Grade level significantly influences academic content, ensuring materials match learners' cognitive abilities and comprehension skills. Tailoring lessons to the appropriate grade enhances understanding, engagement, and knowledge retention. Explore the article to learn how aligning your educational resources with grade levels can optimize student success.
Table of Comparison
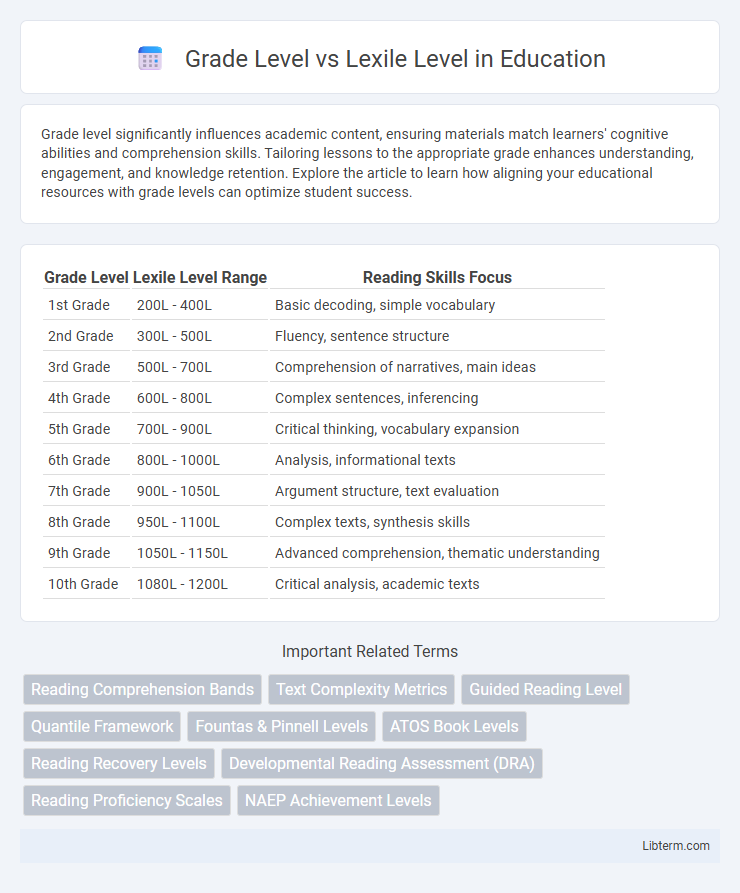
| Grade Level | Lexile Level Range | Reading Skills Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Grade | 200L - 400L | Basic decoding, simple vocabulary |
| 2nd Grade | 300L - 500L | Fluency, sentence structure |
| 3rd Grade | 500L - 700L | Comprehension of narratives, main ideas |
| 4th Grade | 600L - 800L | Complex sentences, inferencing |
| 5th Grade | 700L - 900L | Critical thinking, vocabulary expansion |
| 6th Grade | 800L - 1000L | Analysis, informational texts |
| 7th Grade | 900L - 1050L | Argument structure, text evaluation |
| 8th Grade | 950L - 1100L | Complex texts, synthesis skills |
| 9th Grade | 1050L - 1150L | Advanced comprehension, thematic understanding |
| 10th Grade | 1080L - 1200L | Critical analysis, academic texts |
Understanding Grade Level and Lexile Level
Grade Level indicates the typical school year a student is expected to be in based on reading skills, while Lexile Level measures text complexity and a reader's ability on a scale from below 200L to above 1600L. Understanding Grade Level helps educators match texts to students' curriculum stages, whereas Lexile Level provides a precise numeric value to select reading materials that challenge students appropriately. Both metrics combined allow tailored reading instruction to improve comprehension and literacy development effectively.
The Basics: What is a Grade Level?
A Grade Level represents the typical educational stage at which a student is expected to perform academically, often corresponding to specific age ranges and curriculum standards. It serves as a benchmark to assess whether a student's reading, writing, and comprehension skills align with their peers in the same grade. Educators use Grade Levels to tailor instruction and materials, ensuring content is age-appropriate and meets developmental expectations.
Defining Lexile Level in Reading Assessment
Lexile Level is a standardized measure that quantifies a reader's ability and the difficulty of a text, expressed as a numeric value followed by an "L" (e.g., 850L). Unlike Grade Level, which broadly categorizes reading skills by school year, Lexile Level provides a more precise indicator of text complexity and reader comprehension, enabling targeted reading interventions. This metric is widely used in educational assessments to match students with appropriate reading materials based on their individual Lexile scores.
Key Differences Between Grade Level and Lexile Level
Grade level represents the expected reading ability of students within a specific school grade, while Lexile level quantifies text complexity based on semantic and syntactic features. Grade level simplifies curriculum alignment through broad age-based benchmarks, whereas Lexile level provides precise measurement for matching readers with appropriately challenging texts. Understanding the distinction enhances literacy instruction by combining standardized grade expectations with individualized reading proficiency metrics.
How Are Grade Levels Determined?
Grade levels are determined based on a combination of age, curriculum standards, and developmental milestones that align with typical student progress in reading, math, and other core subjects. Educators use standardized testing, classroom assessments, and state or national education guidelines to establish expectations for students at each grade. This structured approach helps ensure that instructional content matches students' cognitive and academic abilities appropriate for their grade.
The Science Behind Lexile Measurement
The Lexile Level measures text complexity and reader ability on a scientifically developed scale using semantic and syntactic features, providing a more precise assessment than traditional grade levels. Unlike grade levels, which group texts by educational stages, Lexile measures quantify reading difficulty through factors like word frequency and sentence length, aligning readers with materials that optimize growth. This data-driven approach supports personalized learning by matching students' unique reading levels with appropriately challenging texts.
Correlation and Conversion Between Grade and Lexile Levels
Grade level and Lexile level correspond through established conversion charts that map student reading abilities to age-appropriate text complexity. The correlation enables educators to match books and materials to students' reading skills, with Lexile scores typically ranging from 200L for early elementary readers to 1600L for advanced high school readers. Accurate conversion between grade and Lexile levels supports targeted instruction and progress monitoring in literacy development.
Why Lexile Levels Matter for Students and Teachers
Lexile levels provide a precise measurement of a student's reading ability, allowing educators to match texts with appropriate difficulty to foster literacy development. Unlike grade level alone, Lexile measures account for text complexity and individual reading skills, aiding in targeted instruction and personalized learning plans. This tailored approach helps improve comprehension, ensures reading materials are neither too challenging nor too easy, and supports academic growth effectively.
Choosing Reading Materials: Grade Level vs Lexile Level
Choosing reading materials based on Grade Level provides a general age-appropriate guideline, ensuring content aligns with typical curriculum standards, while Lexile Level offers a precise measure of text complexity and reading ability, helping to match readers with texts that challenge without frustration. Combining both metrics improves the selection process, balancing thematic relevance with individual reading proficiency to promote optimal literacy development. Educators and parents should consider Grade Level for content suitability and Lexile Level for skill alignment to support progressive reading growth.
Best Practices for Using Both Metrics in Education
Grade level and Lexile level serve distinct roles in education, with grade level indicating curriculum standards and Lexile level measuring reading comprehension complexity. Best practices involve using grade level to align instructional content with student age and developmental norms while employing Lexile measures to tailor reading materials that match individual reading abilities for targeted growth. Integrating both metrics allows educators to create differentiated instruction, monitor progress effectively, and foster reading proficiency by balancing curriculum demands with personalized learning needs.
Grade Level Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com