Mastering hard skills such as programming, data analysis, and technical writing can significantly enhance your career prospects and job performance. These skills are tangible and measurable, making them essential for meeting specific industry requirements and advancing in competitive fields. Discover how developing your hard skills can open new professional opportunities by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
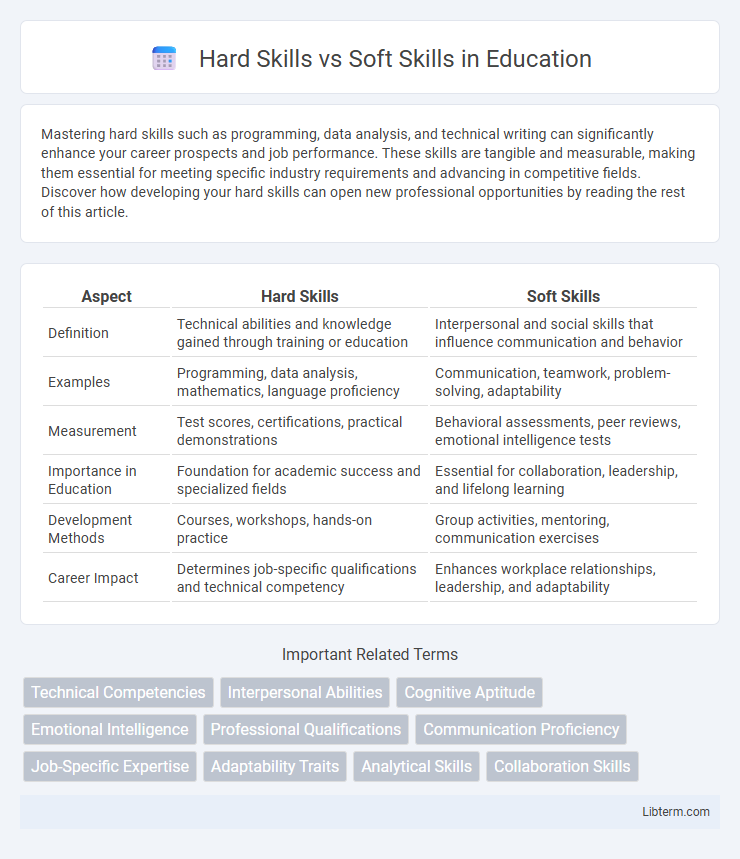
| Aspect | Hard Skills | Soft Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technical abilities and knowledge gained through training or education | Interpersonal and social skills that influence communication and behavior |
| Examples | Programming, data analysis, mathematics, language proficiency | Communication, teamwork, problem-solving, adaptability |
| Measurement | Test scores, certifications, practical demonstrations | Behavioral assessments, peer reviews, emotional intelligence tests |
| Importance in Education | Foundation for academic success and specialized fields | Essential for collaboration, leadership, and lifelong learning |
| Development Methods | Courses, workshops, hands-on practice | Group activities, mentoring, communication exercises |
| Career Impact | Determines job-specific qualifications and technical competency | Enhances workplace relationships, leadership, and adaptability |
Understanding Hard Skills: Definition and Examples
Hard skills are specific, teachable abilities or knowledge sets acquired through education or training, essential for performing technical tasks in various industries. Examples of hard skills include programming languages like Python, data analysis, accounting, graphic design, and proficiency in software tools such as Microsoft Excel or AutoCAD. Mastery of hard skills enhances job performance and is often verified through certifications, tests, or practical demonstrations in professional settings.
What Are Soft Skills? Key Traits and Importance
Soft skills encompass interpersonal abilities such as communication, teamwork, adaptability, and problem-solving that enhance workplace interactions and productivity. These traits enable individuals to manage emotions, build relationships, and navigate social complexities effectively. Employers increasingly prioritize soft skills for fostering collaboration, leadership, and a positive organizational culture.
Hard Skills vs Soft Skills: Core Differences
Hard skills consist of technical abilities and knowledge specific to a job, such as coding, data analysis, or machine operation, and are measurable through certifications or tests. Soft skills involve interpersonal attributes like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, which influence how individuals interact and perform in a workplace. The core difference lies in hard skills being quantifiable and task-focused, while soft skills are subjective and relate to personal behavior and emotional intelligence.
Why Employers Value Both Hard and Soft Skills
Employers value hard skills for their direct application to job-specific tasks and measurable expertise, such as coding, data analysis, or machinery operation. Soft skills like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving enhance workplace collaboration, adaptability, and leadership, driving overall productivity and company culture. Combining both hard and soft skills ensures employees are not only proficient in their roles but also capable of navigating interpersonal dynamics and evolving challenges effectively.
Developing Hard Skills: Training and Education Paths
Developing hard skills involves targeted training programs such as coding bootcamps, technical certifications, and formal education degrees in fields like engineering or data science. Online platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning provide specialized courses to enhance proficiency in areas such as programming, graphic design, and financial analysis. Structured hands-on practice and continuous skill assessment are critical for mastering hard skills that meet industry standards and job requirements.
Building Soft Skills: Strategies for Personal Growth
Building soft skills such as communication, emotional intelligence, and adaptability requires consistent practice in real-life scenarios and reflective self-assessment. Engaging in activities like teamwork, conflict resolution exercises, and active listening workshops enhances interpersonal abilities crucial for career development. Prioritizing continuous feedback and mindfulness fosters personal growth, making soft skills a vital complement to technical hard skills in professional success.
Integrating Hard and Soft Skills in the Workplace
Integrating hard and soft skills in the workplace enhances overall productivity and teamwork by combining technical expertise with effective communication and problem-solving abilities. Employers emphasize hybrid skill sets, ensuring employees not only master industry-specific tools like data analysis or coding but also develop interpersonal skills such as emotional intelligence and adaptability. This balanced approach fosters innovation, improves conflict resolution, and drives successful project management across diverse professional environments.
Hard Skills and Soft Skills in the Hiring Process
Hard skills, such as technical abilities and specialized knowledge, are critical in the hiring process because they demonstrate a candidate's capability to perform specific job tasks efficiently. Employers prioritize hard skills through assessments, certifications, and practical tests to ensure candidates meet the exact requirements of the position. Soft skills complement these competencies by enabling effective communication, teamwork, and adaptability, but hard skills remain the primary criteria for initial candidate screening and qualification.
The Impact of Hard and Soft Skills on Career Progression
Hard skills, such as technical expertise and specialized knowledge, directly influence job performance and eligibility for promotions, often determining entry into specific roles or industries. Soft skills like communication, adaptability, and leadership enhance teamwork, problem-solving, and client interactions, which are critical for long-term career growth and higher-level management positions. Employers prioritize a balanced combination of hard and soft skills to ensure both competence and effective collaboration, accelerating career advancement and professional development.
Future Trends: Evolving Demand for Hard and Soft Skills
Future trends reveal a growing demand for a balanced combination of hard skills such as data analysis, programming, and cybersecurity, alongside soft skills like emotional intelligence, adaptability, and communication. Advances in artificial intelligence and automation elevate the value of technical expertise while simultaneously increasing the importance of creativity, problem-solving, and interpersonal collaboration to complement automated systems. Organizations increasingly prioritize continuous learning and hybrid skill sets to navigate complex, technology-driven work environments effectively.
Hard Skills Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com