Transfer services provide a seamless way to move people or goods from one location to another efficiently and safely. Whether you require airport transfers, freight shipment, or digital data transfer, understanding the options and benefits helps you choose the best solution for your needs. Explore the rest of the article to discover how the right transfer method can optimize your logistics or personal travel experience.
Table of Comparison
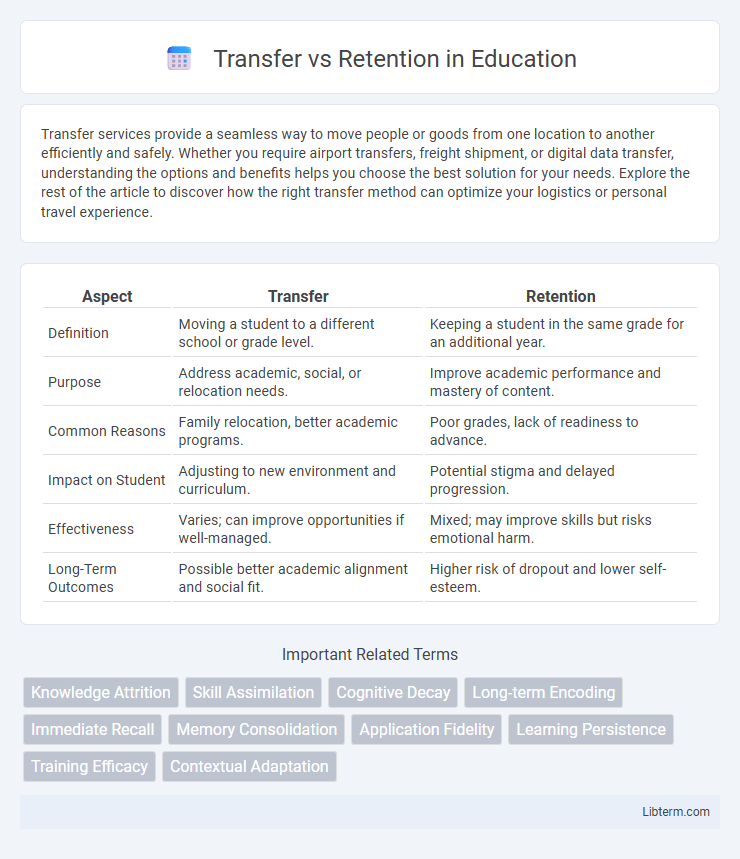
| Aspect | Transfer | Retention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving a student to a different school or grade level. | Keeping a student in the same grade for an additional year. |
| Purpose | Address academic, social, or relocation needs. | Improve academic performance and mastery of content. |
| Common Reasons | Family relocation, better academic programs. | Poor grades, lack of readiness to advance. |
| Impact on Student | Adjusting to new environment and curriculum. | Potential stigma and delayed progression. |
| Effectiveness | Varies; can improve opportunities if well-managed. | Mixed; may improve skills but risks emotional harm. |
| Long-Term Outcomes | Possible better academic alignment and social fit. | Higher risk of dropout and lower self-esteem. |
Understanding the Difference: Transfer vs Retention
Transfer refers to the process of moving or reallocating resources, knowledge, or data from one entity to another, often ensuring continuity or expansion. Retention emphasizes holding or maintaining these assets within the original environment to preserve stability and long-term value. Understanding the difference between transfer and retention is crucial for effective management strategies in business, education, and information technology.
Key Definitions: What is Transfer? What is Retention?
Transfer refers to the ability to apply knowledge or skills learned in one context to new or different situations, enhancing problem-solving and adaptability. Retention is the process of maintaining and recalling information over time, ensuring that learned material remains accessible for future use. Understanding the distinction between transfer and retention is crucial for optimizing educational strategies and improving long-term learning outcomes.
Importance of Transfer in Learning and Performance
Transfer of learning significantly enhances performance by enabling the application of acquired skills and knowledge to new and varied contexts, driving adaptability and problem-solving abilities. Effective transfer leads to deeper understanding, promotes critical thinking, and maximizes educational and training outcomes by bridging theory and real-world practice. Retention alone does not guarantee proficiency; the ability to transfer knowledge ensures long-term relevance and practical utility in dynamic environments.
The Role of Retention in Knowledge Preservation
Retention plays a critical role in knowledge preservation by ensuring that valuable information and skills remain accessible within an organization or individual over time. Effective retention strategies, such as documentation, continuous learning programs, and knowledge repositories, help prevent knowledge loss due to employee turnover or evolving technologies. This sustained knowledge base supports innovation, decision-making, and operational continuity, making retention indispensable for long-term organizational success.
Factors Influencing Effective Transfer of Knowledge
Effective transfer of knowledge depends on factors such as the similarity between learning and application contexts, learner motivation, and the quality of instructional design. Organizational culture that promotes knowledge sharing and access to resources significantly enhances knowledge retention and transfer. Cognitive load management and reinforcement strategies also play critical roles in ensuring that acquired knowledge is effectively applied in practical situations.
Strategies to Enhance Retention in Education
Effective strategies to enhance retention in education include incorporating active learning techniques, such as collaborative projects and problem-solving activities, which deepen understanding and long-term memory. Utilizing spaced repetition and regular formative assessments helps reinforce knowledge and identify gaps early, promoting sustained retention. Creating a supportive learning environment with personalized feedback and clear learning goals also boosts student engagement and commitment to the material.
Common Challenges in Achieving Transfer vs Retention
Common challenges in achieving transfer versus retention include difficulty in applying learned skills to real-world contexts and maintaining knowledge over time without reinforcement. Cognitive overload and lack of motivation often impede the transfer of training, while retention struggles arise from insufficient repetition and ineffective memory cues. Addressing these challenges requires targeted instructional design that emphasizes practice, feedback, and context-relevant learning experiences.
Assessment Methods: Measuring Transfer and Retention
Assessment methods for measuring transfer focus on evaluating how effectively learned skills or knowledge are applied in new or practical contexts, often using performance tasks, simulations, or real-world problem-solving scenarios. Retention assessment involves testing learners' ability to recall and utilize information over time through quizzes, standardized tests, or periodic reviews that gauge long-term memory. Both transfer and retention measurements rely on data analytics and feedback mechanisms to identify learning gaps and optimize instructional strategies.
Transfer and Retention in the Workplace: Best Practices
Transfer in the workplace involves applying learned skills and knowledge to new tasks and environments, enhancing overall performance and job adaptability. Retention focuses on maintaining employee knowledge and skills over time through continuous training, mentorship, and supportive work cultures. Effective practices include designing relevant training programs, regular skill assessments, and fostering a learning environment that encourages knowledge sharing and practical application.
Building a Balanced Approach: Integrating Transfer and Retention
Building a balanced approach to learning requires integrating transfer and retention strategies to enhance long-term skill acquisition and application. Effective retention anchors foundational knowledge through spaced repetition and active recall, while transfer encourages applying learned concepts across various contexts for deeper understanding. Combining these methods optimizes cognitive flexibility, promoting both durable memory and versatile problem-solving abilities.
Transfer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com