Direct instruction is a structured teaching approach that emphasizes clear, explicit teaching of academic skills through step-by-step guidance and modeling. This method ensures that learners receive precise explanations, immediate feedback, and ample practice opportunities to master concepts efficiently. Discover how direct instruction can transform your learning experience by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
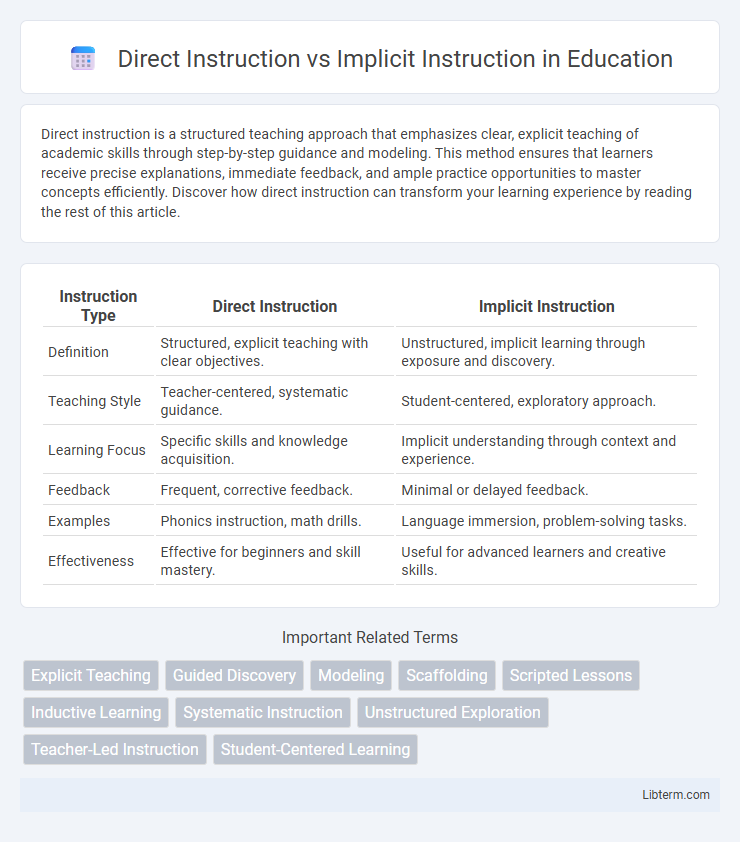
| Instruction Type | Direct Instruction | Implicit Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured, explicit teaching with clear objectives. | Unstructured, implicit learning through exposure and discovery. |
| Teaching Style | Teacher-centered, systematic guidance. | Student-centered, exploratory approach. |
| Learning Focus | Specific skills and knowledge acquisition. | Implicit understanding through context and experience. |
| Feedback | Frequent, corrective feedback. | Minimal or delayed feedback. |
| Examples | Phonics instruction, math drills. | Language immersion, problem-solving tasks. |
| Effectiveness | Effective for beginners and skill mastery. | Useful for advanced learners and creative skills. |
Introduction to Direct and Implicit Instruction
Direct Instruction emphasizes explicit teaching methods where educators clearly present concepts, provide structured guidance, and use systematic practice to ensure student mastery. Implicit Instruction relies on indirect learning approaches, encouraging discovery and understanding through exposure, context, and minimal teacher intervention. Both methods cater to different learning preferences and instructional goals, with Direct Instruction prioritizing clarity and control while Implicit Instruction fosters autonomous problem-solving and conceptual development.
Defining Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction is a structured teaching method characterized by clear, explicit teaching of concepts through scripted lessons, immediate feedback, and systematic skill development. This approach emphasizes teacher-led demonstration, step-by-step guidance, and frequent assessment to ensure mastery of specific learning objectives. Research consistently shows that Direct Instruction improves student outcomes in areas like reading, math, and language acquisition by minimizing ambiguity and maximizing instructional clarity.
Understanding Implicit Instruction
Implicit instruction emphasizes learning through exposure and discovery, relying on context and natural language use rather than explicit explanations. This approach promotes deeper cognitive processing by encouraging learners to infer rules and patterns indirectly, which enhances long-term retention and application. Research highlights that implicit instruction benefits language acquisition by fostering intuitive grasp of grammar and vocabulary in authentic communication settings.
Key Differences Between Direct and Implicit Instruction
Direct instruction emphasizes structured, explicit teaching with clear objectives, step-by-step guidance, and frequent feedback, promoting faster mastery of specific skills. Implicit instruction relies on indirect methods such as discovery learning, modeling, and context-rich environments, encouraging deeper cognitive engagement and long-term retention. The key difference lies in direct instruction's focus on explicit content delivery versus implicit instruction's emphasis on autonomous learning through experience.
Advantages of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction offers clear, structured teaching methods that promote rapid mastery of skills through guided practice and immediate feedback. This approach enhances student engagement and reduces misconceptions by providing explicit explanations and modeling. Research shows that Direct Instruction significantly improves academic achievement, especially in foundational areas like reading and math.
Benefits of Implicit Instruction
Implicit instruction enhances language acquisition by promoting natural learning through exposure and context, which can improve retention and application in real-life situations. It fosters intuitive understanding and communication skills without explicit grammar rules, aiding learners in developing fluency and cognitive flexibility. This approach supports learners with diverse backgrounds by reducing anxiety and increasing motivation through authentic engagement.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Direct Instruction often faces criticism for its rigid structure and limited flexibility, which can hinder creativity and fail to address diverse learner needs. Implicit Instruction struggles with the lack of clear guidance, potentially causing confusion and slower skill acquisition, especially for novice learners. Both approaches require balancing explicit clarity and learner autonomy to effectively support varied educational contexts.
Effectiveness in Different Learning Contexts
Direct Instruction proves highly effective in structured learning environments requiring clear, step-by-step guidance and measurable outcomes, especially in subjects like mathematics and reading. Implicit Instruction excels in contexts fostering critical thinking and creativity, such as language acquisition and problem-solving, by encouraging learners to discover patterns and rules independently. Effectiveness varies based on learner autonomy, content complexity, and the goal of instruction, with blended approaches often optimizing educational results.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Learners
Choosing the right instructional method depends on learners' needs, goals, and contexts, with Direct Instruction providing clear, structured guidance ideal for foundational skills and explicit learning outcomes. Implicit Instruction suits learners benefiting from discovery, creativity, and natural language acquisition by emphasizing immersion and contextual understanding. Assessing learner profiles, content complexity, and desired cognitive engagement ensures an optimized balance between Direct and Implicit Instruction for effective educational outcomes.
Conclusion: Finding Balance Between Instructional Approaches
Effective teaching requires balancing Direct Instruction, which emphasizes structured, explicit teaching of skills and concepts, with Implicit Instruction, where learners infer knowledge through experience and exploration. Research demonstrates that integrating both methods enhances student engagement and retention by catering to diverse learning styles and cognitive development stages. Optimal instructional design strategically blends clear guidance and discovery learning to foster deeper understanding and autonomous problem-solving skills.
Direct Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com