The flipped classroom model transforms traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside of class, allowing in-class time for interactive activities and personalized support. This approach enhances student engagement, deepens understanding, and fosters collaborative learning environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover how this innovative strategy can revolutionize your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
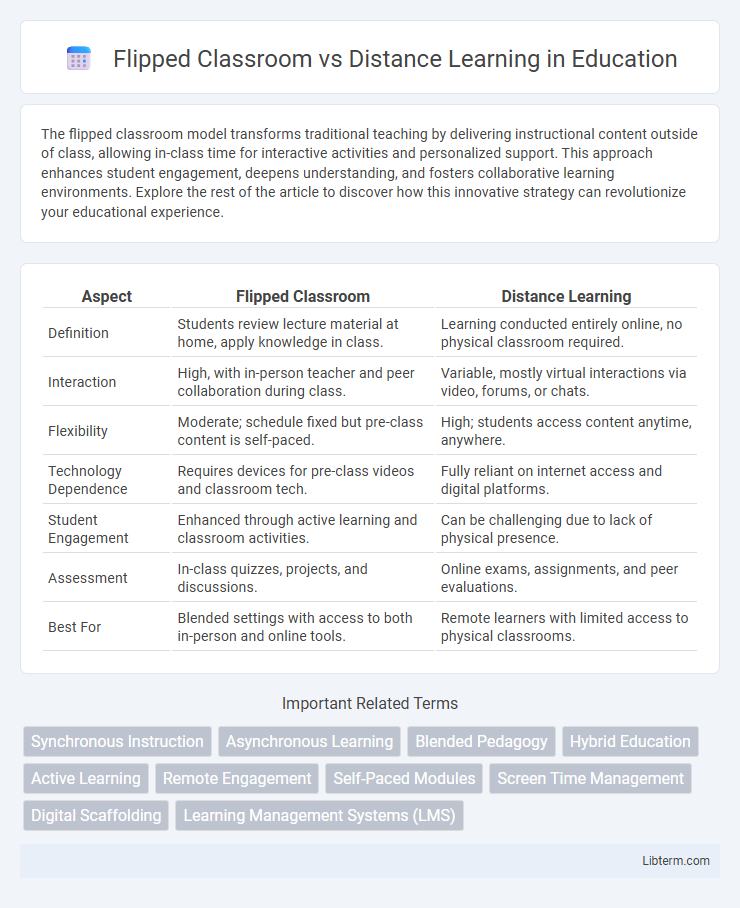
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Distance Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students review lecture material at home, apply knowledge in class. | Learning conducted entirely online, no physical classroom required. |
| Interaction | High, with in-person teacher and peer collaboration during class. | Variable, mostly virtual interactions via video, forums, or chats. |
| Flexibility | Moderate; schedule fixed but pre-class content is self-paced. | High; students access content anytime, anywhere. |
| Technology Dependence | Requires devices for pre-class videos and classroom tech. | Fully reliant on internet access and digital platforms. |
| Student Engagement | Enhanced through active learning and classroom activities. | Can be challenging due to lack of physical presence. |
| Assessment | In-class quizzes, projects, and discussions. | Online exams, assignments, and peer evaluations. |
| Best For | Blended settings with access to both in-person and online tools. | Remote learners with limited access to physical classrooms. |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Distance Learning
The Flipped Classroom model reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online for students to study at home, while class time is dedicated to interactive activities and personalized support. Distance Learning encompasses a broader range of remote education methods, enabling students to engage with coursework virtually from any location, often through platforms like LMS and video conferencing tools. Both approaches emphasize flexibility and learner autonomy but differ in their structure and implementation, with flipped classrooms integrating face-to-face collaboration and distance learning relying primarily on virtual interaction.
Core Concepts and Definitions
The flipped classroom model reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive activities and deeper learning. Distance learning refers to education where students and instructors are separated by physical distance, relying primarily on digital platforms for content delivery, communication, and assessment. Both methods emphasize flexible learning environments but differ in structure, with flipped classrooms blending online and face-to-face interaction, while distance learning operates entirely remotely.
Historical Evolution of Both Models
The flipped classroom model emerged in the early 2000s as educators sought to invert traditional teaching by delivering lecture content online for outside-of-class learning, enabling active, face-to-face engagement during class time. Distance learning, with roots tracing back to the 19th century via correspondence courses, evolved significantly through radio, television, and eventually internet-based platforms by the late 20th century, facilitating remote education access worldwide. Both models have been shaped by technological advancements, shifting from passive content delivery to interactive, learner-centered approaches that emphasize flexibility and accessibility.
Key Differences in Learning Environments
Flipped Classroom emphasizes active, in-person engagement by having students review instructional content at home and apply knowledge through collaborative activities during class. Distance Learning relies on remote technology platforms to deliver lectures and coursework, enabling flexible access but often limiting real-time peer interaction. The distinct learning environments influence the dynamics of student participation, immediate feedback, and practical application of concepts.
Teaching Strategies and Technology Integration
Flipped Classroom leverages pre-recorded lectures and interactive in-class activities to enhance student engagement and promote active learning, utilizing tools like video platforms, learning management systems (LMS), and collaborative software. Distance Learning relies heavily on synchronous and asynchronous technologies such as video conferencing, discussion forums, and digital assessments to facilitate remote instruction and maintain communication between teachers and students. Both teaching strategies integrate advanced educational technologies to optimize content delivery and foster student-centered learning environments tailored to diverse learning needs.
Student Engagement and Participation
Flipped Classroom models significantly enhance student engagement by encouraging active participation through pre-class content review and in-class interactive activities, fostering deeper understanding and collaboration. Distance Learning often faces challenges with student participation due to limited real-time interaction and potential distractions, reducing engagement levels despite flexible access to materials. Integrating synchronous sessions and interactive technology tools can mitigate distance learning engagement issues, aligning it more closely with the interactive benefits of the flipped classroom approach.
Assessment and Feedback Approaches
Flipped Classroom assessment emphasizes formative methods such as quizzes and peer evaluations during in-class active learning, enabling immediate, personalized feedback that enhances student engagement and comprehension. Distance Learning relies heavily on digital tools like automated quizzes, video submissions, and discussion forums, which facilitate flexible, asynchronous feedback but may delay interaction and reduce immediacy. Both approaches benefit from integrating technology-driven analytics to monitor student progress and tailor feedback, yet the Flipped Classroom's in-person component often allows for richer, real-time assessment dialogues.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Model
Flipped Classroom enhances learning engagement by allowing students to review lecture materials at their own pace, promoting active in-class participation, but it requires high self-discipline and access to reliable technology. Distance Learning offers flexibility and accessibility, enabling education beyond geographical constraints, yet it may lead to reduced interpersonal interaction and challenges in maintaining student motivation. Both models demand robust digital infrastructure and present distinct challenges in delivering personalized feedback and fostering collaborative learning environments.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
Flipped Classroom faces challenges such as requiring students' self-discipline and access to pre-class materials, while Distance Learning struggles with student engagement and reliable internet connectivity. Solutions include integrating interactive video content and adaptive learning platforms for Flipped Classroom, alongside robust Learning Management Systems (LMS) and offline resource availability to support Distance Learning. Both models benefit from continuous instructor training and incorporating hybrid approaches to enhance effectiveness and accessibility.
Future Trends in Educational Delivery
Emerging trends in educational delivery highlight a convergence of flipped classroom models and distance learning through hybrid approaches that combine asynchronous online content with interactive in-person or virtual sessions. Advances in AI-driven analytics and adaptive learning platforms are expected to personalize instruction further, enhancing student engagement and outcomes across both modalities. Future classrooms will likely integrate immersive technologies such as augmented reality and virtual reality to support experiential learning beyond traditional distance and flipped formats.
Flipped Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com