Project-Based Learning engages students in active, real-world problem solving, fostering deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. This hands-on approach promotes critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of skills that traditional methods often overlook. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Project-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
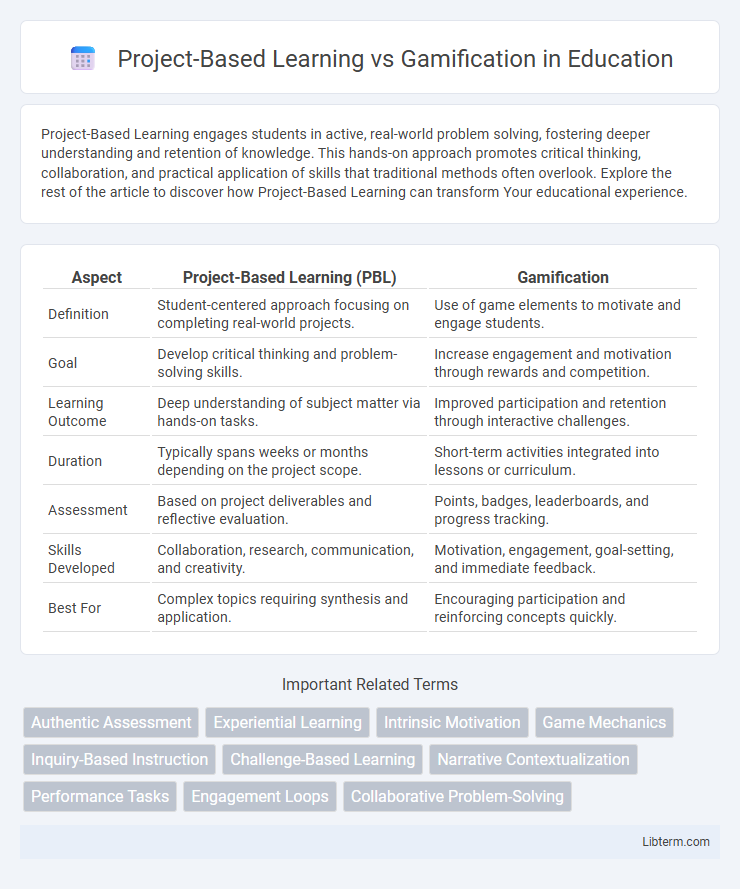
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Gamification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focusing on completing real-world projects. | Use of game elements to motivate and engage students. |
| Goal | Develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. | Increase engagement and motivation through rewards and competition. |
| Learning Outcome | Deep understanding of subject matter via hands-on tasks. | Improved participation and retention through interactive challenges. |
| Duration | Typically spans weeks or months depending on the project scope. | Short-term activities integrated into lessons or curriculum. |
| Assessment | Based on project deliverables and reflective evaluation. | Points, badges, leaderboards, and progress tracking. |
| Skills Developed | Collaboration, research, communication, and creativity. | Motivation, engagement, goal-setting, and immediate feedback. |
| Best For | Complex topics requiring synthesis and application. | Encouraging participation and reinforcing concepts quickly. |
Understanding Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional method that engages students in exploring real-world problems through extended projects, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of knowledge. This approach emphasizes student-driven inquiry, active problem-solving, and the integration of interdisciplinary skills. Research shows PBL enhances retention and prepares learners for complex challenges by simulating authentic work environments.
Defining Gamification in Education
Gamification in education involves incorporating game design elements such as points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges into learning environments to enhance student engagement and motivation. Unlike project-based learning, which centers on hands-on, real-world problem solving, gamification leverages reward systems and interactive features to drive participation and reinforce knowledge retention. Research shows that gamified educational approaches can improve cognitive skills, promote collaboration, and increase persistence in learning tasks.
Core Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning centers on student-driven inquiry, real-world problem solving, and sustained collaboration to foster deep understanding and critical thinking skills. It emphasizes authenticity, allowing learners to engage with meaningful projects that mirror challenges in their community or future careers. This approach highlights reflection and iterative feedback, ensuring continuous growth and mastery of content through active exploration.
Key Features of Gamification
Gamification integrates game design elements such as point scoring, leaderboards, and rewards into educational activities to enhance learner engagement and motivation. It emphasizes real-time feedback, competition, and achievement recognition, promoting sustained participation and a sense of accomplishment. These key features differentiate gamification from Project-Based Learning, which centers on hands-on, collaborative problem-solving over extended periods.
Learning Outcomes: PBL vs Gamification
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application skills, leading to deeper subject comprehension and improved collaboration among students. Gamification boosts learner motivation and engagement through game elements, improving knowledge retention and immediate feedback responsiveness. Studies reveal PBL achieves higher long-term learning outcomes, while gamification excels in sustaining short-term enthusiasm and skill practice.
Engagement and Motivation Comparison
Project-Based Learning enhances engagement by promoting active problem-solving and real-world application, fostering intrinsic motivation through meaningful, hands-on experiences. Gamification boosts motivation by incorporating game elements like points, badges, and leaderboards, driving extrinsic motivation and promoting competition and rewards. Both strategies significantly increase student engagement but differ in approach: Project-Based Learning emphasizes deep, sustained involvement, while Gamification leverages immediate feedback and reward systems.
Skill Development Differences
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in extended, hands-on projects. Gamification emphasizes motivation, engagement, and quick decision-making through game elements like points, badges, and leaderboards, fostering skills in adaptability and competitive strategy. While PBL develops deep analytical and teamwork abilities, gamification primarily cultivates immediate feedback processing and perseverance in skill acquisition.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementation challenges in Project-Based Learning (PBL) often include time constraints, resource limitations, and the need for specialized teacher training, while gamification faces obstacles like balancing educational content with game elements and ensuring technology access. Solutions for PBL involve modular curriculum design, professional development focused on project facilitation, and leveraging community partnerships to enhance resources. For gamification, adopting scalable platforms, integrating adaptive learning technology, and providing equitable access to devices and internet connectivity are critical strategies to overcome implementation barriers.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Project-Based Learning (PBL) engages students in solving complex, real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and collaboration through extended, hands-on projects. Gamification integrates game mechanics into education, increasing motivation and engagement by incorporating elements such as point scoring, leaderboards, and challenges aligned with learning objectives. Case studies demonstrate PBL's effectiveness in STEM education for developing practical skills, while gamification has shown success in language acquisition and employee training by promoting sustained interaction and immediate feedback.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Project-Based Learning (PBL) fosters critical thinking and real-world problem-solving by engaging students in in-depth projects tied to curriculum standards. Gamification leverages game design elements like points, badges, and leaderboards to boost motivation and participation, making lessons more interactive and enjoyable. Selecting the right approach depends on classroom goals: PBL suits deeper exploration of complex topics, while gamification enhances engagement, especially in formative assessment and skill practice.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com