STEAM-D integrates Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics, and Design to foster creativity and critical thinking in problem-solving. This interdisciplinary approach enhances innovation by combining analytical skills with artistic expression, preparing individuals for dynamic challenges in various industries. Discover how STEAM-D can transform your learning experience and career prospects by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
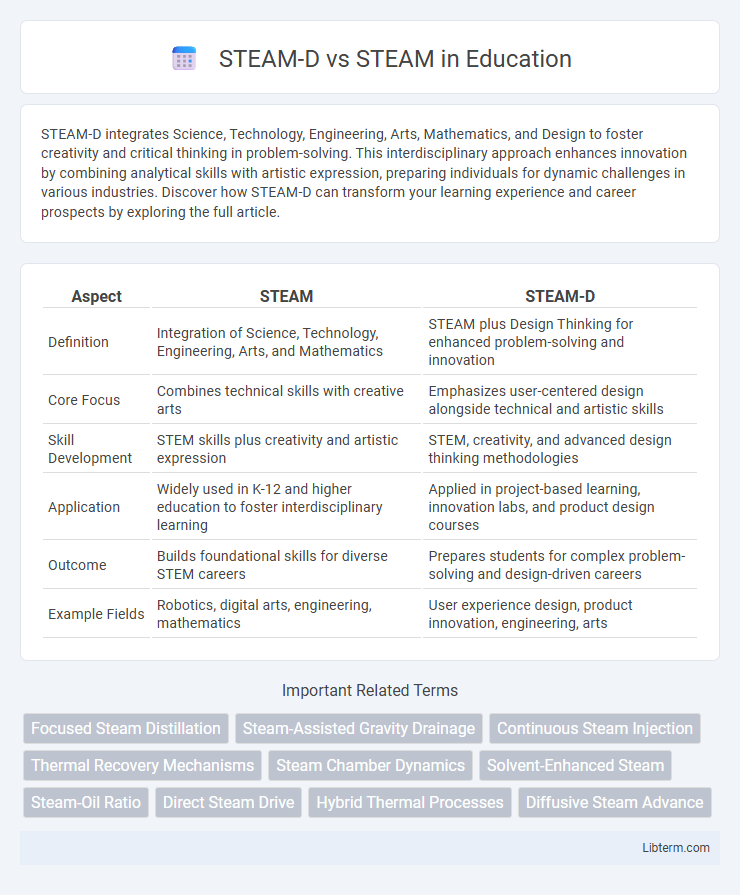
| Aspect | STEAM | STEAM-D |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics | STEAM plus Design Thinking for enhanced problem-solving and innovation |
| Core Focus | Combines technical skills with creative arts | Emphasizes user-centered design alongside technical and artistic skills |
| Skill Development | STEM skills plus creativity and artistic expression | STEM, creativity, and advanced design thinking methodologies |
| Application | Widely used in K-12 and higher education to foster interdisciplinary learning | Applied in project-based learning, innovation labs, and product design courses |
| Outcome | Builds foundational skills for diverse STEM careers | Prepares students for complex problem-solving and design-driven careers |
| Example Fields | Robotics, digital arts, engineering, mathematics | User experience design, product innovation, engineering, arts |
Overview of STEAM and STEAM-D
STEAM integrates Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics to foster creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills in education. STEAM-D expands this framework by incorporating Design, emphasizing innovation and practical application through creative processes and user-centered solutions. Both approaches aim to prepare students for complex real-world challenges by blending interdisciplinary knowledge and hands-on learning.
Defining the STEAM Educational Framework
STEAM-D expands the traditional STEAM educational framework by integrating Design Thinking principles to enhance creativity and problem-solving skills. This interdisciplinary approach combines Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics with design methodologies, fostering innovation and student engagement. Emphasizing hands-on, project-based learning, STEAM-D prepares students for complex real-world challenges through critical thinking and collaborative design processes.
What Sets STEAM-D Apart from STEAM?
STEAM-D distinguishes itself from traditional STEAM by incorporating Design as a core element, emphasizing creative problem-solving and innovation alongside Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics. This added focus on Design encourages interdisciplinary thinking and practical application, fostering students' abilities to develop user-centered solutions in real-world contexts. The integration of Design elevates STEAM-D as a holistic educational framework that balances analytical skills with creative expression, preparing learners for complex challenges across industries.
Core Disciplines in STEAM vs STEAM-D
STEAM-D expands the traditional STEAM framework by integrating Design as a core discipline alongside Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Mathematics, emphasizing creativity and innovation in problem-solving. While STEAM focuses primarily on technical and scientific skills combined with artistic thinking, STEAM-D prioritizes human-centered design principles to enhance user experience and functionality. This inclusion of Design fosters interdisciplinary collaboration and prepares learners to address complex real-world challenges with both analytical and empathetic approaches.
The Role of Design in STEAM-D
The integration of Design within STEAM-D enhances creativity and innovation by emphasizing problem-solving through user-centered approaches. Design thinking cultivates interdisciplinary collaboration, enabling students to prototype and iterate solutions that address real-world challenges effectively. This focus on design transforms STEAM learning into an experiential process, fostering critical skills essential for future-ready careers.
Key Benefits of Integrating Design into STEAM
Integrating Design into STEAM creates STEAM-D, emphasizing design thinking to foster creativity, problem-solving, and innovation in education. This approach enhances students' ability to apply scientific and mathematical concepts through real-world projects, bridging theoretical knowledge with practical application. Key benefits include improved critical thinking, collaboration skills, and preparation for diverse career paths in STEM fields enriched by design principles.
Curriculum Implementation: STEAM vs STEAM-D
STEAM-D curriculum implementation incorporates design thinking principles alongside traditional Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics, enhancing creativity and problem-solving skills through iterative prototyping and user-centered approaches. Unlike standard STEAM programs, STEAM-D emphasizes hands-on workshops and project-based learning that integrate design processes directly into STEM education. This approach fosters deeper engagement by connecting theoretical concepts with practical applications, preparing students for complex, real-world challenges.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
STEAM-D education integrates Design alongside Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics, emphasizing hands-on problem-solving seen in real-world applications like sustainable architecture and product innovation. Case studies reveal enhanced student engagement and creativity when design principles drive project-based learning, fostering skills critical for industries such as automotive engineering and user experience design. This approach bridges theoretical knowledge and practical implementation, preparing learners to tackle complex challenges with innovative solutions in diverse fields.
Challenges in Shifting from STEAM to STEAM-D
Shifting from STEAM to STEAM-D introduces challenges such as integrating Data Science into traditional curricula, which demands significant updates to teaching materials and faculty training. Schools often struggle with limited resources and expertise in data analytics, leading to gaps in effectively combining disciplines like engineering, arts, and mathematics with data-driven approaches. Balancing interdisciplinary collaboration while maintaining rigorous standards across all STEAM-D components requires strategic planning and ongoing assessment.
Future Trends in STEAM and STEAM-D Education
STEAM-D education integrates Design alongside Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics to emphasize creative problem-solving and innovation, driving future trends in interdisciplinary learning. Emerging trends highlight the incorporation of digital design tools, immersive technologies, and project-based learning to foster critical thinking and adaptability in students. This holistic approach aims to better prepare learners for evolving careers in technology, design innovation, and creative industries.
STEAM-D Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com