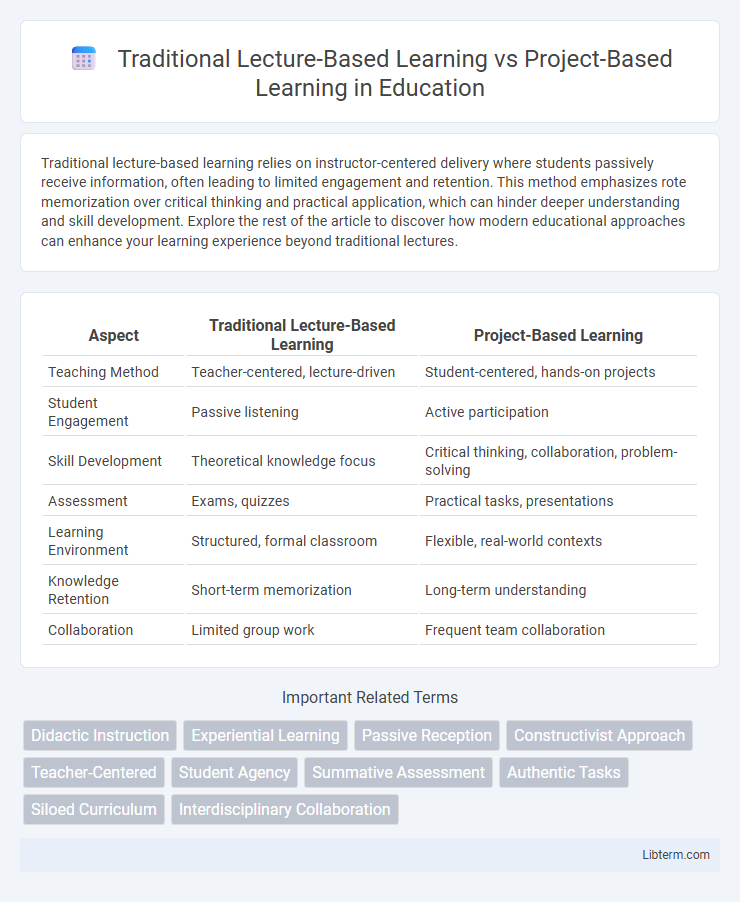
| Aspect | Traditional Lecture-Based Learning | Project-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Method | Teacher-centered, lecture-driven | Student-centered, hands-on projects |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening | Active participation |
| Skill Development | Theoretical knowledge focus | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving |
| Assessment | Exams, quizzes | Practical tasks, presentations |
| Learning Environment | Structured, formal classroom | Flexible, real-world contexts |
| Knowledge Retention | Short-term memorization | Long-term understanding |
| Collaboration | Limited group work | Frequent team collaboration |
Introduction to Learning Methodologies
Traditional lecture-based learning relies on structured, instructor-centered delivery where students passively receive information, emphasizing memorization and standardized assessments. Project-based learning shifts focus to student-centered experiences, promoting critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application through collaborative, hands-on projects. Research highlights increased engagement and retention in project-based learning, while traditional methods offer systematic knowledge acquisition suited for foundational concepts.
Defining Traditional Lecture-Based Learning
Traditional Lecture-Based Learning centers on the instructor delivering structured content through oral presentations, often accompanied by textbooks and visual aids, emphasizing passive knowledge absorption. This method prioritizes memorization and individual assessment through exams, with limited student interaction or practical application during sessions. It remains prevalent in higher education for its efficiency in covering extensive theoretical material within fixed timeframes.
Exploring Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes hands-on, real-world problem solving, fostering critical thinking and collaboration skills that traditional lecture-based learning often lacks. Students engage deeply by working on complex projects over extended periods, which enhances retention and application of knowledge across subjects. Research shows PBL increases motivation and improves academic outcomes by connecting theory to practical experiences.
Key Differences Between Both Approaches
Traditional lecture-based learning emphasizes passive knowledge absorption through direct instruction and teacher-centered presentations, while project-based learning centers on active student engagement through hands-on projects and real-world problem solving. Lecture-based methods prioritize memorization and theoretical understanding, whereas project-based learning fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and application of skills in practical contexts. Assessment in traditional learning often relies on exams and quizzes, contrasting with project-based learning's focus on continuous evaluation, portfolios, and demonstrations of competence.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Traditional lecture-based learning often results in passive student engagement, with motivation relying heavily on external factors such as grades and instructor presence. Project-based learning promotes active participation, fostering intrinsic motivation by allowing students to connect theory with real-world applications and collaborate in problem-solving tasks. Empirical studies reveal higher retention rates and sustained enthusiasm in project-based settings compared to conventional lectures.
Impact on Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Traditional lecture-based learning often emphasizes passive absorption of information, which may limit opportunities for developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. In contrast, project-based learning engages students actively, requiring them to analyze real-world problems, collaborate, and apply knowledge creatively, thereby enhancing cognitive abilities and practical reasoning. Research indicates that project-based learning environments significantly improve students' capacity for critical analysis and adaptive problem solving compared to conventional lectures.
Teacher Roles in Each Learning Model
In traditional lecture-based learning, teachers primarily function as knowledge transmitters who deliver content through structured presentations and direct instruction. In project-based learning, teachers act as facilitators and mentors, guiding students through inquiry, collaboration, and problem-solving activities while fostering critical thinking. This shift in teacher roles enhances student engagement and supports deeper understanding by promoting active participation and personalized feedback.
Assessment Techniques: Tests vs. Projects
Traditional lecture-based learning primarily relies on standardized tests to evaluate student comprehension and retention of factual knowledge, emphasizing individual performance through quizzes, midterms, and final exams. In contrast, project-based learning assesses students through practical, real-world projects that foster critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills, providing a more holistic and applied measure of understanding. Project assessments often include presentations, reports, and peer evaluations, which collectively offer a comprehensive view of student learning beyond rote memorization.
Real-World Application and Skill Development
Project-Based Learning emphasizes real-world application by involving students in hands-on, collaborative projects that simulate authentic challenges, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Traditional Lecture-Based Learning primarily delivers theoretical knowledge through instructor-led presentations, often limiting opportunities for active skill development and practical engagement. Project-Based methods accelerate the acquisition of transferable skills such as teamwork, communication, and adaptability, aligning closely with workforce demands.
Choosing the Right Approach for Different Learners
Traditional lecture-based learning offers structured content delivery suited for learners who benefit from clear, linear explanations and passive knowledge absorption. Project-based learning fosters active engagement and critical thinking, ideal for students who thrive through hands-on experience and problem-solving in real-world contexts. Selecting the appropriate method depends on individual learning styles, subject matter complexity, and the desired development of skills such as collaboration and creativity.
Traditional Lecture-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com