Standardized testing measures student performance using uniform procedures, enabling comparison across different schools and regions. It plays a crucial role in assessing educational effectiveness, guiding policy decisions, and identifying areas needing improvement. Explore the full article to understand how standardized testing impacts your learning journey and education system.
Table of Comparison
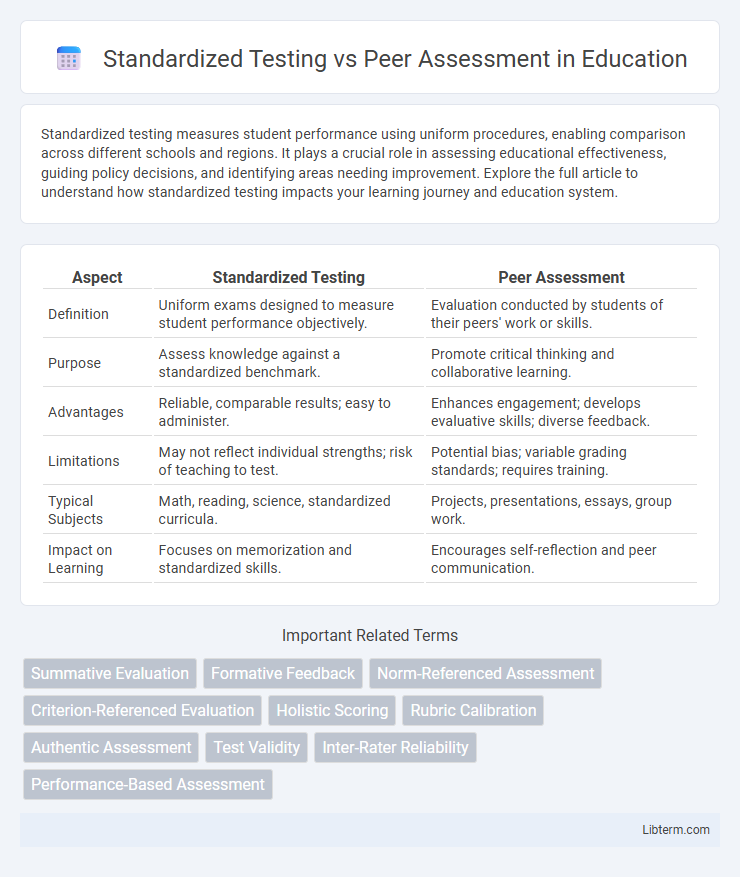
| Aspect | Standardized Testing | Peer Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform exams designed to measure student performance objectively. | Evaluation conducted by students of their peers' work or skills. |
| Purpose | Assess knowledge against a standardized benchmark. | Promote critical thinking and collaborative learning. |
| Advantages | Reliable, comparable results; easy to administer. | Enhances engagement; develops evaluative skills; diverse feedback. |
| Limitations | May not reflect individual strengths; risk of teaching to test. | Potential bias; variable grading standards; requires training. |
| Typical Subjects | Math, reading, science, standardized curricula. | Projects, presentations, essays, group work. |
| Impact on Learning | Focuses on memorization and standardized skills. | Encourages self-reflection and peer communication. |
Introduction to Standardized Testing and Peer Assessment
Standardized testing employs uniform procedures and scoring to objectively measure student performance across large populations, ensuring comparability and reliability in educational assessments. Peer assessment involves students evaluating each other's work, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and self-regulation skills through interactive feedback processes. Both methods provide unique insights into learning, with standardized tests prioritizing consistency and scalability, while peer assessments enhance personalized understanding and engagement.
Historical Context and Evolution
Standardized testing originated in the early 20th century as a method to objectively measure student achievement and compare educational outcomes across diverse populations. Peer assessment has roots in ancient educational practices but gained prominence in the late 20th century as constructivist theories emphasized collaborative learning and self-regulation. Over time, the evolution of both methods reflects shifting educational priorities from uniform benchmarking towards fostering critical thinking and student engagement.
Key Principles and Methodologies
Standardized testing employs uniform procedures and objective scoring to evaluate student performance across broad populations, emphasizing reliability and validity. Peer assessment utilizes collaborative evaluation where students review each other's work based on agreed criteria, fostering critical thinking and active learning. Both methodologies prioritize accurate measurement of learning outcomes but differ in approach: standardized testing relies on structured, quantifiable data, while peer assessment leverages qualitative feedback and social learning dynamics.
Measuring Academic Achievement: Objectivity vs Subjectivity
Standardized testing offers a quantitative measurement of academic achievement through uniform questions and scoring, ensuring objectivity and comparability across diverse student populations. Peer assessment incorporates qualitative feedback, capturing subjective insights on a student's understanding and critical thinking skills, which may reveal competencies not measurable by standardized tests. Balancing both methods can provide a comprehensive evaluation of student performance by combining objective scores with nuanced peer perspectives.
Impact on Student Learning and Motivation
Standardized testing provides quantifiable data on student performance but often induces anxiety, which can hinder intrinsic motivation and deep learning. Peer assessment fosters collaborative learning and critical thinking, enhancing student engagement and motivation by promoting active involvement in the evaluation process. Research indicates that combining both methods can balance objective measurement with personalized feedback to support comprehensive student development.
Reliability and Validity in Assessment Methods
Standardized testing offers high reliability through uniform administration and scoring, ensuring consistent results across diverse populations, but it can lack validity by failing to capture complex skills and contextual understanding. Peer assessment enhances validity by incorporating diverse perspectives and real-world relevance, yet its reliability may be compromised due to subjective biases and inconsistent criteria among evaluators. Balancing reliability and validity requires integrating standardized testing's objectivity with peer assessment's nuanced feedback for comprehensive evaluation.
Equity and Accessibility Considerations
Standardized testing often poses equity challenges due to cultural biases and limited accommodations for diverse learning needs, potentially disadvantaging marginalized students. Peer assessment can enhance accessibility by promoting inclusivity and diverse perspectives, allowing personalized feedback that accommodates varied learning styles. However, peer assessment requires careful structuring to ensure fairness and reliability across different ability levels and backgrounds.
Teacher and Student Perspectives
Standardized testing offers teachers quantifiable data to evaluate student performance objectively, enabling comparisons across diverse populations, while some educators express concerns about its potential to overlook individual learning differences. From the student perspective, standardized tests can induce anxiety and may not fully reflect their knowledge or skills, whereas peer assessment encourages collaboration, immediate feedback, and deeper comprehension. Teachers acknowledge peer assessment's role in fostering critical thinking and active learning but worry about the variability in student evaluative skills and potential biases affecting grade reliability.
Global Trends and Educational Policy
Global trends in educational policy reveal a growing shift from standardized testing toward peer assessment to foster deeper learning and critical thinking skills. Countries adopting peer assessment initiatives report enhanced student engagement, collaborative skills, and reduced test anxiety compared to traditional standardized exams. Policymakers increasingly integrate peer assessment frameworks within curricula to support personalized learning and holistic evaluation approaches worldwide.
Future Directions and Recommendations
Future directions in evaluation emphasize integrating standardized testing with peer assessment to balance objectivity and personalized feedback, enhancing learning outcomes. Leveraging AI-driven analytics can refine peer assessment reliability while maintaining standardized test consistency. Educational systems should adopt hybrid models, fostering collaboration and critical thinking skills alongside measurable academic performance.
Standardized Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com