A skilled tutor can transform your learning experience by providing personalized instruction tailored to your unique needs and goals. With expert guidance, you can overcome challenges and deepen your understanding of complex subjects effectively. Discover how the right tutoring approach can elevate your academic success by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
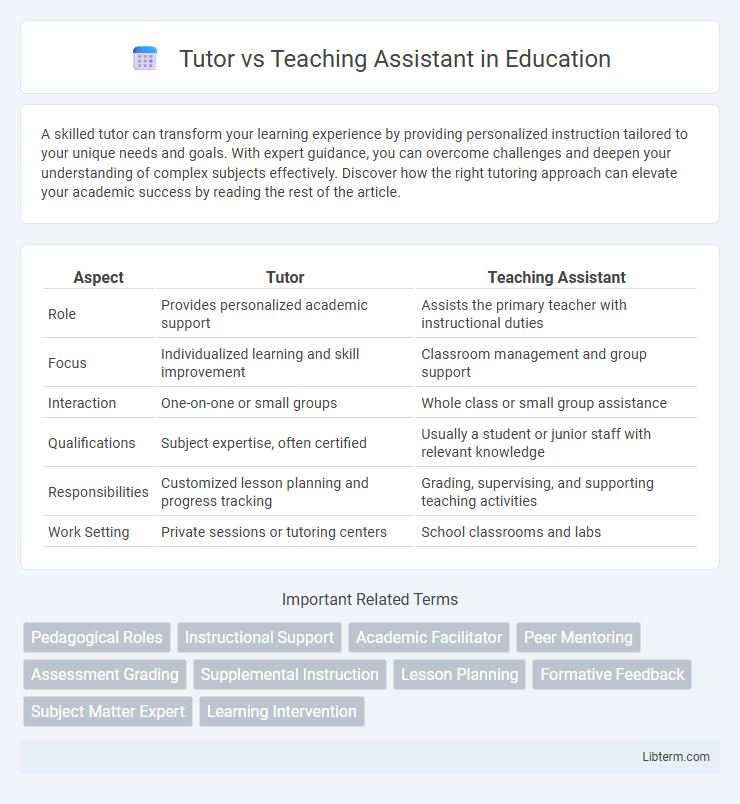
| Aspect | Tutor | Teaching Assistant |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Provides personalized academic support | Assists the primary teacher with instructional duties |
| Focus | Individualized learning and skill improvement | Classroom management and group support |
| Interaction | One-on-one or small groups | Whole class or small group assistance |
| Qualifications | Subject expertise, often certified | Usually a student or junior staff with relevant knowledge |
| Responsibilities | Customized lesson planning and progress tracking | Grading, supervising, and supporting teaching activities |
| Work Setting | Private sessions or tutoring centers | School classrooms and labs |
Introduction to Tutors and Teaching Assistants
Tutors provide personalized, one-on-one academic support tailored to individual learning needs, often specializing in specific subjects or skills. Teaching Assistants (TAs) primarily support instructors by facilitating classroom activities, grading, and helping manage course logistics while assisting multiple students simultaneously. Both roles enhance educational experiences but differ in their scope, interaction style, and responsibilities within academic settings.
Defining the Role of a Tutor
A tutor provides personalized, one-on-one academic support tailored to a student's specific learning needs and pace, often focusing on reinforcing concepts and improving skills outside the traditional classroom setting. Unlike teaching assistants who support instructors by managing class logistics and assisting with grading or instruction, tutors offer individualized attention that addresses gaps in understanding. This role emphasizes mentoring and adapting teaching methods to foster student confidence and mastery of subject matter.
Understanding the Teaching Assistant’s Duties
Teaching Assistants (TAs) typically support professors by managing grading, facilitating discussion sections, and conducting office hours to clarify lecture material. They often bridge the gap between students and instructors by offering personalized assistance and addressing academic questions within large courses. Unlike tutors who provide individualized learning support, TAs are integrated into the course structure and contribute to both instructional and administrative responsibilities.
Key Differences Between Tutors and Teaching Assistants
Tutors provide personalized, one-on-one or small group academic support tailored to individual student needs, often outside the formal classroom setting, focusing on reinforcing understanding and improving skills. Teaching assistants support teachers within a classroom, managing administrative tasks, assisting with lesson preparation, and sometimes leading discussions or grading assignments under the teacher's supervision. The primary distinction lies in tutors' direct instructional role versus teaching assistants' supportive and organizational functions within the educational environment.
Qualifications Required for Tutors vs Teaching Assistants
Tutors typically require subject-matter expertise often demonstrated through relevant degrees or certifications and strong communication skills to provide personalized academic support. Teaching Assistants usually need a minimum of a bachelor's degree in the subject area, sometimes pursuing or enrolled in graduate studies, along with experience in instructional or classroom settings. Certification or formal training in education techniques is more commonly mandatory for teaching assistants compared to tutors, who may rely more on practical knowledge and specialized tutoring credentials.
Skills and Qualities: Tutors vs Teaching Assistants
Tutors usually possess strong one-on-one communication skills, personalized instructional strategies, and subject-specific expertise to tailor lessons according to individual student needs. Teaching Assistants demonstrate organizational skills, the ability to support classroom management, and proficiency in assisting with grading and administrative tasks while facilitating group learning. Both roles require patience, adaptability, and a solid understanding of educational content, but tutors focus more on individualized academic support, whereas teaching assistants balance instructional aid with broader classroom responsibilities.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Tutors provide personalized, one-on-one support that targets specific learning gaps, leading to improved student comprehension and higher academic performance. Teaching Assistants (TAs) facilitate classroom learning by supporting instructors with grading, managing discussions, and clarifying course materials, which enhances overall class engagement and understanding. Studies indicate that personalized tutoring interventions yield more significant gains in student learning outcomes compared to the broader support roles typically offered by teaching assistants.
Working Environments and Settings
Tutors typically work in personalized, one-on-one or small group settings, often in private homes, tutoring centers, or online platforms, allowing for flexible schedules tailored to individual student needs. Teaching Assistants generally operate within classroom environments in schools, colleges, or universities, supporting lead teachers during lessons, managing group activities, and assisting with grading and administrative tasks. The working environment for Teaching Assistants is more structured and institution-based, whereas tutors enjoy varied and adaptable settings focused on personalized instruction.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Role
Tutors offer personalized, one-on-one instruction tailored to individual learning styles, enhancing comprehension and academic performance, but they may face challenges in adapting to diverse student needs and maintaining consistent availability. Teaching Assistants support classroom management and assist with grading, providing valuable assistance to instructors and helping manage larger groups, yet they often encounter challenges related to balancing their responsibilities with their own studies and limited authority in decision-making. Both roles are crucial in educational settings, with tutors excelling in focused academic support and teaching assistants contributing to overall classroom efficiency and student engagement.
Choosing Between a Tutor and a Teaching Assistant
Choosing between a tutor and a teaching assistant depends on the level of personalized support and subject expertise needed, as tutors offer one-on-one, tailored instruction while teaching assistants provide classroom-based assistance and help with grading. Tutors are ideal for students seeking focused guidance on specific topics or exam preparation, whereas teaching assistants support broader classroom dynamics and administrative tasks. Assessing the learning environment and individual academic goals will help determine whether a tutor's targeted approach or a teaching assistant's collaborative role is more beneficial.
Tutor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com