Clear and precise requirements form the foundation of any successful project, ensuring that all stakeholders align on objectives and deliverables. Well-defined requirements reduce the risk of misunderstandings and costly revisions by providing a detailed roadmap for development. Discover how to craft effective requirements that will empower your team and drive project success by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
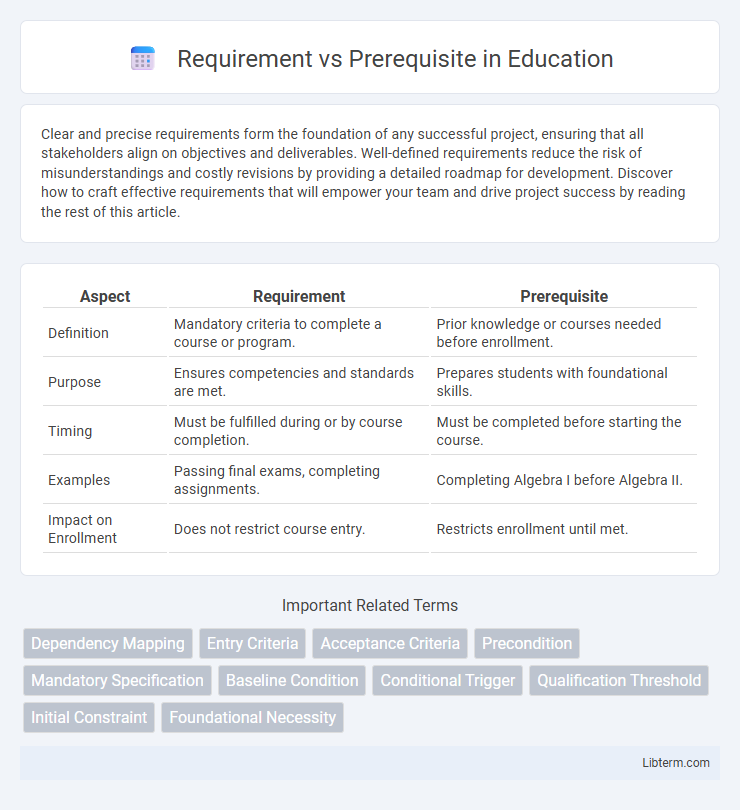
| Aspect | Requirement | Prerequisite |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mandatory criteria to complete a course or program. | Prior knowledge or courses needed before enrollment. |
| Purpose | Ensures competencies and standards are met. | Prepares students with foundational skills. |
| Timing | Must be fulfilled during or by course completion. | Must be completed before starting the course. |
| Examples | Passing final exams, completing assignments. | Completing Algebra I before Algebra II. |
| Impact on Enrollment | Does not restrict course entry. | Restricts enrollment until met. |
Understanding Requirement and Prerequisite: Key Definitions
Requirement refers to a specific condition or capability that must be fulfilled or possessed to achieve a goal, often outlining necessary criteria or standards. Prerequisite denotes a condition or task that must be completed or met before another action or process can begin, serving as a foundational step. Understanding the distinction between requirement as a mandatory condition and prerequisite as a prior necessary condition is crucial for effective project planning and execution.
Distinguishing Differences: Requirement vs Prerequisite
A requirement is a mandatory condition or qualification that must be met for a process, project, or role, while a prerequisite is a specific prior condition or step that must be completed before proceeding to the next stage. Requirements define what is needed for successful completion or eligibility, whereas prerequisites establish the necessary foundation or preparation before starting. Understanding the distinction helps ensure compliance with criteria and proper sequencing in workflows or academic programs.
Importance of Requirements in Project Planning
Requirements define the essential features and functions that a project must fulfill to meet stakeholder expectations, serving as the foundation for successful project planning. Prerequisites are the conditions or tasks that must be completed before starting the project, but requirements drive the project's scope, objectives, and deliverables. Clear, well-documented requirements ensure accurate resource allocation, risk management, and timeline estimation, significantly reducing project failure rates and enhancing overall efficiency.
The Role of Prerequisites in Process Workflow
Prerequisites serve as foundational conditions that must be met before a process workflow can commence, ensuring smooth progression and preventing workflow bottlenecks. They establish essential inputs, permissions, or prior knowledge required to maintain efficiency and reduce errors in subsequent steps. By defining clear prerequisites, project managers and system designers enhance process reliability and optimize resource allocation.
Examples of Requirements in Various Industries
Requirements define specific criteria or standards a product or service must meet, such as the ISO 9001 quality management standards in manufacturing or the HIPAA compliance requirements in healthcare IT systems. In software development, requirements include defining user functionalities like login authentication or data encryption features essential for secure applications. Construction projects often have requirements like environmental impact assessments and material strength specifications to ensure safety and regulatory compliance.
Common Types of Prerequisites in Educational Settings
Common types of prerequisites in educational settings include prior coursework, skill proficiency, and standardized test scores, all designed to ensure students possess the foundational knowledge necessary for advanced study. Enrollment often requires completion of specific classes or demonstration of competencies, such as passing a placement exam or achieving a minimum grade in relevant subjects. These prerequisites help maintain academic standards and support student success by aligning course demands with learners' preparation levels.
Impact of Missing Requirements on Project Outcomes
Missing requirements in a project often lead to scope creep, increased costs, and delayed timelines, critically impacting overall project success. Prerequisites ensure all necessary conditions are met before project initiation, reducing the risk of unforeseen obstacles and resource misallocations. Failure to identify and address both requirements and prerequisites can result in incomplete deliverables and stakeholder dissatisfaction.
How Prerequisites Influence Success Rates
Prerequisites set the foundational knowledge or skills required before engaging in a task or course, ensuring learners are adequately prepared to achieve desired outcomes. Meeting these prerequisites significantly influences success rates by minimizing knowledge gaps, reducing cognitive overload, and facilitating smoother progression through advanced material. Clear prerequisite criteria enable targeted support and resource allocation, ultimately enhancing performance and retention in educational and professional settings.
Strategies for Managing Requirements and Prerequisites
Effectively managing requirements and prerequisites involves clearly defining and documenting each to ensure project alignment and resource availability. Techniques such as requirement traceability matrices and regular stakeholder communication help monitor changes and dependencies, minimizing risks and delays. Leveraging tools for requirement prioritization and prerequisite validation enables targeted resource allocation and smoother project execution.
Best Practices for Documenting and Communicating Needs
Clear differentiation between requirements and prerequisites enhances project planning and stakeholder understanding; requirements define essential conditions or capabilities for success, while prerequisites specify conditions that must be met beforehand. Best practices for documenting needs include using precise, measurable language in requirements specifications and listing prerequisites separately with clear dependencies. Effective communication involves regular updates through collaborative tools and ensuring all team members acknowledge and understand both categories to prevent project delays or misalignment.
Requirement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com