Phonics is a fundamental method for teaching reading by connecting sounds with letters or groups of letters in an alphabetic writing system. It helps improve your ability to decode new words, enhancing both reading fluency and comprehension. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective phonics strategies and techniques.
Table of Comparison
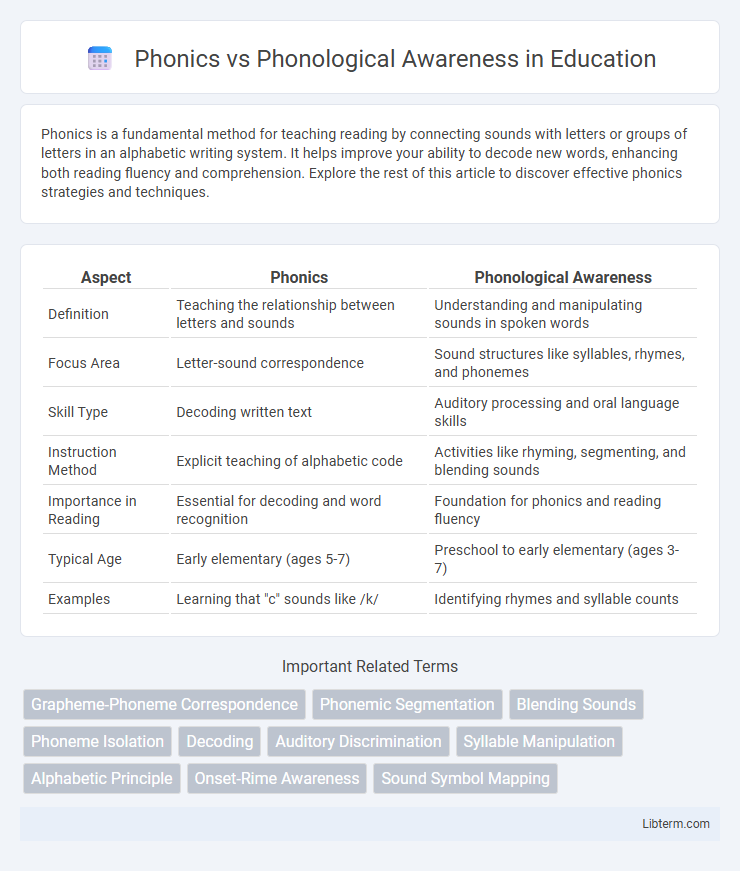
| Aspect | Phonics | Phonological Awareness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching the relationship between letters and sounds | Understanding and manipulating sounds in spoken words |
| Focus Area | Letter-sound correspondence | Sound structures like syllables, rhymes, and phonemes |
| Skill Type | Decoding written text | Auditory processing and oral language skills |
| Instruction Method | Explicit teaching of alphabetic code | Activities like rhyming, segmenting, and blending sounds |
| Importance in Reading | Essential for decoding and word recognition | Foundation for phonics and reading fluency |
| Typical Age | Early elementary (ages 5-7) | Preschool to early elementary (ages 3-7) |
| Examples | Learning that "c" sounds like /k/ | Identifying rhymes and syllable counts |
Understanding Phonics: Definition and Key Concepts
Phonics is a method of teaching reading that emphasizes the relationship between letters and their corresponding sounds, enabling learners to decode words by sounding them out. Key concepts include letter-sound correspondence, blending sounds to form words, and segmenting words into individual phonemes. This approach is essential for developing accurate and fluent reading skills by systematically connecting written language to spoken language.
What is Phonological Awareness? A Comprehensive Overview
Phonological awareness is the ability to recognize and manipulate the sound structures of spoken language, including phonemes, syllables, and rhymes. It encompasses skills such as segmenting words into individual sounds, blending sounds to form words, and identifying phoneme patterns, which are critical for early literacy development. This foundational skill differs from phonics, which involves the relationship between sounds and their corresponding letters or letter patterns in written language.
Core Differences Between Phonics and Phonological Awareness
Phonics involves the relationship between letters and their corresponding sounds, focusing on decoding and spelling skills, while phonological awareness encompasses a broader set of auditory skills including recognizing and manipulating sounds in spoken language such as rhymes, syllables, and onset-rime segments. Phonics requires the visual recognition of letters, making it essential for reading and writing, whereas phonological awareness is purely auditory and foundational for developing reading readiness. Effective early literacy instruction integrates both phonics and phonological awareness to build strong decoding abilities and overall language processing.
The Role of Phonics in Early Reading Development
Phonics plays a crucial role in early reading development by teaching children the relationship between letters and sounds, enabling them to decode words systematically. This skill supports accurate word recognition, which is essential for fluent reading and comprehension. While phonological awareness involves broader sound recognition skills, phonics specifically bridges these sounds to written language, forming the foundation for literacy acquisition.
The Importance of Phonological Awareness for Literacy Success
Phonological awareness is the ability to recognize and manipulate sounds in spoken language, serving as a critical foundation for phonics instruction and overall literacy development. Strong phonological awareness skills enable children to decode words more efficiently, directly impacting reading fluency and comprehension. Research consistently shows that early phonological awareness predicts later success in reading and writing, making it essential for effective literacy education.
Skills Involved in Phonics Instruction
Phonics instruction emphasizes decoding skills that connect letters to sounds, focusing on letter-sound correspondence, blending, and segmenting words. It involves recognizing graphemes, applying sound patterns, and practice in reading and spelling to improve word recognition and fluency. Mastery of phonics skills supports accurate and automatic decoding necessary for proficient reading development.
Essential Components of Phonological Awareness Activities
Phonological awareness activities focus on recognizing and manipulating spoken sounds, including skills like rhyming, syllable segmentation, and onset-rime blending, which are critical for early reading development. Essential components emphasize auditory skills such as phoneme isolation, deletion, and substitution, enabling children to understand sound structures before linking them to letters, as seen in phonics. Targeting these foundational skills strengthens decoding abilities and supports literacy acquisition in young learners.
How and When to Teach Phonics versus Phonological Awareness
Phonological awareness, the ability to recognize and manipulate sounds at the word, syllable, and phoneme levels, should be introduced early in preschool and kindergarten to build a strong auditory foundation. Phonics instruction, which teaches the relationship between letters and sounds, is most effective when started in kindergarten or first grade, once children can identify sounds within words. Teaching phonological awareness before phonics ensures children develop the necessary listening skills needed to decode written language efficiently.
Common Misconceptions about Phonics and Phonological Awareness
Phonics involves the relationship between letters and sounds, while phonological awareness is the broader skill of recognizing and manipulating sounds in spoken language, including rhymes and syllables. A common misconception is that phonics instruction alone suffices for reading proficiency, ignoring that phonological awareness is a foundational skill that must develop first to support effective phonics learning. Many educators erroneously assume phonological awareness only refers to phonics, overlooking its role in auditory processing and early literacy skill development.
Integrating Phonics and Phonological Awareness in Classroom Practice
Integrating phonics and phonological awareness in classroom practice enhances early literacy by combining letter-sound correspondence with sound manipulation skills. Effective instruction involves activities such as segmenting sounds in words while simultaneously connecting these sounds to their written counterparts, reinforcing decoding and spelling abilities. Research shows that this integrated approach accelerates reading fluency, vocabulary development, and overall comprehension in young learners.
Phonics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com