A Reading Specialist enhances literacy skills through targeted strategies tailored to diverse learners, while an ESL Teacher focuses on developing English language proficiency for non-native speakers. Both roles require expertise in language acquisition, instructional methods, and cultural sensitivity to foster effective learning environments. Discover how these professionals can support Your educational journey in the full article.
Table of Comparison
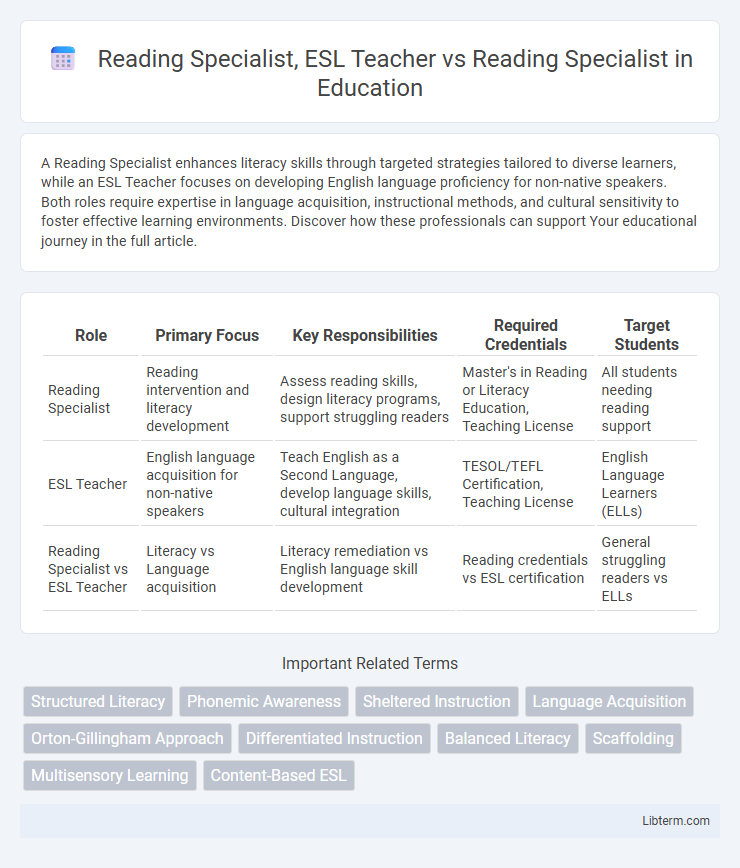
| Role | Primary Focus | Key Responsibilities | Required Credentials | Target Students |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reading Specialist | Reading intervention and literacy development | Assess reading skills, design literacy programs, support struggling readers | Master's in Reading or Literacy Education, Teaching License | All students needing reading support |
| ESL Teacher | English language acquisition for non-native speakers | Teach English as a Second Language, develop language skills, cultural integration | TESOL/TEFL Certification, Teaching License | English Language Learners (ELLs) |
| Reading Specialist vs ESL Teacher | Literacy vs Language acquisition | Literacy remediation vs English language skill development | Reading credentials vs ESL certification | General struggling readers vs ELLs |
Understanding the Role of a Reading Specialist
A Reading Specialist focuses on assessing and improving students' reading skills by implementing targeted interventions and literacy programs. An ESL Teacher, while also addressing reading, specializes in supporting English language learners to develop proficiency across speaking, listening, reading, and writing. Understanding the role of a Reading Specialist reveals a primary emphasis on diagnosing reading difficulties and collaborating with teachers to enhance literacy instruction school-wide.
Key Responsibilities of ESL Teachers
ESL Teachers primarily focus on developing English language proficiency through speaking, listening, reading, and writing skills tailored to non-native speakers. Key responsibilities include designing language acquisition lesson plans, assessing student progress in linguistic skills, and implementing strategies that accommodate diverse cultural backgrounds. Unlike Reading Specialists who concentrate on diagnosing and improving reading difficulties, ESL Teachers emphasize comprehensive language development to support overall academic achievement.
Educational Requirements: Reading Specialist vs. ESL Teacher
Reading Specialists typically require a master's degree in reading education or literacy, along with certification in reading instruction or intervention. ESL Teachers generally need a bachelor's degree in education or a related field, plus specialized TESOL or ESL certification to effectively teach English language learners. Both roles demand ongoing professional development, but Reading Specialists often have more advanced credentialing focused on literacy assessment and remediation.
Core Skills and Competencies Compared
Reading Specialists excel in phonemic awareness, decoding, and fluency interventions to support struggling readers, while ESL Teachers specialize in language acquisition, vocabulary development, and cultural adaptation for English learners. Both roles require strong assessment and differentiated instruction skills, but Reading Specialists focus more on literacy diagnostics and remediation strategies. ESL Teachers emphasize second language pedagogy, cross-linguistic transfer, and scaffolding techniques tailored to multilingual classrooms.
Teaching Approaches: Literacy vs. Language Acquisition
Reading Specialists focus on literacy development through targeted interventions in phonics, fluency, and comprehension strategies to enhance reading skills. ESL Teachers prioritize language acquisition by employing techniques such as scaffolding, vocabulary building, and cultural immersion to support English language learners. Teaching approaches for Reading Specialists center on decoding and text analysis, while ESL Teachers emphasize communicative competence and language proficiency.
Target Student Populations
Reading Specialists primarily support students struggling with literacy development across diverse grade levels, focusing on diagnosing reading difficulties and implementing evidence-based interventions to improve reading comprehension and fluency. ESL Teachers specialize in assisting English language learners (ELLs) by developing language acquisition skills tailored to students whose first language is not English, emphasizing vocabulary, grammar, and cultural context. While Reading Specialists target a broad range of literacy challenges, ESL Teachers concentrate specifically on language barriers faced by bilingual or multilingual learners.
Certification and Training Differences
Reading Specialists typically require certification in reading instruction, such as the Reading Specialist certification or endorsements that focus on literacy development, while ESL Teachers need specialized ESL or TESOL certification to address language acquisition and bilingual education. Training for Reading Specialists emphasizes diagnostics, intervention strategies, and literacy assessment, whereas ESL Teachers are trained in second-language pedagogy, cultural competency, and language proficiency frameworks. Both roles demand ongoing professional development, but Reading Specialists concentrate on enhancing reading skills, and ESL Teachers focus on language learning and support for English learners.
Collaboration With Classroom Teachers
Reading Specialists collaborate closely with classroom teachers to design targeted literacy interventions tailored to individual student needs, enhancing reading proficiency. ESL Teachers work alongside content teachers to integrate language development strategies within subject instruction, promoting comprehension for English language learners. Both roles emphasize teamwork but differ in focus: Reading Specialists prioritize decoding and fluency skills, while ESL Teachers concentrate on language acquisition and cultural adaptation.
Career Opportunities and Advancement
Reading Specialists with ESL expertise have broader career opportunities in diverse educational settings, including bilingual schools and language intervention programs, enhancing their marketability. They often advance to roles such as curriculum developers or literacy coaches specializing in second language acquisition, while traditional Reading Specialists typically progress within general literacy support and intervention roles. The dual specialization in ESL and reading intervention increases potential for leadership positions focused on multicultural education and inclusive literacy strategies.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Role Fits You?
A Reading Specialist focuses on improving students' literacy skills through targeted intervention and assessment, while an ESL Teacher specializes in language acquisition for English learners. Both roles require expertise in reading strategies, but ESL Teachers incorporate cultural and linguistic support tailored to non-native speakers. Choosing the right path depends on your passion for either broad literacy development or specialized language instruction for diverse populations.
Reading Specialist, ESL Teacher Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com