Lecture-based teaching delivers structured content clearly and efficiently, allowing educators to cover extensive material in a limited time. This method promotes focused learning and offers opportunities for immediate clarification of complex concepts. Discover how you can maximize the benefits of lecture-based teaching by exploring effective strategies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
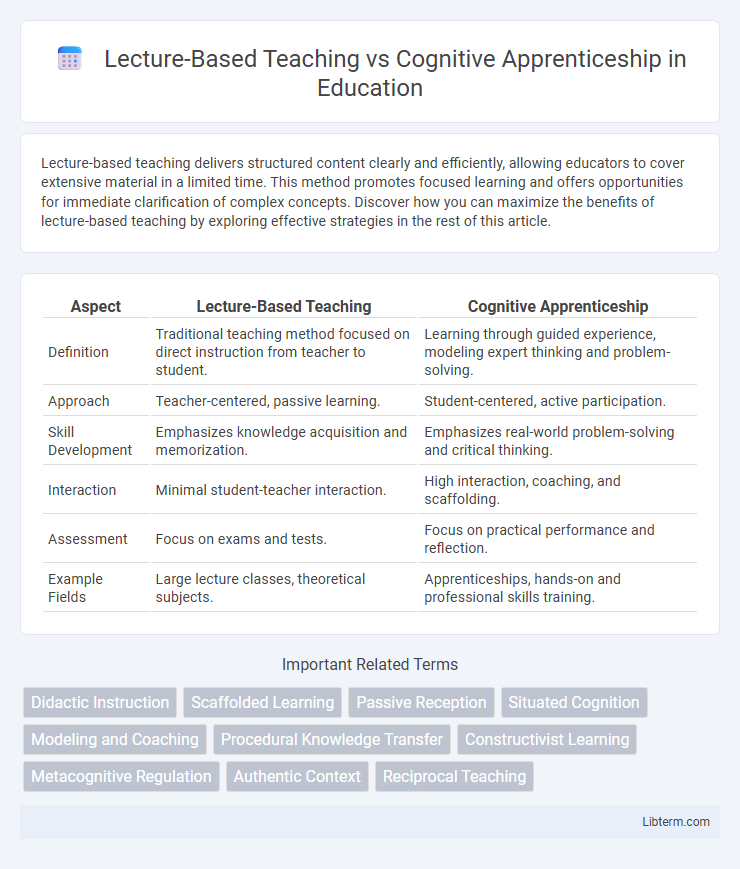
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Teaching | Cognitive Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional teaching method focused on direct instruction from teacher to student. | Learning through guided experience, modeling expert thinking and problem-solving. |
| Approach | Teacher-centered, passive learning. | Student-centered, active participation. |
| Skill Development | Emphasizes knowledge acquisition and memorization. | Emphasizes real-world problem-solving and critical thinking. |
| Interaction | Minimal student-teacher interaction. | High interaction, coaching, and scaffolding. |
| Assessment | Focus on exams and tests. | Focus on practical performance and reflection. |
| Example Fields | Large lecture classes, theoretical subjects. | Apprenticeships, hands-on and professional skills training. |
Introduction to Teaching Methodologies
Lecture-based teaching primarily emphasizes direct knowledge transmission from instructor to students through structured presentations, often limiting opportunities for active engagement and practical application. Cognitive apprenticeship, by contrast, integrates expert modeling, scaffolding, and situated learning to develop learners' problem-solving skills within authentic contexts. This teaching methodology supports deeper understanding by fostering collaboration, reflection, and gradual skill mastery through guided practice.
Defining Lecture-Based Teaching
Lecture-Based Teaching is a traditional instructional method where educators deliver structured content verbally to students, emphasizing information transmission and passive learning. It prioritizes clear organization of knowledge and standardized assessments to measure comprehension. This approach contrasts with Cognitive Apprenticeship, which focuses on guided hands-on experiences and active skill development.
Understanding Cognitive Apprenticeship
Cognitive apprenticeship emphasizes learning through guided experience, where experts model cognitive processes and scaffold students' problem-solving strategies in authentic contexts. This method fosters deeper understanding by making thinking processes visible, enhancing critical thinking and metacognitive skills. Unlike lecture-based teaching, it engages learners actively, promoting skill transfer and practical application.
Core Principles of Both Approaches
Lecture-based teaching centers on direct transmission of knowledge from instructor to students, emphasizing structured content delivery and passive learning through listening and note-taking. Cognitive apprenticeship relies on modeling expert thinking processes, scaffolding, and authentic problem-solving in real contexts to promote active learning and skill acquisition. Both approaches differ in engagement levels but share the goal of facilitating understanding and application of knowledge.
Student Engagement and Interaction
Lecture-Based Teaching often limits student engagement to passive listening, reducing opportunities for meaningful interaction and critical thinking. Cognitive Apprenticeship emphasizes active learning through modeling, coaching, and scaffolding, fostering deeper student involvement and collaboration. This interactive approach enhances skill acquisition and retention by embedding learning in authentic, context-rich experiences.
Knowledge Retention and Application
Lecture-based teaching often emphasizes passive knowledge acquisition, resulting in lower long-term retention and limited practical application. Cognitive apprenticeship engages learners through modeling, coaching, and scaffolding, enhancing deep understanding and the ability to transfer skills to real-world contexts. Studies indicate that cognitive apprenticeship significantly improves retention rates and facilitates more effective application of complex concepts compared to traditional lectures.
Instructor Roles and Responsibilities
Lecture-based teaching positions the instructor primarily as a knowledge transmitter, responsible for organizing content and delivering information clearly to students. In cognitive apprenticeship, the instructor acts as a mentor and coach, modeling expert thinking and problem-solving strategies while gradually fading support as learners gain proficiency. This approach requires active engagement in scaffolding, feedback, and facilitating authentic learning experiences to develop practical skills.
Advantages and Limitations of Lecture-Based Teaching
Lecture-Based Teaching efficiently delivers structured knowledge to large groups, ensuring content consistency and comprehensive coverage of foundational concepts. However, it often limits student engagement, critical thinking, and practical skill development due to its passive learning nature. The lack of interactive elements may hinder deep cognitive processing and the application of knowledge in real-world contexts.
Benefits and Challenges of Cognitive Apprenticeship
Cognitive Apprenticeship enhances learning by immersing students in authentic tasks with expert modeling, fostering deep understanding through guided practice and reflection. This method promotes critical thinking, problem-solving, and transfer of knowledge to real-world situations, unlike traditional lecture-based teaching which often emphasizes passive knowledge reception. Challenges include the need for skilled mentors, significant time investment, and potential scalability issues in large or resource-limited educational settings.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Learning
Selecting the right approach between lecture-based teaching and cognitive apprenticeship depends on learning objectives and student needs. Lecture-based teaching efficiently delivers large amounts of information to diverse groups, optimizing content absorption through structured presentation. Cognitive apprenticeship fosters deep understanding by integrating real-world problem-solving and expert guidance, enhancing practical skills and critical thinking in authentic contexts.
Lecture-Based Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com