Academic success hinges on effective study strategies, time management, and critical thinking skills that foster comprehensive learning. Developing these skills can improve your ability to analyze complex information and excel in various subjects. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for enhancing your academic performance.
Table of Comparison
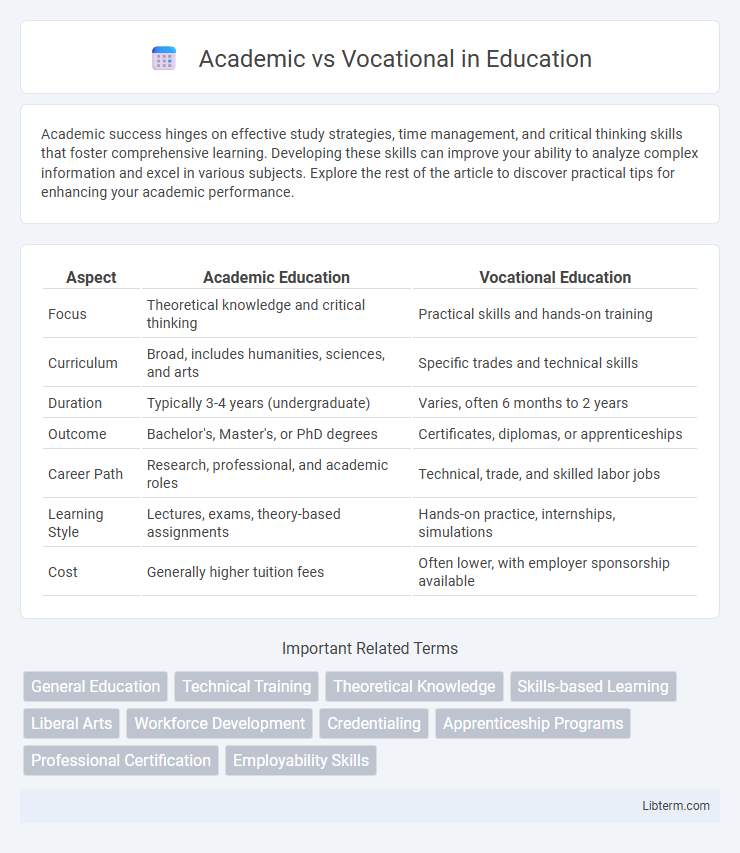
| Aspect | Academic Education | Vocational Education |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Theoretical knowledge and critical thinking | Practical skills and hands-on training |
| Curriculum | Broad, includes humanities, sciences, and arts | Specific trades and technical skills |
| Duration | Typically 3-4 years (undergraduate) | Varies, often 6 months to 2 years |
| Outcome | Bachelor's, Master's, or PhD degrees | Certificates, diplomas, or apprenticeships |
| Career Path | Research, professional, and academic roles | Technical, trade, and skilled labor jobs |
| Learning Style | Lectures, exams, theory-based assignments | Hands-on practice, internships, simulations |
| Cost | Generally higher tuition fees | Often lower, with employer sponsorship available |
Introduction to Academic and Vocational Education
Academic education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills, preparing students for higher education and research-oriented careers. Vocational education focuses on practical skills and hands-on training, equipping learners with specific competencies for immediate employment in trades or technical fields. Both pathways offer specialized curricula designed to meet diverse career goals and industry demands.
Defining Academic Pathways
Academic pathways emphasize theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills, preparing students for higher education and research-oriented careers. These programs typically include subjects such as mathematics, science, literature, and humanities, fostering a broad intellectual foundation. Academic education aims to develop analytical abilities and subject mastery essential for university admission and scholarly pursuits.
Understanding Vocational Training
Vocational training provides specialized education focused on practical skills and hands-on experience for specific trades or professions, such as plumbing, electrical work, or culinary arts. This form of training often includes apprenticeships, workshops, and industry certifications that prepare students for immediate entry into the workforce. Emphasizing career readiness, vocational programs bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world applications, making them essential for sectors where technical expertise is paramount.
Key Differences Between Academic and Vocational Routes
Academic education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills, typically preparing students for university degrees and research-oriented careers. Vocational education focuses on practical skills and hands-on training tailored to specific trades or professions, enabling direct entry into the workforce. The key difference lies in the approach: academic routes prioritize conceptual understanding, while vocational routes emphasize skill acquisition and immediate job readiness.
Skills Developed in Academic Programs
Academic programs primarily develop critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and research skills essential for theoretical understanding and intellectual growth. These programs emphasize theoretical knowledge acquisition, fostering abilities in problem-solving, communication, and independent learning. Mastery of complex concepts and the capacity to synthesize information from diverse disciplines are key skills cultivated through academic education.
Practical Skills Gained from Vocational Training
Vocational training emphasizes practical skills development, enabling learners to perform specific trades such as plumbing, carpentry, or culinary arts with hands-on experience. Unlike academic education, which prioritizes theoretical knowledge, vocational programs prepare students for immediate employment by teaching industry-relevant techniques and problem-solving skills. This focus on applied learning enhances job readiness and aligns closely with labor market demands, leading to higher employability in specialized fields.
Career Opportunities After Academic Study
Academic study provides a strong foundation for careers in research, education, healthcare, and technology sectors by emphasizing theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills. Graduates typically pursue roles such as university professors, scientists, engineers, or medical professionals, where advanced qualifications and continuous learning are essential. Career opportunities often include higher earning potential and positions that require specialized expertise or advanced degrees.
Job Prospects with Vocational Qualifications
Vocational qualifications often lead to specialized job prospects in industries such as healthcare, technology, and skilled trades, where practical skills are in high demand. Employers value vocational training for its direct applicability to roles like electrician, dental hygienist, or IT technician, providing graduates with faster entry into the workforce. These qualifications typically result in competitive salaries and career advancement opportunities due to hands-on experience and industry-specific knowledge.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between academic and vocational education involves evaluating individual career goals, learning preferences, and job market demand. Academic paths often emphasize theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills, suited for professions requiring advanced degrees, while vocational training focuses on practical skills and hands-on experience tailored for specific trades. Consider factors such as industry growth projections, salary expectations, and personal aptitude to align education choices with long-term professional success.
Future Trends in Education and Workforce Demands
Academic education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills, preparing students for professions in research, medicine, and law. Vocational education targets practical skills and hands-on training, aligning closely with industries such as manufacturing, technology, and healthcare services. Future workforce demands highlight the growing need for hybrid models that integrate academic theory with vocational expertise to adapt to rapid technological advancements and sector-specific skill shortages.
Academic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com