Professional competency encompasses a blend of skills, knowledge, and behaviors that enable individuals to perform their job roles effectively and efficiently. Mastery of these competencies enhances your ability to meet workplace demands and contributes to career advancement. Explore this article to discover how developing professional competency can transform your career trajectory.
Table of Comparison
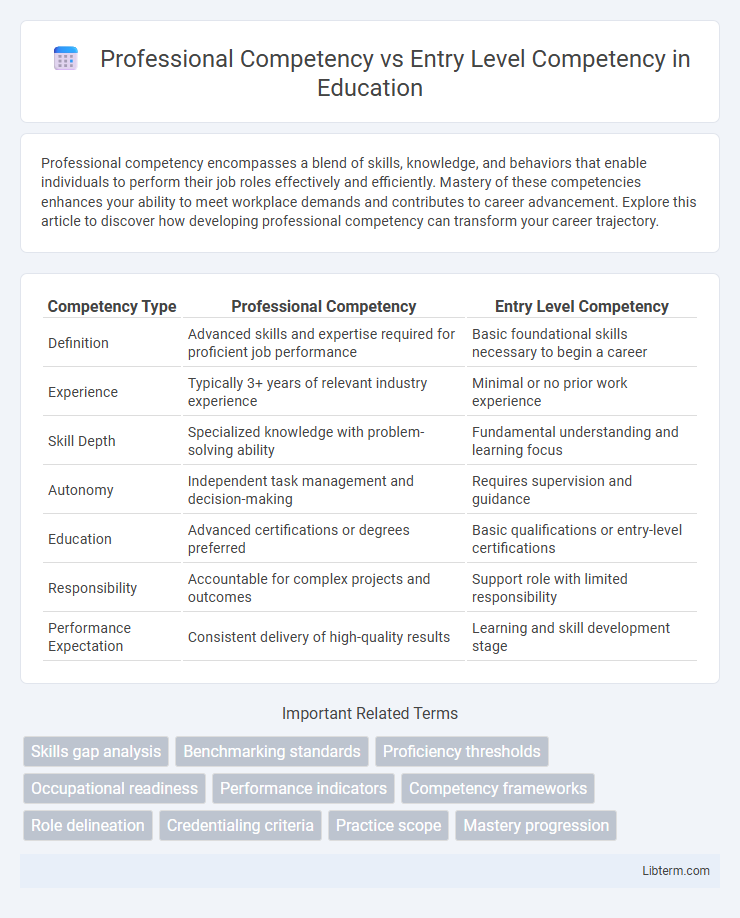
| Competency Type | Professional Competency | Entry Level Competency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advanced skills and expertise required for proficient job performance | Basic foundational skills necessary to begin a career |
| Experience | Typically 3+ years of relevant industry experience | Minimal or no prior work experience |
| Skill Depth | Specialized knowledge with problem-solving ability | Fundamental understanding and learning focus |
| Autonomy | Independent task management and decision-making | Requires supervision and guidance |
| Education | Advanced certifications or degrees preferred | Basic qualifications or entry-level certifications |
| Responsibility | Accountable for complex projects and outcomes | Support role with limited responsibility |
| Performance Expectation | Consistent delivery of high-quality results | Learning and skill development stage |
Defining Professional Competency
Professional competency encompasses advanced skills, knowledge, and behaviors expected from individuals performing specialized roles with expertise and autonomy. It includes critical thinking, problem-solving, effective communication, and the ability to adapt to evolving industry standards, distinguishing it from entry-level competency which covers foundational skills and basic job requirements. Defining professional competency involves assessing proficiency beyond routine tasks, emphasizing continuous learning, ethical judgment, and leadership capabilities.
Understanding Entry Level Competency
Entry Level Competency refers to the foundational skills and knowledge required for new professionals to perform basic job functions effectively. This competency level emphasizes understanding core concepts, technical abilities, and workplace behaviors essential for adapting to organizational standards. Mastery of Entry Level Competency ensures a smooth transition into more advanced Professional Competency, which involves strategic decision-making and specialized expertise.
Key Differences Between Professional and Entry Level Competencies
Professional competency involves advanced skills, practical experience, and industry-specific knowledge that enable effective decision-making and problem-solving in complex scenarios. Entry level competency typically requires foundational knowledge, basic technical abilities, and strong learning potential necessary for initial job responsibilities. The key differences lie in the depth of expertise, autonomy in task execution, and the scope of responsibilities between professional and entry level competencies.
Core Skills Required for Entry Level Professionals
Entry level competency centers on foundational skills such as effective communication, basic problem-solving, and adaptability, essential for integrating into professional environments. Professional competency expands to include advanced technical knowledge, strategic thinking, and leadership abilities, reflecting deeper expertise and experience. Core skills like teamwork, time management, and proficiency in relevant software remain critical at the entry level to support career growth and productivity.
Advanced Skills Marking Professional Competency
Professional competency encompasses advanced skills such as critical thinking, strategic decision-making, and complex problem-solving that distinguish experienced professionals from entry-level workers. Entry-level competency primarily involves foundational knowledge and basic task execution, lacking the nuanced understanding and adaptive expertise seen in professional competency. Mastery of advanced skills marks the transition to professional competency, enabling effective leadership, innovation, and high-impact performance in specialized fields.
Transitioning from Entry Level to Professional Competency
Transitioning from entry-level competency to professional competency requires mastering advanced skills, gaining practical experience, and demonstrating critical thinking within the relevant industry. This progression involves moving beyond foundational knowledge, acquiring specialized expertise, and consistently applying best practices to solve complex problems. Emphasizing continuous learning, mentorship, and performance evaluation accelerates development toward professional standards.
Role of Education and Training in Competency Development
Professional competency encompasses advanced skills and knowledge acquired through extensive education, specialized training, and practical experience, enabling individuals to perform complex tasks effectively. Entry level competency, often established through foundational education and basic training, provides essential skills required for initial job roles but lacks the depth necessary for independent decision-making and leadership. Education and training serve as critical drivers in transitioning from entry level to professional competency by continuously updating expertise, refining technical abilities, and fostering critical thinking crucial for career advancement.
Workplace Expectations: Entry Level vs Professional
Workplace expectations for entry-level competency emphasize foundational skills, adaptability, and the ability to follow directions under supervision, while professional competency demands advanced expertise, strategic problem-solving, and proactive decision-making. Entry-level employees are expected to learn and execute routine tasks efficiently, whereas professionals must demonstrate leadership, critical thinking, and independent judgment in complex scenarios. Employers prioritize continuous improvement and accountability at the professional level, contrasting with the developmental focus of entry-level roles.
Assessment and Evaluation of Competencies
Assessment and evaluation of professional competency involve rigorous measurement of advanced skills, knowledge, and experience compared to entry-level competency, which focuses on foundational abilities and basic understanding. Competency evaluations for professionals typically include practical performance tests, peer reviews, and situational judgment assessments to ensure proficiency in complex tasks and decision-making. Entry-level competency assessments emphasize theoretical knowledge and fundamental skills through written exams, simulations, and supervised practical exercises.
Strategies for Advancing Professional Competency
Developing professional competency requires targeted strategies such as continuous education, practical experience, and mentorship to bridge the gap from entry-level skills. Emphasizing specialized training programs and certifications enhances expertise, while real-world problem-solving fosters critical thinking and adaptability. Regular self-assessment and feedback integration ensure sustained growth and alignment with industry standards.
Professional Competency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com