Project-Based Learning immerses students in hands-on, real-world challenges that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach encourages collaboration, creativity, and deep understanding of subject matter by engaging learners in meaningful projects. Discover how integrating Project-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience by exploring the benefits and best practices in the following article.
Table of Comparison
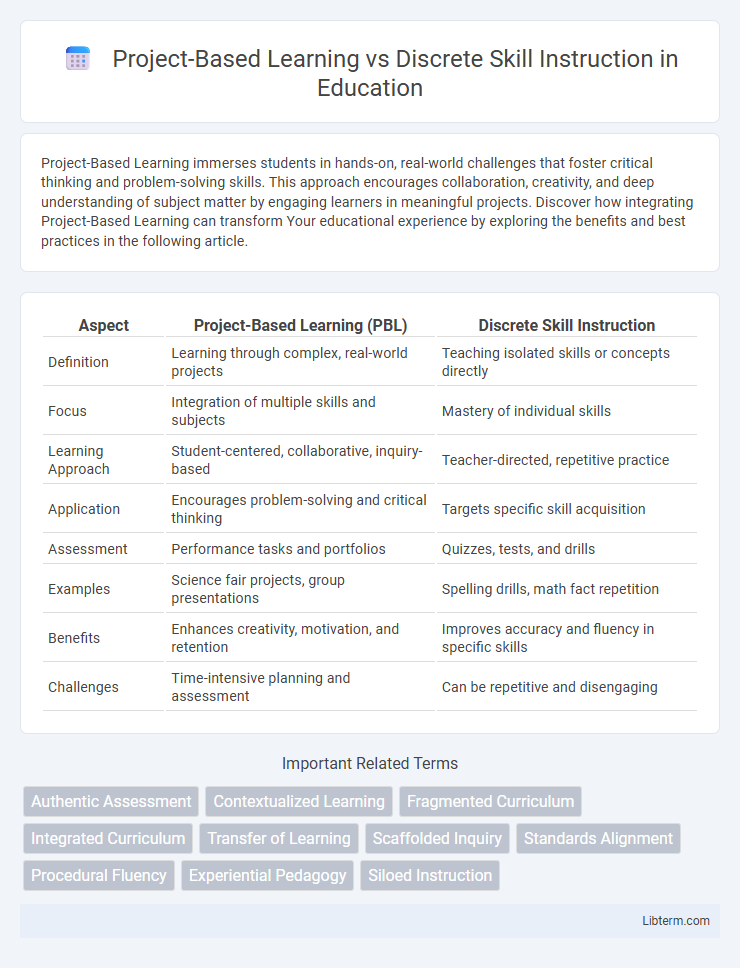
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Discrete Skill Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through complex, real-world projects | Teaching isolated skills or concepts directly |
| Focus | Integration of multiple skills and subjects | Mastery of individual skills |
| Learning Approach | Student-centered, collaborative, inquiry-based | Teacher-directed, repetitive practice |
| Application | Encourages problem-solving and critical thinking | Targets specific skill acquisition |
| Assessment | Performance tasks and portfolios | Quizzes, tests, and drills |
| Examples | Science fair projects, group presentations | Spelling drills, math fact repetition |
| Benefits | Enhances creativity, motivation, and retention | Improves accuracy and fluency in specific skills |
| Challenges | Time-intensive planning and assessment | Can be repetitive and disengaging |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning and Discrete Skill Instruction
Project-Based Learning (PBL) immerses students in real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and applied knowledge through sustained inquiry. Discrete Skill Instruction targets specific competencies or facts with focused, step-by-step teaching aimed at mastery and immediate application. While PBL emphasizes holistic understanding and integration of multiple skills, discrete instruction concentrates on isolated skill acquisition for foundational learning.
Defining Project-Based Learning: Key Features
Project-Based Learning emphasizes student-centered exploration through real-world projects that foster critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Key features include extended inquiry, integration of multiple disciplines, and production of a tangible final product demonstrating applied knowledge. This approach contrasts with Discrete Skill Instruction, which targets isolated competencies through repetitive practice and direct teaching methods.
Understanding Discrete Skill Instruction: Core Principles
Discrete Skill Instruction emphasizes teaching specific, well-defined skills through clear objectives, focused practice, and immediate feedback. It relies on task analysis to break down complex skills into manageable components, ensuring mastery before progressing. This method supports mastery learning by reinforcing accuracy and fluency in individual skills critical for overall competence.
Cognitive Benefits: Comparing Learning Outcomes
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging students in real-world challenges, promoting deeper cognitive processing and retention. Discrete skill instruction effectively builds foundational knowledge and specific competencies through targeted practice, aiding mastery of particular tasks. Studies indicate PBL fosters higher-order cognitive abilities and transfer of knowledge, while discrete instruction supports efficient acquisition of core skills essential for complex learning.
Student Engagement in Project-Based vs. Skill-Based Approaches
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances student engagement by immersing learners in real-world problems, fostering collaboration, critical thinking, and sustained interest through active participation. In contrast, Discrete Skill Instruction often emphasizes repetitive practice and isolated tasks, which may result in lower intrinsic motivation and engagement. Research indicates that students involved in PBL demonstrate higher levels of curiosity, persistence, and deeper understanding than those engaged solely in skill-based learning environments.
Curriculum Integration and Real-World Application
Project-Based Learning (PBL) integrates multiple curriculum areas by engaging students in complex, real-world problems that require critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity, fostering deeper understanding and long-term retention. Discrete Skill Instruction often isolates specific competencies or content areas, focusing on mastery of individual skills rather than interdisciplinary connections. PBL's emphasis on authentic contexts enhances students' ability to apply knowledge in practical situations, bridging classroom learning with real-world challenges more effectively than traditional skill-focused approaches.
Assessment Strategies in Both Instructional Methods
Assessment strategies in Project-Based Learning emphasize authentic, performance-based evaluations such as portfolios, presentations, and peer assessments that capture critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world application of knowledge. In contrast, Discrete Skill Instruction relies heavily on formative and summative assessments like quizzes, tests, and worksheets to measure mastery of specific, isolated skills and factual recall. Effective educators blend both approaches by integrating ongoing, criteria-based rubrics within project assessments alongside traditional tests to ensure comprehensive evaluation of student learning outcomes.
Teacher Roles and Classroom Dynamics
Project-Based Learning (PBL) positions teachers as facilitators who guide student inquiry, foster collaboration, and encourage critical thinking by creating dynamic, student-centered environments. In contrast, Discrete Skill Instruction requires teachers to act as direct instructors, delivering specific content and skills through structured lessons and assessments. Classroom dynamics in PBL emphasize active, hands-on learning with peer interaction, whereas discrete skill instruction relies on teacher-led, individual practice focused on mastery of isolated skills.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Project-Based Learning often faces challenges such as the time-intensive nature of designing and assessing complex projects, which can limit coverage of discrete skills and content standards. Discrete Skill Instruction may struggle with student engagement and fails to develop critical thinking or real-world application, leading to fragmented understanding. Both approaches require careful balancing to address diverse learning needs and curriculum goals while mitigating limitations like reduced depth in projects or lack of contextual learning in skill drills.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right approach between Project-Based Learning (PBL) and Discrete Skill Instruction depends on factors such as learning objectives, student engagement, and complexity of skills. PBL is ideal for developing critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, while discrete skill instruction effectively targets specific competencies and foundational knowledge. Educators should consider curriculum goals, available resources, and student learning preferences to optimize instructional outcomes.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com