Teacher-centered instruction focuses on the teacher as the primary source of knowledge, controlling the pace and direction of lessons. This approach emphasizes lectures, rote memorization, and structured activities designed to maintain students' attention and reinforce key concepts. Explore the rest of this article to understand how teacher-centered methods impact learning outcomes and classroom dynamics.
Table of Comparison
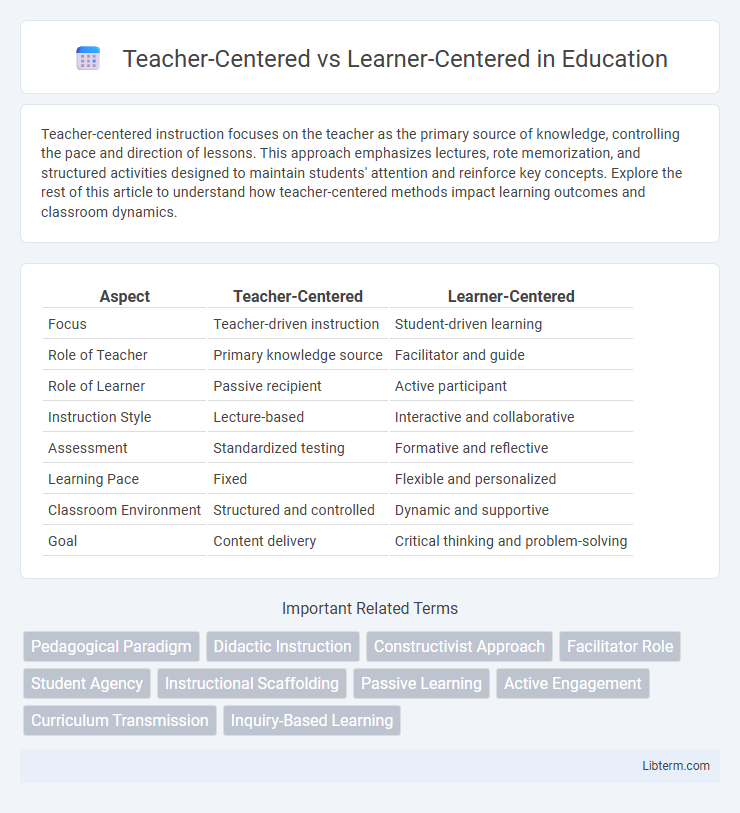
| Aspect | Teacher-Centered | Learner-Centered |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Teacher-driven instruction | Student-driven learning |
| Role of Teacher | Primary knowledge source | Facilitator and guide |
| Role of Learner | Passive recipient | Active participant |
| Instruction Style | Lecture-based | Interactive and collaborative |
| Assessment | Standardized testing | Formative and reflective |
| Learning Pace | Fixed | Flexible and personalized |
| Classroom Environment | Structured and controlled | Dynamic and supportive |
| Goal | Content delivery | Critical thinking and problem-solving |
Introduction to Teaching Paradigms
Teacher-centered paradigms emphasize structured instruction where educators control content delivery, fostering knowledge transmission and classroom management. Learner-centered approaches prioritize active student engagement, promoting critical thinking and personalized learning experiences to enhance comprehension. Understanding these paradigms informs effective teaching strategies tailored to diverse educational goals and learner needs.
Defining Teacher-Centered Approaches
Teacher-centered approaches prioritize the instructor as the primary source of knowledge, often involving direct instruction, lectures, and a structured curriculum. This model emphasizes standardized assessments, classroom management, and teacher control over learning pace and content delivery. The approach is designed to ensure content mastery through repetition, clear objectives, and a hierarchical classroom environment.
Understanding Learner-Centered Approaches
Learner-centered approaches prioritize active student engagement, critical thinking, and personalized instruction to enhance knowledge retention and skill development. These methods emphasize collaboration, self-directed learning, and adapting teaching strategies to meet diverse learner needs. Research demonstrates that learner-centered environments improve motivation, deepen understanding, and foster lifelong learning habits.
Key Differences Between Teacher-Centered and Learner-Centered
Teacher-centered approaches prioritize direct instruction, where the teacher controls curriculum, pace, and assessment methods, often emphasizing memorization and standardized testing. Learner-centered methods focus on student engagement, promoting critical thinking and collaboration with personalized learning paths and formative assessments. Key differences include the role of the teacher as a knowledge transmitter versus a facilitator, and the student's role as passive recipient versus active participant in the learning process.
Benefits of Teacher-Centered Learning
Teacher-centered learning provides structured guidance that ensures consistent curriculum coverage and clear expectations, which can enhance knowledge retention and assessment performance. The authoritative role of the teacher facilitates efficient classroom management and the delivery of expert insights, fostering a disciplined learning environment. This approach benefits learners who thrive under direct instruction and prefer clear, organized content delivery.
Advantages of Learner-Centered Education
Learner-centered education fosters critical thinking and enhances student engagement by prioritizing active participation and personalized learning experiences. It promotes collaboration, creativity, and deeper understanding through hands-on activities and real-world problem solving. This approach supports diverse learning styles and helps develop self-regulation and lifelong learning skills essential for academic success and personal growth.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Teacher-centered approaches often face challenges such as limited student engagement and reduced opportunities for critical thinking, as the focus remains on direct instruction and content delivery. Learner-centered methods can encounter limitations including difficulties in classroom management and inconsistent learning outcomes due to varying student autonomy and self-motivation levels. Both approaches must address these constraints to create effective, balanced educational environments that foster knowledge retention and active participation.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Teacher-centered approaches often result in lower student engagement as instruction is predominantly lecture-based, limiting active participation and critical thinking. Learner-centered methods promote higher achievement by fostering collaboration, personalized learning, and intrinsic motivation, leading to deeper understanding and retention. Research indicates that student-centered classrooms increase engagement metrics and improve standardized test scores compared to traditional teacher-driven environments.
Best Practices for Blending Both Approaches
Effective blending of teacher-centered and learner-centered approaches involves using direct instruction to provide foundational knowledge while incorporating active learning strategies that engage students in critical thinking and collaboration. Best practices include balancing structured lectures with student-led discussions, applying formative assessments to tailor instruction, and integrating technology to support personalized learning. This hybrid model enhances student motivation and achievement by combining authoritative guidance with opportunities for independent exploration.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Teacher-centered classrooms emphasize structured instruction with the educator as the primary knowledge source, promoting clear expectations and consistent assessment. Learner-centered classrooms prioritize student engagement, critical thinking, and personalized learning experiences to foster autonomy and deeper understanding. Selecting the right approach depends on factors like subject matter, student needs, and classroom dynamics to maximize educational outcomes.
Teacher-Centered Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com