A dean plays a crucial role in managing academic departments, overseeing faculty, and enhancing educational programs within a college or university. Effective deans foster a collaborative environment that supports student success and faculty development, aligning institutional goals with evolving educational standards. Explore the full article to understand how your experience with a dean can impact your academic journey.
Table of Comparison
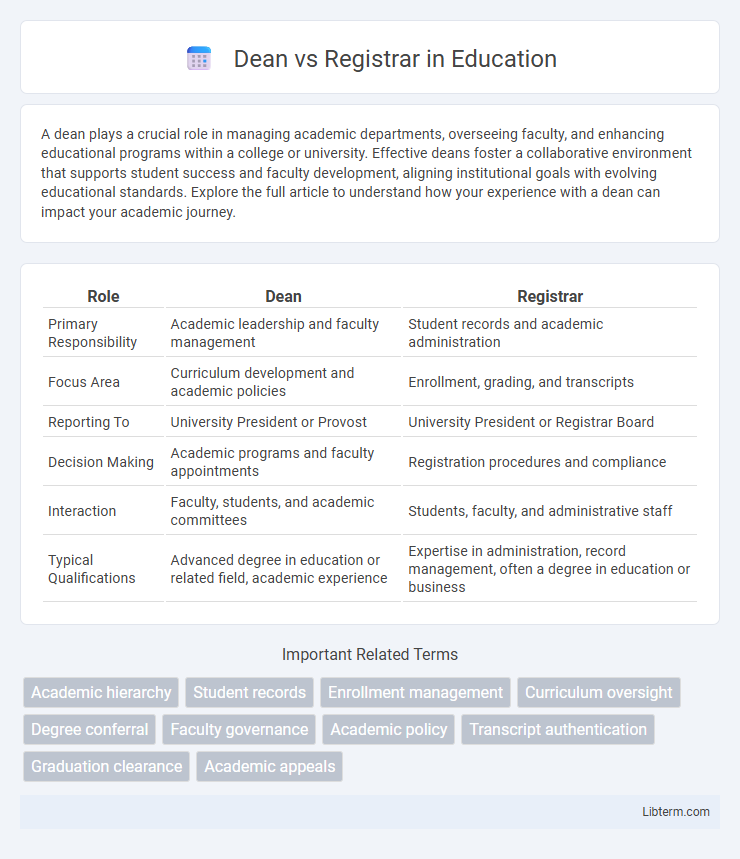
| Role | Dean | Registrar |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Academic leadership and faculty management | Student records and academic administration |
| Focus Area | Curriculum development and academic policies | Enrollment, grading, and transcripts |
| Reporting To | University President or Provost | University President or Registrar Board |
| Decision Making | Academic programs and faculty appointments | Registration procedures and compliance |
| Interaction | Faculty, students, and academic committees | Students, faculty, and administrative staff |
| Typical Qualifications | Advanced degree in education or related field, academic experience | Expertise in administration, record management, often a degree in education or business |
Introduction: Understanding the Roles of Dean and Registrar
The Dean oversees academic departments, faculty management, and curriculum development, ensuring educational excellence and strategic planning within a college or university. The Registrar manages student records, enrollment processes, and compliance with academic policies, playing a crucial role in maintaining institutional data integrity. Both positions are vital for the smooth operation and academic governance of higher education institutions.
Key Responsibilities of a Dean
A Dean is primarily responsible for academic leadership, overseeing curriculum development, faculty recruitment, and ensuring the quality of educational programs within a specific college or faculty. They manage budget allocation, strategic planning, and serve as the key liaison between faculty members and university administration. Unlike a Registrar, who handles student records and enrollment processes, the Dean focuses on promoting academic excellence and faculty development.
Core Functions of a Registrar
A Registrar oversees the administration of student records, course enrollment, and academic scheduling, ensuring compliance with institutional policies and legal requirements. They manage the maintenance and confidentiality of transcripts, diplomas, and grade reports while coordinating registration processes and graduation audits. The Registrar plays a critical role in supporting academic operations by facilitating data integrity, reporting, and communication between students, faculty, and administration.
Academic Leadership: The Dean’s Influence
The Dean exercises significant academic leadership by shaping curriculum development, overseeing faculty appointments, and guiding research priorities to align with institutional goals. Their role includes fostering a scholarly environment that promotes innovation and academic excellence across departments. This influence contrasts with the Registrar's administrative focus on student records and compliance, positioning the Dean as a central figure in strategic academic decision-making.
Administrative Excellence: The Registrar’s Impact
The Registrar's office drives administrative excellence by efficiently managing student records, course registrations, and compliance with academic policies, ensuring seamless institutional operations. Their expertise in data accuracy and regulatory adherence supports academic integrity and enhances the overall student experience. This administrative precision distinguishes the Registrar's role from the Dean's focus on academic leadership and strategic vision.
Qualifications and Career Paths
Deans typically hold advanced degrees such as a PhD or EdD in their academic discipline and have extensive experience in teaching, research, and academic leadership, often progressing from faculty positions to department chairs before becoming deans. Registrars generally possess qualifications in higher education administration or business, sometimes complemented by certifications like the ARMA (Association of Registrars of the University and College), advancing through roles in student services or academic administration to manage enrollment, records, and compliance. Career paths for deans emphasize academic scholarship and strategic leadership within colleges or schools, whereas registrars focus on operational management, regulatory adherence, and institutional data accuracy.
Collaboration Between Deans and Registrars
Deans and registrars collaborate closely to ensure academic programs run smoothly and policies are effectively implemented. Deans provide strategic academic leadership and curriculum oversight, while registrars manage student records, enrollment, and compliance with institutional regulations. Their partnership enhances student services, maintains data integrity, and supports institutional accreditation processes.
Decision-Making Authority: Who Holds What Power?
The Dean holds primary decision-making authority over academic policies, curriculum development, faculty appointments, and student affairs within their specific college or faculty. The Registrar manages administrative decisions related to student records, enrollment, exam scheduling, and compliance with institutional regulations but typically lacks academic policy control. While the Dean influences strategic academic directions, the Registrar ensures operational execution and procedural adherence within the institution.
Student Interaction: Dean vs Registrar Roles
The Dean primarily engages with students on academic policies, disciplinary matters, and overall academic guidance, shaping their educational experience and resolving high-level student issues. The Registrar manages student records, course enrollment, and grade reporting, ensuring smooth administrative processes and up-to-date academic documentation. While the Dean addresses strategic academic concerns and student advocacy, the Registrar focuses on operational tasks that maintain academic integrity and compliance.
Dean vs Registrar: Key Differences and Similarities
The Dean oversees academic policies, faculty matters, and curriculum development within a specific college or school, while the Registrar manages student records, enrollment, and course scheduling institution-wide. Both roles are crucial in higher education administration, ensuring academic integrity and efficient student services. Their collaboration supports a cohesive academic environment, balancing policy implementation with administrative operations.
Dean Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com