The Humanities Pathway explores subjects such as history, literature, philosophy, and cultural studies, offering a deep understanding of human society and creative expression. This interdisciplinary approach enhances critical thinking, communication skills, and ethical reasoning. Discover how this pathway can shape Your intellectual growth and career opportunities by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
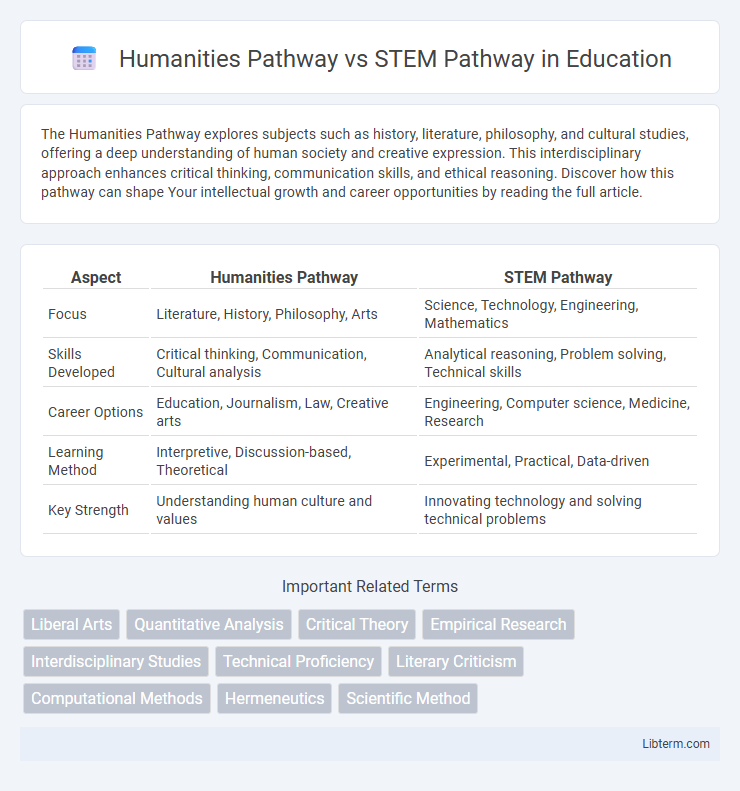
| Aspect | Humanities Pathway | STEM Pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Literature, History, Philosophy, Arts | Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, Communication, Cultural analysis | Analytical reasoning, Problem solving, Technical skills |
| Career Options | Education, Journalism, Law, Creative arts | Engineering, Computer science, Medicine, Research |
| Learning Method | Interpretive, Discussion-based, Theoretical | Experimental, Practical, Data-driven |
| Key Strength | Understanding human culture and values | Innovating technology and solving technical problems |
Understanding Humanities and STEM Pathways
Understanding Humanities pathways involves exploring subjects such as literature, history, philosophy, and arts, which cultivate critical thinking, cultural awareness, and ethical reasoning. STEM pathways focus on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, emphasizing analytical skills, problem-solving, and innovation. Both pathways develop distinct cognitive abilities essential for diverse academic and professional fields.
Core Differences Between Humanities and STEM
Humanities pathway emphasizes critical thinking, cultural understanding, and communication skills through subjects like literature, history, and philosophy, while STEM pathway focuses on analytical problem-solving, quantitative reasoning, and technical expertise in fields such as science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Humanities encourage exploring human experiences and societal contexts, fostering creativity and ethical considerations, whereas STEM concentrates on empirical data, experimentation, and innovation-driven solutions. The core difference lies in their approach to knowledge: Humanities interpret and question human conditions, while STEM applies scientific methods to understand and manipulate the physical world.
Curriculum Structure: Humanities vs STEM
The Humanities pathway emphasizes critical thinking, analysis, and understanding of cultural, historical, and philosophical contexts, integrating subjects like literature, history, and social sciences. The STEM pathway centers on analytical skills, problem-solving, and technical knowledge, focusing on mathematics, science, technology, and engineering disciplines. Curriculum structures in Humanities prioritize qualitative analysis and theoretical frameworks, while STEM curricula prioritize quantitative data, experiments, and practical applications.
Key Skills Developed in Each Pathway
The Humanities Pathway cultivates critical thinking, effective communication, and cultural awareness, emphasizing analytical reading, writing, and ethical reasoning. The STEM Pathway develops problem-solving, quantitative analysis, and technical proficiency, concentrating on scientific inquiry, mathematics, and engineering principles. Both pathways build collaboration and creativity, tailored to their respective disciplines' practical and theoretical demands.
Career Opportunities for Humanities Graduates
Humanities graduates often pursue careers in education, communications, public relations, law, and cultural management, leveraging their critical thinking, writing, and analytical skills. Job roles may include content strategist, social worker, museum curator, or policy analyst, offering diverse opportunities across public and private sectors. These positions benefit from strong interpersonal and problem-solving abilities inherent in humanities studies, supporting career growth in areas centered on human behavior, ethics, and cultural understanding.
Career Opportunities for STEM Graduates
STEM graduates benefit from diverse career opportunities in high-demand fields such as software engineering, data science, biotechnology, and environmental engineering. Rapid technological advancements and increased industry reliance on innovation drive substantial job growth, offering competitive salaries and job security in sectors like information technology, healthcare, and renewable energy. Employers prioritize STEM skills due to their critical role in solving complex problems, enhancing productivity, and fostering economic development.
Job Market Trends: Humanities vs STEM
The job market trends reveal a growing demand for STEM professionals driven by rapid technological advancements and digital transformation across industries, resulting in higher employment rates and salary prospects in fields like software development, engineering, and data science. Humanities graduates often pursue careers in education, communication, and the arts, with increasing emphasis on roles that require critical thinking, cultural awareness, and creative problem-solving, though job growth in these areas tends to be slower and more competitive. Employers value interdisciplinary skills, encouraging a blend of humanities insight and STEM expertise to address complex challenges in sectors like healthcare, technology, and public policy.
Salary Expectations: Humanities vs STEM
STEM pathway careers typically offer higher average salary expectations, with fields like engineering, computer science, and biotechnology reporting median annual incomes often exceeding $80,000. Humanities pathway professions, including roles in education, social sciences, and the arts, generally present lower salary ranges, averaging around $50,000 to $60,000 annually, though they excel in flexibility and critical thinking skills. Salary disparities reflect market demand, industry growth, and specialized technical skills prevalent in STEM compared to broader analytical abilities emphasized in humanities.
Choosing the Right Pathway Based on Interests
Selecting the Humanities pathway suits individuals passionate about literature, history, philosophy, and cultural studies, fostering critical thinking and communication skills. The STEM pathway appeals to those drawn to science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, emphasizing problem-solving and analytical abilities. Aligning your choice with personal interests and career goals ensures greater academic engagement and long-term success.
Future Prospects and Interdisciplinary Opportunities
Humanities Pathway students develop critical thinking, cultural insight, and communication skills that are highly valued in sectors such as education, law, and public policy, offering prospects in roles focused on social impact and ethical decision-making. STEM Pathway graduates gain expertise in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, leading to strong demand in innovation-driven industries like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energy. Interdisciplinary opportunities are expanding as fields like digital humanities and environmental science merge STEM methodologies with humanities perspectives, enabling graduates to tackle complex global challenges through integrated approaches.
Humanities Pathway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com