Fad-based practices often promise quick fixes or dramatic results but lack scientific backing and long-term effectiveness. These methods can lead to confusion and disappointment, diverting your focus from sustainable, evidence-based strategies. Discover the truth behind these trends and learn how to make informed decisions by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
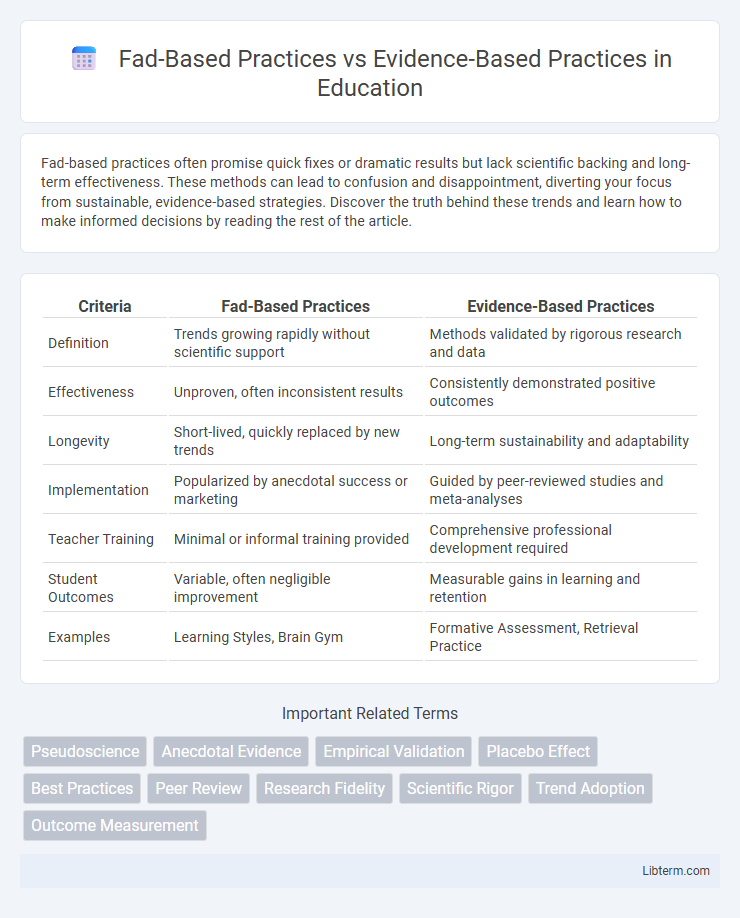
| Criteria | Fad-Based Practices | Evidence-Based Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trends growing rapidly without scientific support | Methods validated by rigorous research and data |
| Effectiveness | Unproven, often inconsistent results | Consistently demonstrated positive outcomes |
| Longevity | Short-lived, quickly replaced by new trends | Long-term sustainability and adaptability |
| Implementation | Popularized by anecdotal success or marketing | Guided by peer-reviewed studies and meta-analyses |
| Teacher Training | Minimal or informal training provided | Comprehensive professional development required |
| Student Outcomes | Variable, often negligible improvement | Measurable gains in learning and retention |
| Examples | Learning Styles, Brain Gym | Formative Assessment, Retrieval Practice |
Introduction to Fad-Based vs Evidence-Based Practices
Fad-based practices often gain rapid popularity despite lacking rigorous scientific support, potentially leading to inconsistent or ineffective results. Evidence-based practices rely on methodical research, clinical expertise, and validated data to ensure reliable and reproducible outcomes. Understanding the distinction between these approaches is crucial for effective decision-making and sustainable professional success.
Defining Fad-Based Practices
Fad-based practices are methodologies or interventions that gain rapid popularity despite lacking rigorous scientific validation or consistent empirical support. These practices often rely on anecdotal evidence, trend-driven adoption, and persuasive marketing rather than systematic research findings or peer-reviewed studies. The absence of reproducible outcomes and long-term efficacy data distinguishes fad-based approaches from evidence-based practices grounded in validated research protocols.
Understanding Evidence-Based Practices
Evidence-based practices (EBPs) prioritize the integration of current, high-quality research evidence with clinical expertise and patient preferences to ensure optimal outcomes across healthcare, education, and social services. Unlike fad-based practices, which often gain popularity without rigorous validation, EBPs rely on systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, and meta-analyses to guide decision-making. Implementing EBPs reduces variability in treatment effectiveness, enhances professional accountability, and ensures interventions are grounded in scientifically proven methodologies.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Fad-based practices prioritize trends and popular methods often lacking rigorous scientific validation, leading to inconsistent outcomes and potential risks. Evidence-based practices rely on systematic research, empirical data, and well-documented results, ensuring reliability and effectiveness across various fields. The key difference lies in the foundation of credibility--fad-based practices depend on anecdotal success and hype, while evidence-based approaches uphold standards of peer-reviewed studies and reproducible results.
The Appeal and Risks of Fad-Based Practices
Fad-based practices in healthcare and education often gain rapid popularity due to their promise of quick, effortless solutions, appealing to individuals seeking immediate results without rigorous scrutiny. These practices risk undermining professional standards and patient or student outcomes by promoting unvalidated methods lacking scientific backing or consistent effectiveness. Overreliance on such fads can lead to resource wastage, diminished trust in evidence-based interventions, and potential harm when misleading claims replace proven strategies.
Benefits of Evidence-Based Practices
Evidence-based practices enhance decision-making by integrating the latest research, clinical expertise, and patient preferences, leading to improved outcomes and consistent quality of care. These practices reduce the risks associated with unproven interventions commonly seen in fad-based approaches, promoting safety and effectiveness. Health professionals relying on evidence-based methods demonstrate higher accountability and adaptability to evolving scientific knowledge.
Common Examples in Various Fields
Fad-based practices such as detox diets in nutrition, rapid weight loss programs in fitness, and trendy management techniques like open office plans often gain quick popularity but lack scientific validation. Evidence-based practices include interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in psychology, evidence-based medicine protocols in healthcare, and Six Sigma methodologies in business, which rely on rigorous research and proven outcomes. Distinguishing between these approaches is crucial as evidence-based practices ensure effectiveness and reliability, while fad-based methods may lead to inconsistent or harmful results.
Identifying Red Flags of Fad-Based Methods
Identifying red flags of fad-based practices involves recognizing overly simplistic solutions promising quick, dramatic results without scientific backing or peer-reviewed research. These methods often rely on testimonials, lack transparency in methodology, and ignore established evidence-based guidelines, raising concerns about safety and efficacy. Health professionals recommend prioritizing treatments supported by rigorous clinical trials and consensus from reputable organizations to ensure reliable, effective care.
How to Transition Towards Evidence-Based Practices
Transitioning towards evidence-based practices requires integrating rigorous scientific research into decision-making processes and systematically evaluating current methods for efficacy and outcomes. Organizations should prioritize training staff in critical appraisal skills and implement standardized protocols that promote data-driven approaches over anecdotal or trend-driven methods. Establishing continuous feedback loops and utilizing reliable metrics ensures sustained adoption and refinement of evidence-based practices.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Science Over Trends
Prioritizing evidence-based practices ensures decisions are grounded in rigorous scientific research rather than fleeting trends, leading to more reliable and effective outcomes. Fad-based practices risk inefficiency and potential harm by lacking empirical support and reproducibility. Emphasizing validated data over popular but unproven methods strengthens long-term success and credibility in any professional or clinical setting.
Fad-Based Practices Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com