Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) in schools focuses on allocating resources based on specific activities and their associated costs, enabling efficient financial management tailored to educational priorities. This method identifies key school functions, such as teaching, administration, and extracurricular programs, to ensure funds directly support essential activities that enhance student outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to learn how ABB can optimize your school's budget planning and improve resource allocation.
Table of Comparison
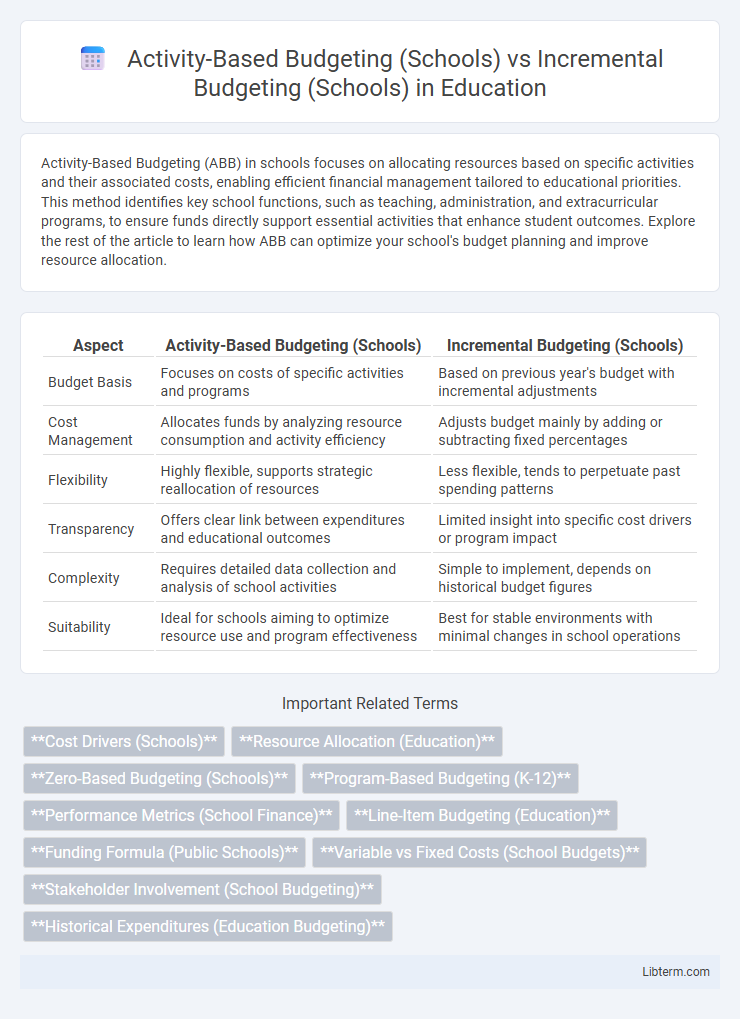
| Aspect | Activity-Based Budgeting (Schools) | Incremental Budgeting (Schools) |
|---|---|---|
| Budget Basis | Focuses on costs of specific activities and programs | Based on previous year's budget with incremental adjustments |
| Cost Management | Allocates funds by analyzing resource consumption and activity efficiency | Adjusts budget mainly by adding or subtracting fixed percentages |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, supports strategic reallocation of resources | Less flexible, tends to perpetuate past spending patterns |
| Transparency | Offers clear link between expenditures and educational outcomes | Limited insight into specific cost drivers or program impact |
| Complexity | Requires detailed data collection and analysis of school activities | Simple to implement, depends on historical budget figures |
| Suitability | Ideal for schools aiming to optimize resource use and program effectiveness | Best for stable environments with minimal changes in school operations |
Introduction to School Budgeting Methods
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) in schools allocates funds based on specific activities and resource needs, enhancing accuracy by linking expenses to educational programs such as classroom instruction, extracurricular activities, and facility maintenance. Incremental Budgeting adjusts previous year's allocations by fixed percentages, often leading to inefficiencies due to lack of alignment with current school priorities or changes in student enrollment. Schools implementing ABB benefit from improved transparency and strategic resource management compared to the traditional, simpler incremental approach.
What is Activity-Based Budgeting in Schools?
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) in schools allocates funds based on specific educational activities and their associated costs, aligning resources directly with student learning outcomes and operational effectiveness. Unlike Incremental Budgeting, which adjusts previous budgets with minor changes, ABB identifies key activities such as curriculum development, extracurricular programs, and facility maintenance, enabling precise cost control and strategic resource allocation. This method improves transparency and accountability by linking expenditures to educational priorities and measurable performance metrics.
Key Principles of Incremental Budgeting in Schools
Incremental budgeting in schools emphasizes adjusting the previous year's budget by a fixed percentage to account for inflation or minor changes in programs and enrollment. This method relies on historical data, making it straightforward and less time-consuming for school administrators. It often results in stability but may limit opportunities for reallocating resources toward emerging priorities or innovation in educational programs.
Comparing Budget Flexibility: ABB vs Incremental
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) offers greater budget flexibility in schools by allocating funds based on specific activities and their associated costs, allowing for more precise adjustments according to changing educational priorities and program demands. In contrast, Incremental Budgeting in schools relies on previous budget levels with minor adjustments, resulting in less adaptability and potential inefficiencies when reallocating resources to emerging needs or innovative initiatives. Schools using ABB can quickly respond to shifts in student enrollment or curriculum changes, while Incremental Budgeting may perpetuate outdated spending patterns due to its rigid structure.
Impact on Resource Allocation and Efficiency
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) in schools allocates resources based on specific activities and their costs, leading to more precise and efficient use of funds by identifying high-impact areas such as classroom instruction and extracurricular programs. Incremental Budgeting allocates resources based on previous budgets with adjustments, often resulting in less flexibility and potential misallocation by perpetuating historical spending patterns rather than assessing current needs. ABB enhances resource efficiency by aligning expenditures with strategic goals, while Incremental Budgeting may limit optimizations due to its incremental nature.
Transparency and Accountability in Both Methods
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) in schools enhances transparency by linking budget allocations directly to specific educational activities and outcomes, enabling stakeholders to clearly see how funds support student learning objectives. Incremental Budgeting relies on previous years' budgets with adjustments, often obscuring detailed financial flows and limiting accountability for resource effectiveness. ABB's detailed allocation fosters stronger accountability by allowing educators and administrators to justify expenditures based on measurable activity performance, while Incremental Budgeting tends to maintain status quo spending patterns with less rigorous oversight.
Implementation Challenges for Schools
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) implementation in schools faces challenges such as accurately identifying and measuring all educational activities and linking them to costs, which requires detailed data collection and expert staff training. Incremental Budgeting in schools struggles with the risk of perpetuating inefficient spending patterns and lacks flexibility, as it primarily focuses on adjusting previous budgets without thorough evaluation of current educational needs. Both methods demand significant administrative effort, with ABB requiring comprehensive activity analysis and Incremental Budgeting often criticized for its simplicity and potential to ignore changing school priorities.
Effect on Educational Outcomes and Student Performance
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) in schools allocates funds based on specific educational activities and resource usage, resulting in targeted investments that directly enhance student performance through improved instructional quality and resource efficiency. Incremental Budgeting, relying on previous allocations with minor adjustments, often perpetuates inefficient spending patterns, limiting the ability to address evolving educational needs and potentially stagnating academic outcomes. Empirical studies indicate that schools employing ABB demonstrate higher gains in standardized test scores and graduation rates compared to those using incremental approaches, highlighting ABB's positive effect on educational outcomes.
Stakeholder Involvement in Budgeting Decisions
Activity-Based Budgeting in schools involves detailed stakeholder engagement, including teachers, administrators, and department heads, to identify resource needs based on specific activities and programs. Incremental Budgeting relies primarily on historical financial data, with limited input from stakeholders, focusing on adjusting previous budgets by small increments. Enhanced stakeholder involvement in Activity-Based Budgeting promotes transparency and alignment with educational goals, whereas Incremental Budgeting may restrict collaborative decision-making and innovation.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Approach for Schools
Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) in schools allocates funds based on specific activities and resource demands, ensuring precise tracking of costs and enhancing resource efficiency. Incremental Budgeting, by adjusting previous budgets with incremental changes, offers simplicity but may perpetuate inefficiencies and overlook evolving school needs. Selecting the right budgeting approach involves assessing the school's complexity, resource availability, and need for detailed financial transparency to support strategic educational goals.
Activity-Based Budgeting (Schools) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com