Information literacy empowers you to critically evaluate and effectively use information from diverse sources, enhancing decision-making and problem-solving skills. Mastering these competencies is essential in navigating today's vast digital landscape and avoiding misinformation. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding and strengthen your information literacy skills.
Table of Comparison
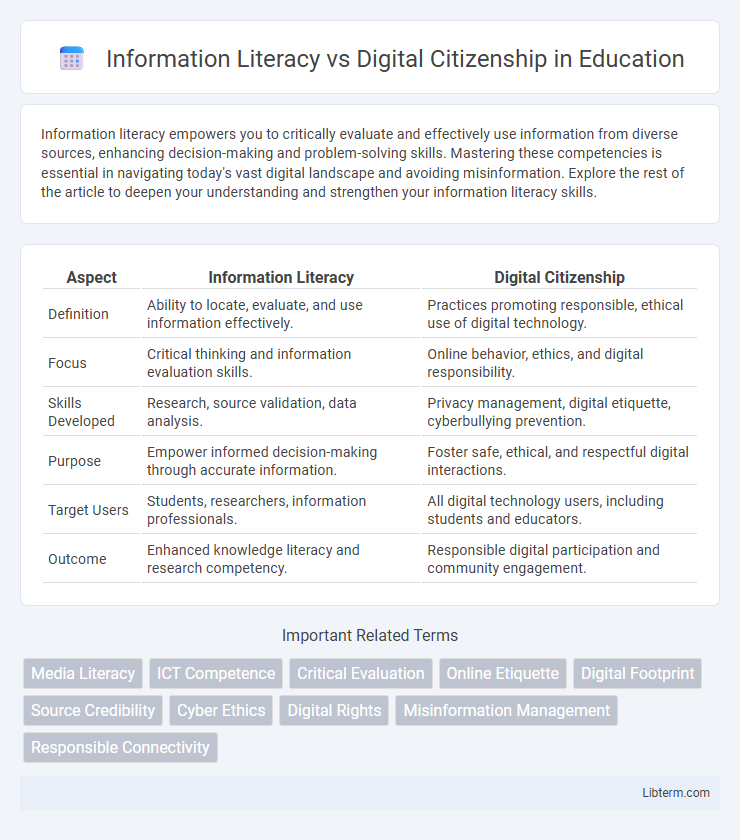
| Aspect | Information Literacy | Digital Citizenship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to locate, evaluate, and use information effectively. | Practices promoting responsible, ethical use of digital technology. |
| Focus | Critical thinking and information evaluation skills. | Online behavior, ethics, and digital responsibility. |
| Skills Developed | Research, source validation, data analysis. | Privacy management, digital etiquette, cyberbullying prevention. |
| Purpose | Empower informed decision-making through accurate information. | Foster safe, ethical, and respectful digital interactions. |
| Target Users | Students, researchers, information professionals. | All digital technology users, including students and educators. |
| Outcome | Enhanced knowledge literacy and research competency. | Responsible digital participation and community engagement. |
Introduction to Information Literacy and Digital Citizenship
Information literacy involves the ability to locate, evaluate, and use information effectively, fostering critical thinking and informed decision-making in various contexts. Digital citizenship encompasses responsible and ethical behavior in online environments, emphasizing safety, privacy, and respectful communication. Understanding both concepts is essential for navigating today's interconnected digital world with competence and integrity.
Defining Information Literacy
Information literacy involves the ability to locate, evaluate, and use information effectively and ethically across various digital and traditional formats. It encompasses critical thinking skills required to assess the credibility and relevance of sources in an era saturated with data and misinformation. Mastering information literacy is essential for making informed decisions and engaging responsibly in digital environments.
Understanding Digital Citizenship
Understanding Digital Citizenship involves recognizing the responsible use of technology to engage in ethical, safe, and effective online interactions. It encompasses digital literacy skills such as protecting privacy, respecting intellectual property, and practicing respectful communication within virtual communities. Mastery of digital citizenship promotes accountable behavior that supports positive digital footprints and helps prevent cyberbullying and misinformation.
Key Differences Between Information Literacy and Digital Citizenship
Information literacy centers on the ability to locate, evaluate, and effectively use information across various formats, emphasizing critical thinking and research skills. Digital citizenship encompasses responsible and ethical behavior in online environments, including understanding digital rights, privacy, and respectful communication. The key difference lies in information literacy's focus on managing information accurately, while digital citizenship prioritizes appropriate online conduct and digital citizenship skills.
Overlapping Skills and Competencies
Information literacy and digital citizenship share overlapping skills such as critical thinking, evaluating digital content for credibility, and responsible online communication. Both competencies emphasize understanding digital privacy, ethical behavior, and effective information management across various platforms. Mastery in these areas enables individuals to navigate the digital landscape safely and make informed, ethical decisions online.
Importance in the Digital Age
Information literacy empowers individuals to critically evaluate and effectively use digital content, preventing misinformation and enhancing decision-making skills. Digital citizenship emphasizes responsible and ethical behavior online, fostering safe, respectful, and inclusive digital communities. Both are essential in navigating the digital age, ensuring users can access, analyze, and participate in digital environments responsibly and confidently.
Challenges in Promoting Information Literacy
Promoting information literacy faces challenges such as overcoming digital misinformation, limited critical thinking skills, and unequal access to reliable digital resources. Educators must address cognitive biases and the rapid evolution of digital platforms that complicate discerning credible information. Furthermore, integrating information literacy within digital citizenship frameworks requires continuous adaptation to technological changes and diverse learner needs.
Fostering Responsible Digital Citizenship
Fostering responsible digital citizenship involves cultivating information literacy skills that enable individuals to critically evaluate online sources, recognize misinformation, and respect digital rights and responsibilities. Emphasizing digital ethics, privacy awareness, and respectful online communication helps build a safe and inclusive digital environment. Integrating information literacy with digital citizenship education prepares users to engage thoughtfully and responsibly in digital communities.
Integrating Both in Education
Integrating information literacy and digital citizenship in education equips students with critical skills to evaluate and use information responsibly while fostering ethical behavior in online environments. Combining these competencies enhances students' ability to navigate digital platforms effectively, promoting media literacy alongside respect for privacy, intellectual property, and digital etiquette. Educational curricula that blend information literacy with digital citizenship prepare learners to participate actively and safely in the digital world, bridging technical proficiency with ethical awareness.
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital World Responsibly
Mastering information literacy equips individuals with critical thinking skills required to evaluate and use digital content effectively. Embracing digital citizenship fosters ethical behavior, online safety, and respectful interactions within digital communities. Together, these competencies ensure responsible navigation and active participation in the digital world.
Information Literacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com