Academic learning involves acquiring knowledge and skills through structured education, focusing on critical thinking, problem-solving, and subject mastery. Effective academic learning strategies enhance comprehension, retention, and application of information in real-world scenarios. Explore this article to discover methods that can improve your academic success and lifelong learning journey.
Table of Comparison
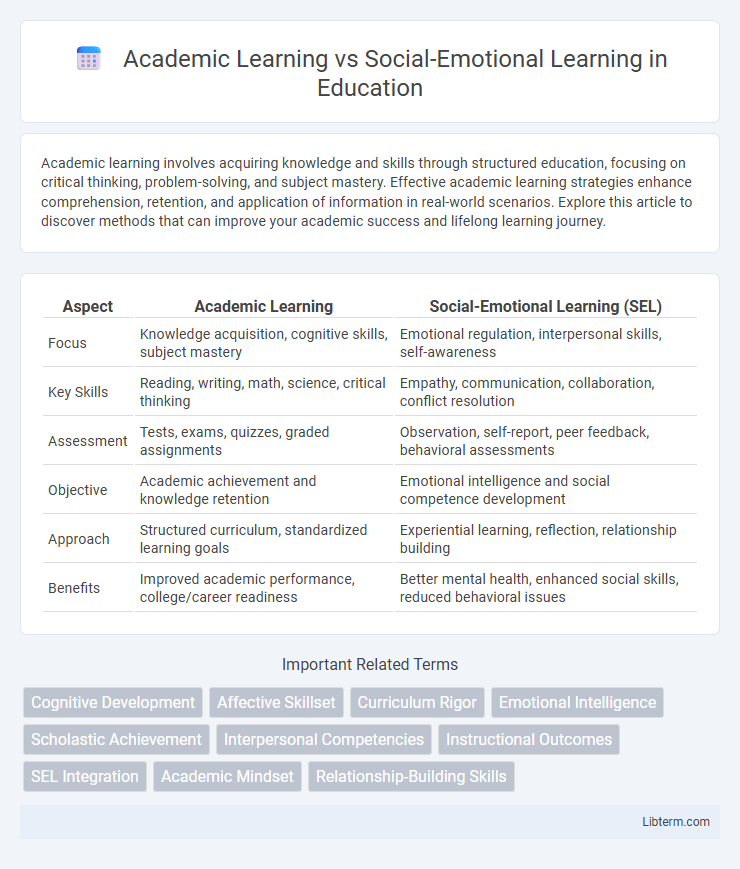
| Aspect | Academic Learning | Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Knowledge acquisition, cognitive skills, subject mastery | Emotional regulation, interpersonal skills, self-awareness |
| Key Skills | Reading, writing, math, science, critical thinking | Empathy, communication, collaboration, conflict resolution |
| Assessment | Tests, exams, quizzes, graded assignments | Observation, self-report, peer feedback, behavioral assessments |
| Objective | Academic achievement and knowledge retention | Emotional intelligence and social competence development |
| Approach | Structured curriculum, standardized learning goals | Experiential learning, reflection, relationship building |
| Benefits | Improved academic performance, college/career readiness | Better mental health, enhanced social skills, reduced behavioral issues |
Introduction to Academic and Social-Emotional Learning
Academic learning focuses on mastering core subjects such as mathematics, science, language arts, and social studies to develop critical thinking and knowledge acquisition. Social-emotional learning (SEL) emphasizes skills like self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and relationship-building, which are essential for personal and interpersonal success. Integrating both academic and social-emotional learning creates a holistic education approach that enhances student engagement, resilience, and overall achievement.
Defining Academic Learning: Goals and Methods
Academic learning centers on acquiring knowledge and skills in core subjects such as mathematics, science, language arts, and social studies through structured curricula and evidence-based instructional strategies. Its primary goals include developing critical thinking, mastery of content, and cognitive skills that enable students to analyze information and solve problems effectively. Methods often involve explicit teaching, formative assessments, and progress tracking to ensure measurable academic achievement and competency development.
What is Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)?
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) refers to the process through which children and adults acquire and effectively apply the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary to understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions. Unlike academic learning, which primarily focuses on cognitive skills and knowledge acquisition, SEL emphasizes emotional intelligence, social skills, and self-awareness essential for personal and academic success. Research shows that integrating SEL in schools improves students' social behavior, reduces emotional distress, and enhances academic outcomes.
Key Differences Between Academic Learning and SEL
Academic learning focuses on knowledge acquisition and cognitive skill development through subjects like math, science, and language arts, emphasizing measurable outcomes and standardized testing. Social-emotional learning (SEL) centers on cultivating skills such as self-awareness, emotional regulation, empathy, and interpersonal communication, promoting mental health and positive relationships. Key differences lie in their objectives: academic learning targets intellectual growth, while SEL prioritizes emotional intelligence and social competence essential for overall well-being and success.
The Importance of Academic Achievement
Academic achievement plays a crucial role in shaping students' future career opportunities and overall life success by providing essential knowledge and critical thinking skills. Mastery of subjects like mathematics, science, and language arts enhances cognitive development and equips learners with the ability to solve complex problems. Strong academic performance also contributes to higher graduation rates and access to college scholarships, making it a fundamental priority in education systems.
The Role of SEL in Student Development
Social-emotional learning (SEL) plays a critical role in student development by enhancing emotional regulation, empathy, and interpersonal skills, which directly support academic success. Research shows that students engaged in SEL programs demonstrate higher graduation rates and improved classroom behavior, contributing to a more positive learning environment. Integrating SEL into the curriculum fosters resilience and self-awareness, essential for lifelong learning and personal growth.
Integrating Academic Learning and SEL in Classrooms
Integrating academic learning and social-emotional learning (SEL) in classrooms enhances student engagement by fostering critical thinking alongside emotional regulation and interpersonal skills. Research shows that embedding SEL strategies into academic content improves both academic outcomes and student well-being, creating a holistic educational environment. Schools implementing coordinated SEL programs report higher achievement scores, reduced behavioral issues, and increased student motivation, demonstrating the mutual reinforcement of cognitive and emotional development.
Benefits of Balancing Academic and SEL Approaches
Balancing academic learning with social-emotional learning (SEL) enhances student engagement, improves emotional regulation, and promotes critical thinking skills essential for academic success. Research shows that integrated SEL programs contribute to higher test scores, better classroom behavior, and increased graduation rates. Schools that prioritize both academic content and SEL foster holistic development, equipping students with resilience and collaboration skills crucial for lifelong achievement.
Challenges in Combining Academic and Social-Emotional Learning
Integrating academic learning with social-emotional learning (SEL) presents challenges such as balancing curriculum time to address both cognitive skills and emotional development effectively. Educators often struggle with insufficient training and resources to implement SEL strategies alongside academic standards. Moreover, assessing SEL outcomes remains complex, complicating efforts to measure progress and justify the integration within traditional academic frameworks.
Future Trends in Education: Merging Academic and SEL Frameworks
Future trends in education emphasize the integration of academic learning with social-emotional learning (SEL) frameworks to cultivate holistic student development. Innovative curricula are designed to enhance cognitive skills while fostering emotional intelligence, resilience, and interpersonal skills critical for 21st-century success. Schools increasingly adopt data-driven SEL assessments alongside academic benchmarks, promoting personalized learning environments that support both intellectual growth and social-emotional well-being.
Academic Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com