Deductive teaching starts with presenting general principles before moving to specific examples, helping learners quickly grasp the core concepts. This method streamlines information processing and enhances retention by providing clear, structured guidance from the outset. Explore the rest of the article to see how deductive teaching can improve your learning outcomes.
Table of Comparison
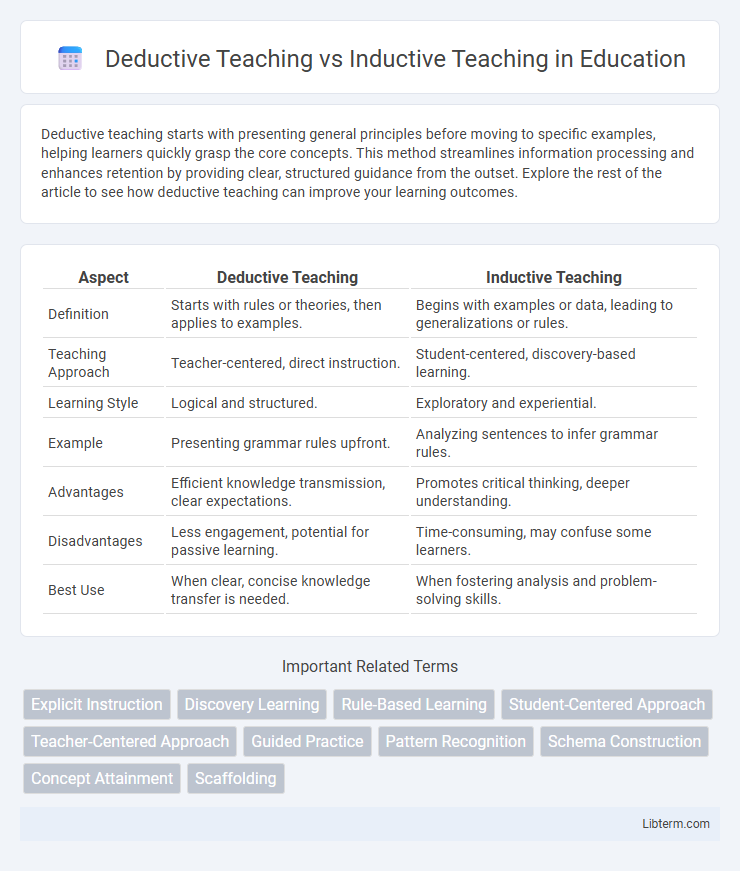
| Aspect | Deductive Teaching | Inductive Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Starts with rules or theories, then applies to examples. | Begins with examples or data, leading to generalizations or rules. |
| Teaching Approach | Teacher-centered, direct instruction. | Student-centered, discovery-based learning. |
| Learning Style | Logical and structured. | Exploratory and experiential. |
| Example | Presenting grammar rules upfront. | Analyzing sentences to infer grammar rules. |
| Advantages | Efficient knowledge transmission, clear expectations. | Promotes critical thinking, deeper understanding. |
| Disadvantages | Less engagement, potential for passive learning. | Time-consuming, may confuse some learners. |
| Best Use | When clear, concise knowledge transfer is needed. | When fostering analysis and problem-solving skills. |
Introduction to Deductive and Inductive Teaching
Deductive teaching presents general rules or principles first, followed by specific examples to illustrate the concepts, enhancing clarity and structure in learning. Inductive teaching reverses this order by introducing specific examples or observations initially, encouraging students to infer the underlying rules, which fosters critical thinking and discovery. Both methods cater to different learning styles and objectives, impacting comprehension and retention depending on the educational context.
Defining Deductive Teaching Methods
Deductive teaching methods involve presenting general principles or rules first, followed by specific examples to illustrate the concepts. This approach emphasizes direct instruction and structured learning, promoting clarity and efficiency in knowledge acquisition. It is widely used in disciplines requiring precise understanding, such as mathematics and grammar.
Understanding Inductive Teaching Approaches
Inductive teaching approaches emphasize learning through observation, pattern recognition, and discovery, allowing students to construct their own understanding based on specific examples. This learner-centered method enhances critical thinking and retention by engaging students in active exploration rather than passive reception of rules. Research shows that inductive teaching fosters deeper conceptual understanding, particularly in subjects like language acquisition and science education.
Key Differences Between Deductive and Inductive Teaching
Deductive teaching starts with general principles or rules, followed by specific examples to illustrate the concept, facilitating straightforward knowledge transfer and focused learning outcomes. Inductive teaching encourages learners to observe patterns or examples first, promoting critical thinking and discovery-based learning by guiding students to infer rules independently. The key difference lies in the direction of reasoning: deductive moves from theory to application, while inductive progresses from observation to theory formulation.
Advantages of Deductive Teaching
Deductive teaching offers clear structure by presenting general rules or principles before moving to specific examples, which enhances comprehension and retention. This method is time-efficient and straightforward, making it suitable for learners who need explicit guidance and quick mastery of concepts. It also facilitates easier assessment and error correction by directly addressing established rules.
Benefits of Inductive Teaching
Inductive teaching promotes active learning by encouraging students to discover concepts through observation and pattern recognition, leading to deeper comprehension and retention. This approach supports critical thinking and problem-solving skills by allowing learners to construct knowledge based on real-world examples and experiences. Research shows that inductive methods enhance engagement and motivation, making it effective for diverse learning styles and fostering long-term understanding.
When to Use Deductive vs Inductive Methods
Deductive teaching excels in situations where clear rules, formulas, or procedures must be conveyed efficiently, making it ideal for subjects like mathematics and grammar that require structured understanding. Inductive teaching is best used when students need to develop critical thinking and discovery skills by exploring patterns, examples, or real-world data, often applied in science and inquiry-based learning contexts. Choosing between these methods depends on the learning objectives, with deductive methods favoring rule mastery and inductive methods promoting conceptual understanding and application.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Deductive teaching faces challenges such as limited student engagement and reduced critical thinking opportunities due to its top-down, teacher-centered structure. Inductive teaching can be time-consuming and may overwhelm learners who lack sufficient background knowledge, leading to potential confusion or frustration. Both approaches require careful balancing to address diverse learner needs and optimize knowledge retention and application.
Practical Examples in the Classroom
Deductive teaching presents rules or concepts first, followed by practical examples such as grammar drills where students apply given rules to sentences. Inductive teaching uses specific examples like reading passages or experiments, encouraging students to infer rules or patterns independently. Classroom activities like guided discovery exercises promote inductive learning by engaging students in observation and hypothesis formation.
Choosing the Right Method for Effective Learning
Selecting the right teaching method depends on the learning objectives and student needs, with deductive teaching offering clear, structured guidance through rule presentation, while inductive teaching fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to discover concepts independently. Deductive approaches work well for straightforward, rule-based subjects like grammar, whereas inductive methods suit complex, inquiry-based learning that promotes deeper understanding and retention. Balancing both methods and aligning them with curriculum goals enhances overall effectiveness and learner engagement.
Deductive Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com