Mastering subject knowledge is essential for building expertise and credibility in any field. It enables you to make informed decisions, solve problems effectively, and communicate with confidence. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding and strengthen your skills.
Table of Comparison
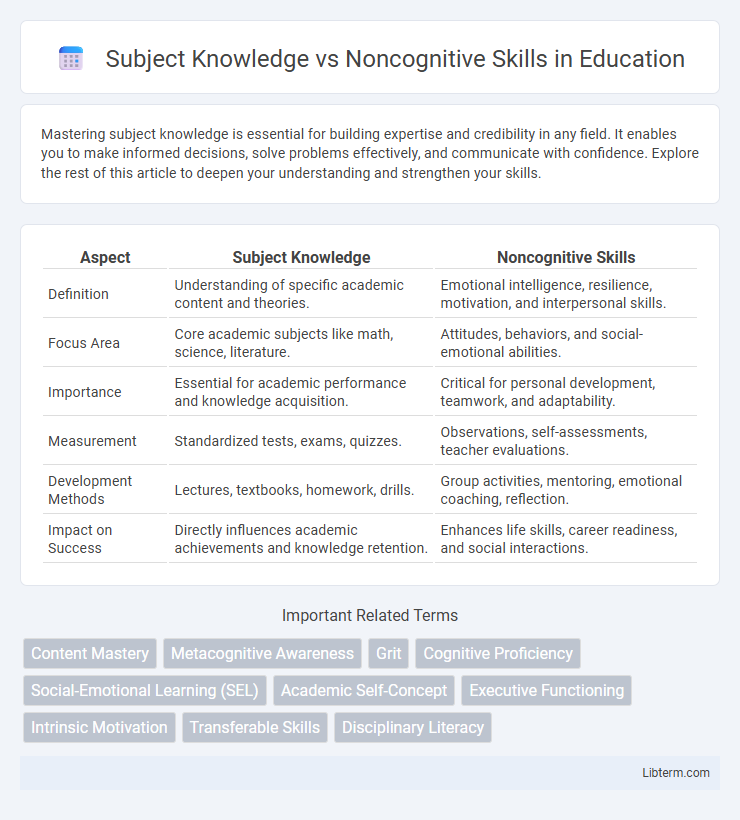
| Aspect | Subject Knowledge | Noncognitive Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding of specific academic content and theories. | Emotional intelligence, resilience, motivation, and interpersonal skills. |
| Focus Area | Core academic subjects like math, science, literature. | Attitudes, behaviors, and social-emotional abilities. |
| Importance | Essential for academic performance and knowledge acquisition. | Critical for personal development, teamwork, and adaptability. |
| Measurement | Standardized tests, exams, quizzes. | Observations, self-assessments, teacher evaluations. |
| Development Methods | Lectures, textbooks, homework, drills. | Group activities, mentoring, emotional coaching, reflection. |
| Impact on Success | Directly influences academic achievements and knowledge retention. | Enhances life skills, career readiness, and social interactions. |
Understanding Subject Knowledge: Definition and Importance
Subject knowledge refers to the comprehensive understanding of specific content, concepts, facts, and theories within a particular academic discipline or field. It is crucial for effective teaching and learning, as it enables educators and students to engage deeply with the material, apply critical thinking, and transfer knowledge across contexts. Mastery of subject knowledge forms the foundation for achieving academic success and fostering intellectual growth in various educational settings.
What Are Noncognitive Skills? Key Concepts Explained
Noncognitive skills refer to a range of personal attributes, behaviors, and attitudes such as self-control, motivation, perseverance, and social skills that influence an individual's ability to succeed beyond academic knowledge. These skills are critical for adapting to challenges, managing emotions, and fostering collaboration in educational and professional settings. Unlike subject knowledge, noncognitive skills are key drivers of long-term achievement and personal development.
Comparing Subject Knowledge and Noncognitive Skills
Subject knowledge encompasses specific content expertise and cognitive abilities essential for academic achievement, while noncognitive skills include traits like resilience, motivation, and social-emotional competence that influence behavior and learning engagement. Research shows that integrating noncognitive skills with subject knowledge leads to improved student outcomes, highlighting the complementary nature of these dimensions. Educational strategies that balance mastery of subject matter with development of perseverance and self-regulation maximize both intellectual growth and long-term success.
The Role of Subject Knowledge in Academic Success
Subject knowledge forms the foundation of academic success by enabling students to grasp complex concepts, solve discipline-specific problems, and perform well in assessments. Research demonstrates that mastery of core subjects such as mathematics, science, and language arts directly correlates with higher grades and standardized test scores. While noncognitive skills like motivation and perseverance support learning, robust subject knowledge is essential for achieving deep understanding and long-term academic achievement.
How Noncognitive Skills Influence Learning Outcomes
Noncognitive skills such as perseverance, time management, and emotional regulation significantly influence learning outcomes by enhancing students' ability to engage with and retain subject knowledge. Studies show that learners with strong noncognitive skills demonstrate better problem-solving abilities and higher academic achievement compared to those relying solely on cognitive skills. Developing these skills fosters resilience and motivation, which are critical for mastering complex subjects and achieving long-term educational success.
Integrating Subject Knowledge and Noncognitive Skills in Education
Integrating subject knowledge with noncognitive skills such as resilience, collaboration, and emotional intelligence enhances student learning outcomes and prepares them for real-world challenges. Educational frameworks that combine cognitive content mastery with skill development foster critical thinking, adaptability, and effective communication. This holistic approach supports academic achievement while promoting personal growth and social competence essential for lifelong success.
Assessing Subject Knowledge vs Noncognitive Skills
Assessing subject knowledge involves measuring a learner's mastery of specific content areas through standardized tests, quizzes, and performance tasks that evaluate factual recall and conceptual understanding. Noncognitive skills assessment focuses on evaluating traits such as motivation, perseverance, collaboration, and emotional regulation, often using self-report surveys, behavioral observations, or situational judgment tests. Effective educational evaluation integrates both assessments to provide a comprehensive view of student capabilities, linking cognitive proficiency with essential life skills.
Teaching Strategies for Balancing Cognitive and Noncognitive Skills
Effective teaching strategies balance subject knowledge with noncognitive skills by integrating critical thinking exercises and emotional intelligence activities into lesson plans. Strategies such as collaborative projects and reflective journaling foster both cognitive understanding and interpersonal skills, enhancing student engagement and resilience. Incorporating formative assessments supports ongoing development of content mastery alongside motivation and self-regulation abilities.
Real-World Applications: Subject Mastery and Soft Skills
Subject knowledge equips individuals with expert understanding and technical expertise essential for solving complex problems in fields such as engineering, medicine, and law. Noncognitive skills, including communication, teamwork, and emotional intelligence, enhance collaboration and adaptability in dynamic work environments. Combining subject mastery with soft skills optimizes career success by ensuring both analytical proficiency and effective interpersonal interactions in real-world professional settings.
The Future of Education: Harmonizing Knowledge and Skills
The future of education requires harmonizing subject knowledge with noncognitive skills such as emotional intelligence, adaptability, and critical thinking to prepare students for complex real-world challenges. Integrating cognitive mastery with skills like collaboration and resilience enhances learners' ability to innovate and thrive in dynamic environments. Educational frameworks that balance academic content and socio-emotional competencies drive holistic development and lifelong success.
Subject Knowledge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com