Mastery-based assessment evaluates your understanding by requiring demonstration of key skills at a high proficiency level before progressing. This approach fosters deep learning, ensuring concepts are fully grasped rather than superficially covered. Discover how mastery-based assessment can transform your educational experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
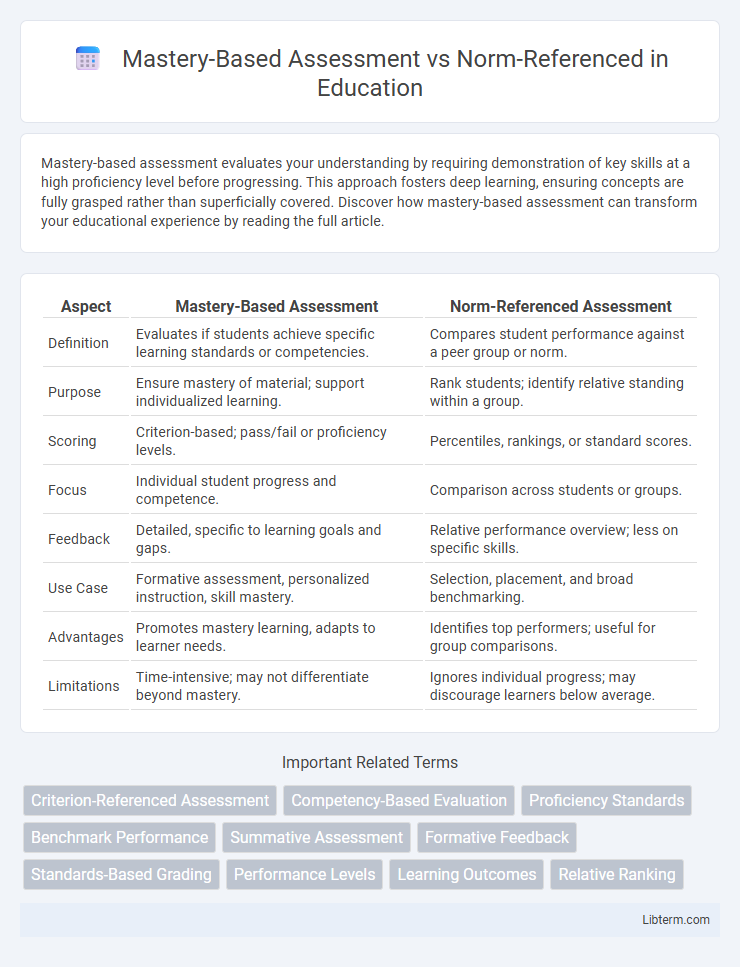
| Aspect | Mastery-Based Assessment | Norm-Referenced Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates if students achieve specific learning standards or competencies. | Compares student performance against a peer group or norm. |
| Purpose | Ensure mastery of material; support individualized learning. | Rank students; identify relative standing within a group. |
| Scoring | Criterion-based; pass/fail or proficiency levels. | Percentiles, rankings, or standard scores. |
| Focus | Individual student progress and competence. | Comparison across students or groups. |
| Feedback | Detailed, specific to learning goals and gaps. | Relative performance overview; less on specific skills. |
| Use Case | Formative assessment, personalized instruction, skill mastery. | Selection, placement, and broad benchmarking. |
| Advantages | Promotes mastery learning, adapts to learner needs. | Identifies top performers; useful for group comparisons. |
| Limitations | Time-intensive; may not differentiate beyond mastery. | Ignores individual progress; may discourage learners below average. |
Understanding Mastery-Based Assessment
Mastery-Based Assessment measures student learning by evaluating whether individual learners have achieved specific competencies or skills, ensuring mastery before progressing. It emphasizes personalized learning pace and targeted feedback, driving deeper comprehension and skill acquisition. This approach contrasts with Norm-Referenced Assessment, which compares students against each other rather than a fixed set of criteria.
What Is Norm-Referenced Assessment?
Norm-referenced assessment evaluates a student's performance by comparing it to the performance of a defined peer group, typically using standardized tests to rank individuals on a percentile scale. This method identifies relative standing rather than specific skill mastery, making it useful for selection and placement decisions. The focus lies in differentiating students rather than measuring absolute knowledge or competency levels.
Key Differences Between Mastery and Norm-Referenced Approaches
Mastery-based assessment evaluates students against predefined learning objectives, ensuring individuals achieve specific competencies before advancing, while norm-referenced assessment ranks students relative to peers, emphasizing comparative performance. Mastery assessments prioritize individual progress and skill mastery, using criterion-referenced benchmarks, whereas norm-referenced assessments rely on percentile ranks and standardized scoring to identify relative standing in a population. The key difference lies in mastery-based focusing on achieving set standards versus norm-referenced focusing on ordinal ranking within a group.
Benefits of Mastery-Based Assessment
Mastery-based assessment prioritizes individual student progress by measuring whether learners have achieved specific competencies, resulting in personalized pacing and targeted support. This approach fosters deeper understanding and skill retention by emphasizing mastery over comparison with peers. It also encourages a growth mindset, reducing anxiety and motivating continuous improvement by recognizing each student's unique learning journey.
Limitations of Norm-Referenced Assessment
Norm-referenced assessments measure student performance relative to peers, often overlooking individual learning progress and mastery of specific skills. These tests can perpetuate achievement gaps by focusing on ranking rather than personalized learning growth. Consequently, norm-referenced assessments provide limited insight into a learner's actual competency or readiness for subsequent educational challenges.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Mastery-based assessment enhances student motivation and engagement by prioritizing individual learning progress and mastery of skills over relative performance, fostering a growth mindset and intrinsic motivation. Norm-referenced assessment often leads to competition and comparison, which can demotivate lower-performing students and reduce overall engagement. Implementing mastery-based approaches encourages personalized feedback and continuous improvement, directly supporting sustained student involvement and confidence in learning outcomes.
Equity in Learning: Mastery vs Norm-Referenced
Mastery-based assessment promotes equity in learning by evaluating students against predefined criteria, ensuring all learners achieve a high level of understanding before advancing. Norm-referenced assessment ranks students relative to peers, often perpetuating disparities by favoring those with prior advantages. Focusing on mastery supports inclusive education by recognizing individual progress and addressing diverse learning needs effectively.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Mastery-based assessment faces implementation challenges such as the need for individualized pacing, which demands significant teacher training and resource allocation to ensure accurate measurement of student progress. Norm-referenced assessments struggle with addressing diverse learning styles and cultural backgrounds, often requiring data analysis tools to interpret results fairly and effectively. Solutions include integrating adaptive technologies for mastery-based assessments and using statistical adjustments in norm-referenced formats to enhance equity and reliability in diverse classrooms.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Mastery-based assessment emphasizes individual proficiency with real-world examples like Duolingo's language tests, which measure users' skill mastery rather than rank. In contrast, norm-referenced assessments such as the SAT or GRE compare scores across a population, illustrating differences in performance relative to peers. Case studies in education reform demonstrate mastery-based systems improve personalized learning outcomes by focusing on competence and practical application rather than percentile ranking.
Choosing the Right Assessment Approach for Your Context
Mastery-based assessment evaluates students against predefined learning objectives, emphasizing individual proficiency and progress, making it ideal for personalized learning environments and competency-based education. Norm-referenced assessment compares student performance to a peer group, useful for ranking and identifying achievement gaps within a population, especially in large-scale standardized testing. Selecting the right approach depends on your educational goals: mastery-based assessments suit contexts prioritizing skill mastery and formative feedback, while norm-referenced assessments support summative evaluation and comparative analysis.
Mastery-Based Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com