Authorization ensures that only individuals with the proper permissions can access specific resources or perform certain actions, enhancing security and preventing unauthorized use. Implementing robust authorization protocols safeguards sensitive data and maintains compliance with regulatory standards. Discover how effective authorization strategies can protect your digital environment by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
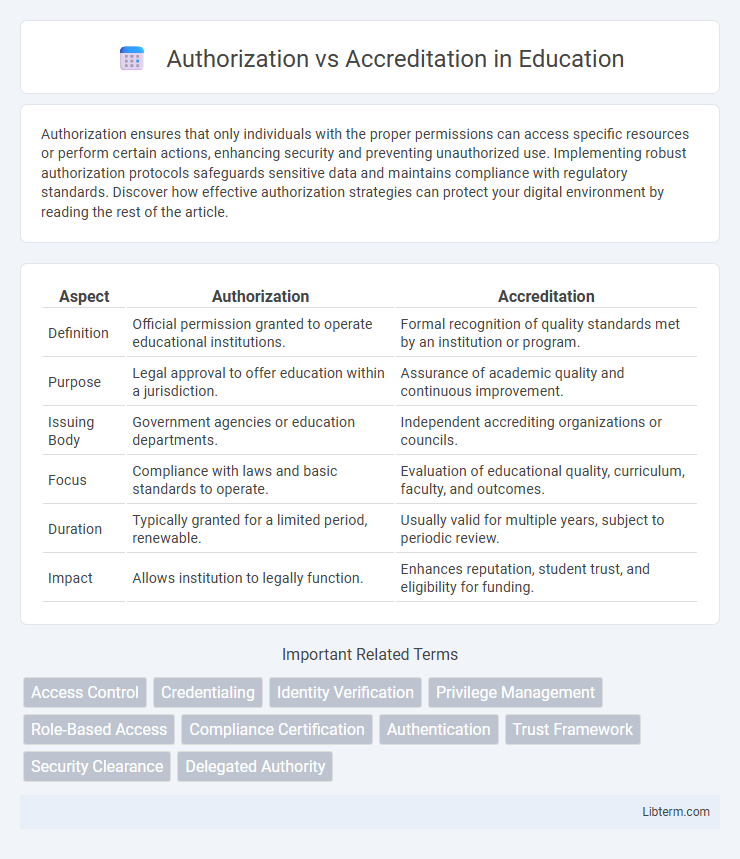
| Aspect | Authorization | Accreditation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official permission granted to operate educational institutions. | Formal recognition of quality standards met by an institution or program. |
| Purpose | Legal approval to offer education within a jurisdiction. | Assurance of academic quality and continuous improvement. |
| Issuing Body | Government agencies or education departments. | Independent accrediting organizations or councils. |
| Focus | Compliance with laws and basic standards to operate. | Evaluation of educational quality, curriculum, faculty, and outcomes. |
| Duration | Typically granted for a limited period, renewable. | Usually valid for multiple years, subject to periodic review. |
| Impact | Allows institution to legally function. | Enhances reputation, student trust, and eligibility for funding. |
Introduction to Authorization and Accreditation
Authorization is the process by which an organization grants permission to use specific systems, resources, or data based on defined access controls and policies. Accreditation involves a formal evaluation and certification process confirming that a system, service, or entity meets predetermined security and compliance standards. Understanding the distinction ensures organizations implement effective governance frameworks to protect sensitive information.
Defining Authorization
Authorization is the process of granting or denying specific access rights to users, systems, or processes based on predefined policies and roles. It ensures that only authenticated entities can perform actions or access resources within a computing environment according to their assigned permissions. Authorization is critical for maintaining security boundaries and enforcing access control measures in both physical and digital systems.
Defining Accreditation
Accreditation is a formal process through which an authoritative body evaluates and certifies that an organization or system meets established standards and requirements for quality and competency. Unlike authorization, which grants permission to operate or access resources, accreditation emphasizes ongoing compliance and validation of performance. This process ensures trust, credibility, and accountability within industries such as healthcare, education, and information security.
Key Differences Between Authorization and Accreditation
Authorization grants permission for specific actions or access within a system, whereas accreditation is a formal recognition that an organization or system meets established standards. Authorization involves assigning roles and access rights, often managed through security policies, while accreditation evaluates overall compliance and effectiveness through rigorous assessments. Key differences include scope--authorization is task-specific and immediate, accreditation is comprehensive and long-term--and purpose, with authorization ensuring controlled access and accreditation validating quality and trustworthiness.
Importance in Compliance and Security
Authorization ensures that users or systems have explicit permission to access specific resources based on roles and policies, playing a critical role in enforcing compliance with organizational security protocols. Accreditation involves a formal evaluation and approval process verifying that systems or processes meet established security standards, which is essential for maintaining trusted compliance frameworks. Together, authorization controls access precision while accreditation guarantees overall system integrity, forming the foundation of a robust security posture.
Authorization Processes Explained
Authorization processes involve granting specific permissions or access rights to users or systems based on predefined policies, roles, and security levels. This process ensures that only authenticated and vetted entities can perform actions or access resources, often documented through access control lists or role-based access control (RBAC) mechanisms. Effective authorization protocols are essential for maintaining data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO/IEC 27001.
Accreditation Procedures and Standards
Accreditation procedures involve comprehensive evaluation against established standards to ensure an organization or system meets specific quality and competency criteria. Standards for accreditation typically include rigorous assessments of processes, performance metrics, and compliance with industry regulations, ensuring consistent and reliable outcomes. This structured approach differentiates accreditation from authorization by emphasizing ongoing adherence to best practices and continuous improvement.
Common Use Cases for Authorization
Authorization is a critical process to control access to resources based on user roles and permissions, commonly implemented in IT systems such as databases, cloud services, and enterprise applications. Common use cases include restricting access to sensitive data, enabling role-based access control (RBAC) in corporate networks, and managing user permissions in content management systems (CMS). Authorization ensures that individuals or systems can perform only allowed actions, enhancing security and compliance with regulatory standards.
Typical Applications of Accreditation
Accreditation is commonly applied in sectors like healthcare, education, and information security to ensure organizations meet predefined standards of quality and competence. It provides formal recognition by authoritative bodies that an institution or program adheres to established criteria, enhancing trust and credibility. Unlike authorization, which grants permission to operate or access resources, accreditation typically validates overall compliance and continuous improvement in performance and safety standards.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting between authorization and accreditation depends on organizational goals and compliance requirements; authorization grants permission to operate under specific terms, while accreditation verifies adherence to established standards. Effective security and quality management strategies integrate both processes to enhance trust and operational legitimacy. Decision-makers must weigh operational control needs against formal recognition to determine the most suitable approach for their context.
Authorization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com