Standardized testing plays a crucial role in measuring academic achievement and comparing student performance across various regions. Understanding the benefits and challenges of these assessments helps you navigate their impact on education policies and personal learning strategies. Explore the rest of the article to discover how standardized testing shapes your educational experience and outcomes.
Table of Comparison
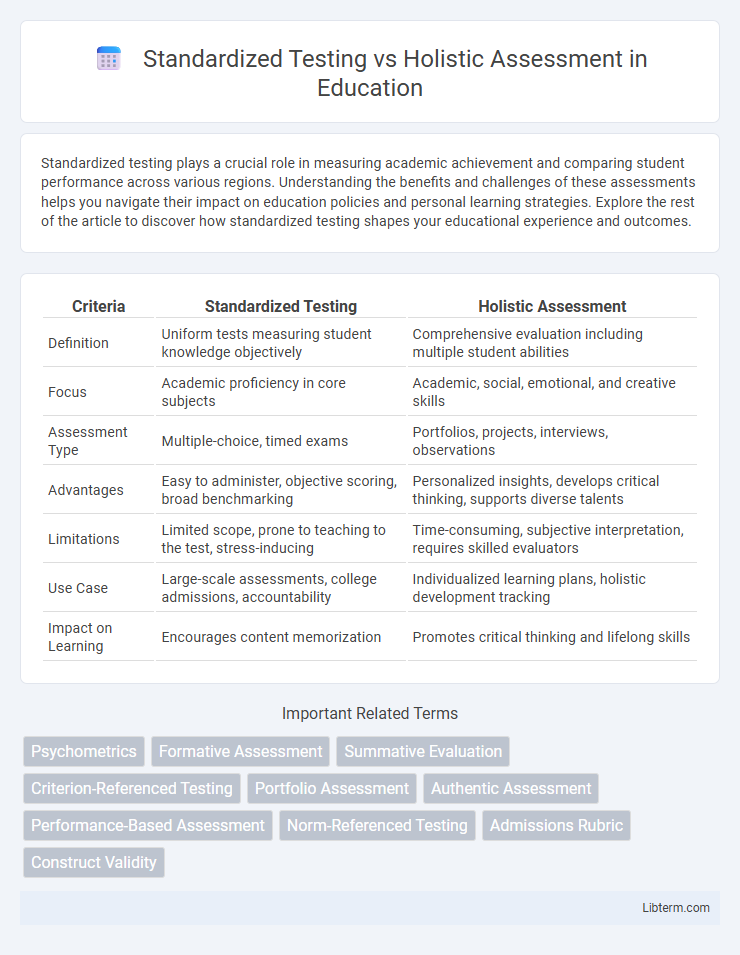
| Criteria | Standardized Testing | Holistic Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform tests measuring student knowledge objectively | Comprehensive evaluation including multiple student abilities |
| Focus | Academic proficiency in core subjects | Academic, social, emotional, and creative skills |
| Assessment Type | Multiple-choice, timed exams | Portfolios, projects, interviews, observations |
| Advantages | Easy to administer, objective scoring, broad benchmarking | Personalized insights, develops critical thinking, supports diverse talents |
| Limitations | Limited scope, prone to teaching to the test, stress-inducing | Time-consuming, subjective interpretation, requires skilled evaluators |
| Use Case | Large-scale assessments, college admissions, accountability | Individualized learning plans, holistic development tracking |
| Impact on Learning | Encourages content memorization | Promotes critical thinking and lifelong skills |
Introduction to Standardized Testing and Holistic Assessment
Standardized testing evaluates student performance through uniform exams that measure specific academic skills under consistent conditions, enabling large-scale comparison and accountability. Holistic assessment considers a broad range of student abilities, including critical thinking, creativity, and social-emotional skills, often using portfolios, presentations, and teacher observations. Both approaches aim to inform educational outcomes but differ significantly in scope, measurement methods, and impact on student evaluation.
Defining Standardized Testing: Key Features
Standardized testing involves uniform procedures for administration and scoring to ensure consistency and objectivity across all test takers. Key features include fixed test formats, multiple-choice questions, and time limits designed to measure specific skills or knowledge areas. These tests provide quantifiable data used for comparing performance across individuals or groups in educational and professional settings.
Understanding Holistic Assessment: Core Principles
Holistic assessment emphasizes evaluating a student's overall learning process, critical thinking, creativity, and social skills rather than relying solely on standardized test scores. It incorporates multiple sources of evidence, including portfolios, presentations, and peer evaluations, to provide a comprehensive view of a learner's abilities. This approach aligns with educational frameworks that prioritize personalized learning and the development of 21st-century skills beyond rote memorization.
Historical Evolution of Student Assessment Methods
Standardized testing originated in the early 20th century as a uniform method to evaluate student performance, aiming to provide objective data for educational decisions. Over time, critics highlighted its limitations, such as cultural bias and inability to measure critical thinking, leading to the rise of holistic assessment approaches in the late 20th century. Holistic assessment considers multiple student dimensions, including creativity, collaboration, and emotional development, reflecting a more comprehensive understanding of learning outcomes.
Advantages of Standardized Testing
Standardized testing offers a consistent and objective measure of student performance, enabling reliable comparison across different schools and regions. It provides quantifiable data that helps educators identify gaps in knowledge and tailor instruction accordingly. Additionally, standardized tests facilitate accountability by setting clear benchmarks for academic achievement and informing policy decisions.
Benefits of Holistic Assessment
Holistic assessment offers a comprehensive evaluation of a student's skills, creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence beyond traditional test scores. It fosters personalized learning by considering diverse learning styles and real-world problem-solving abilities, promoting deeper understanding and long-term retention. This approach supports a more inclusive education system, accommodating varied talents and reducing the pressure associated with standardized testing.
Common Criticisms of Standardized Testing
Standardized testing faces common criticisms for promoting a narrow curriculum focused on test preparation rather than critical thinking and creativity. Critics argue it often disadvantages students from diverse backgrounds due to cultural biases and fails to accurately reflect individual learning styles or abilities. High-stakes environments can increase student anxiety and do not account for social, emotional, or practical skills gained outside traditional academics.
Challenges and Limitations of Holistic Assessment
Holistic assessment faces challenges such as subjectivity in grading, which can lead to inconsistent results and potential biases. The process requires significant time, trained evaluators, and clear rubrics to ensure fairness, making it resource-intensive compared to standardized tests. Additionally, holistic methods may struggle with scaling and comparability across diverse student populations and institutions.
Impact on Student Achievement and Equity
Standardized testing provides quantifiable data that can identify achievement gaps but often overlooks individual learning styles, potentially reinforcing inequities among marginalized students. Holistic assessment incorporates diverse evaluation methods such as portfolios, presentations, and peer reviews, fostering a more inclusive understanding of student abilities and promoting equitable opportunities for academic success. Research indicates that integrating holistic approaches with standardized measures enhances student engagement and supports equitable achievement outcomes across diverse populations.
Future Trends in Educational Assessment
Future trends in educational assessment emphasize integrating technology-driven adaptive testing with holistic evaluation methods to capture a comprehensive understanding of student abilities and growth. Artificial intelligence and data analytics enable personalized learning insights beyond standardized testing scores, promoting skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and socio-emotional development. This shift towards blended assessment models aligns with educational goals for cultivating lifelong learners equipped for dynamic and complex future environments.
Standardized Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com