The official curriculum outlines the standardized educational framework designed to ensure consistent learning outcomes across schools. It serves as a guide for educators in planning lessons and assessing student progress, aligning with national education standards. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the official curriculum impacts your child's education and academic success.
Table of Comparison
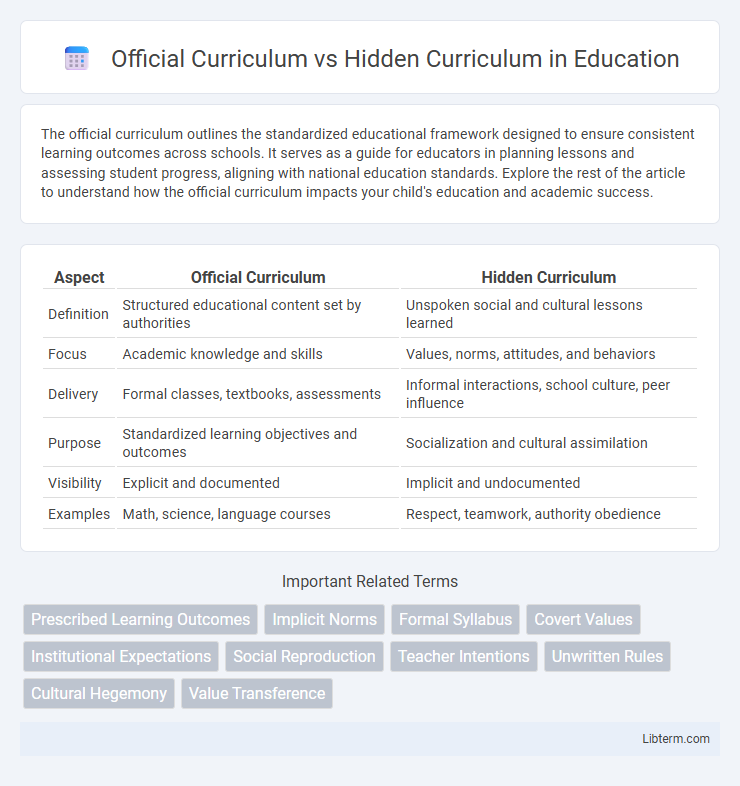
| Aspect | Official Curriculum | Hidden Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured educational content set by authorities | Unspoken social and cultural lessons learned |
| Focus | Academic knowledge and skills | Values, norms, attitudes, and behaviors |
| Delivery | Formal classes, textbooks, assessments | Informal interactions, school culture, peer influence |
| Purpose | Standardized learning objectives and outcomes | Socialization and cultural assimilation |
| Visibility | Explicit and documented | Implicit and undocumented |
| Examples | Math, science, language courses | Respect, teamwork, authority obedience |
Understanding the Official Curriculum
The official curriculum consists of the formally documented educational content, learning objectives, and standards established by educational authorities to guide teaching and assessment. It provides a structured framework designed to ensure consistent knowledge acquisition and skill development across educational institutions. Understanding the official curriculum is essential for aligning teaching strategies with mandated educational goals and measuring student outcomes effectively.
Defining the Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, and norms that students learn indirectly through the educational environment and social interactions, rather than through formal instruction. It encompasses behaviors, attitudes, and expectations conveyed by teachers, peers, and institutional culture that often shape students' social development and worldview. Unlike the official curriculum, which outlines explicit academic goals and content, the hidden curriculum influences character formation and socialization within the school context.
Key Differences Between Official and Hidden Curriculum
The official curriculum outlines the structured academic content and learning objectives mandated by educational authorities, such as standardized subjects, assessments, and learning outcomes. In contrast, the hidden curriculum encompasses the implicit lessons, values, social norms, and behaviors conveyed through the school environment and teacher-student interactions. Key differences include the official curriculum's formal documentation and explicit goals versus the hidden curriculum's informal, often unspoken influence on students' social development and cultural assimilation.
Origins and Purposes of Both Curricula
The official curriculum originates from educational authorities to deliver standardized knowledge and skills aligned with national standards and societal goals. The hidden curriculum emerges informally through school culture, social interactions, and institutional practices, shaping students' attitudes, values, and social norms. Both curricula serve to prepare students for societal participation, with the official curriculum emphasizing academic competencies and the hidden curriculum reinforcing behavioral and social expectations.
Impact on Student Learning and Development
The official curriculum provides structured knowledge and skill development aligned with educational standards, ensuring measurable academic progress. The hidden curriculum influences student learning and development through implicit lessons in social norms, values, and behaviors, shaping attitudes and interpersonal skills. Together, they significantly impact students' cognitive growth and socio-emotional development, affecting overall educational outcomes.
Examples of Hidden Curriculum in Schools
Hidden curriculum in schools includes implicit lessons such as social norms, values, and behaviors taught through classroom interactions, school culture, and teacher expectations. Examples include reinforcing punctuality, obedience to authority, competitiveness, and gender roles, which are not explicitly stated in the official curriculum but significantly impact student development. These unwritten lessons shape students' attitudes, social skills, and perceptions of societal roles beyond academic content.
Teacher Roles in Shaping Both Curricula
Teachers actively implement the official curriculum by delivering structured lessons aligned with educational standards while simultaneously influencing the hidden curriculum through their attitudes, behaviors, and classroom management. Their role extends beyond instruction to modeling social norms, values, and expectations that shape students' interpersonal skills and moral development. Effective teachers recognize the impact of both curricula on student outcomes and strategically foster positive learning environments that reinforce formal knowledge along with implicit cultural lessons.
Challenges in Addressing Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum encompasses implicit lessons, values, and norms conveyed through school culture and teacher attitudes, often contradicting the official curriculum's explicit goals. Challenges in addressing the hidden curriculum include its pervasive and unconscious nature, making it difficult for educators to recognize and modify these implicit messages. Efforts to align hidden curriculum with official educational objectives require continuous reflection, professional development, and systemic change to foster equitable and inclusive learning environments.
Strategies for Bridging Curriculum Gaps
Effective strategies for bridging gaps between the official curriculum and the hidden curriculum involve integrating explicit discussions about values, norms, and expectations within classroom activities to align implicit lessons with formal educational goals. Educators can employ reflective practices and collaborative learning environments that encourage students to critically analyze both the formal content and the underlying social messages conveyed through school culture and peer interactions. Implementing professional development programs focused on cultural competence and inclusive pedagogy helps teachers recognize hidden curricula influences, ensuring a more cohesive and equitable learning experience.
Future Directions for Curriculum Reform
Future directions for curriculum reform emphasize integrating the official curriculum with the hidden curriculum to foster holistic student development and critical thinking skills. There is increasing advocacy for transparency in the implicit values and norms conveyed through school culture and practices, ensuring alignment with equity and inclusivity goals. Leveraging technology and interdisciplinary approaches can bridge gaps between formal content and informal learning experiences, preparing students for dynamic, real-world challenges.
Official Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com