Problem-Based Learning engages students by presenting real-world challenges that require critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving skills. This approach encourages active participation, deeper understanding, and retention of knowledge through practical application. Explore the rest of this article to discover how Problem-Based Learning can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
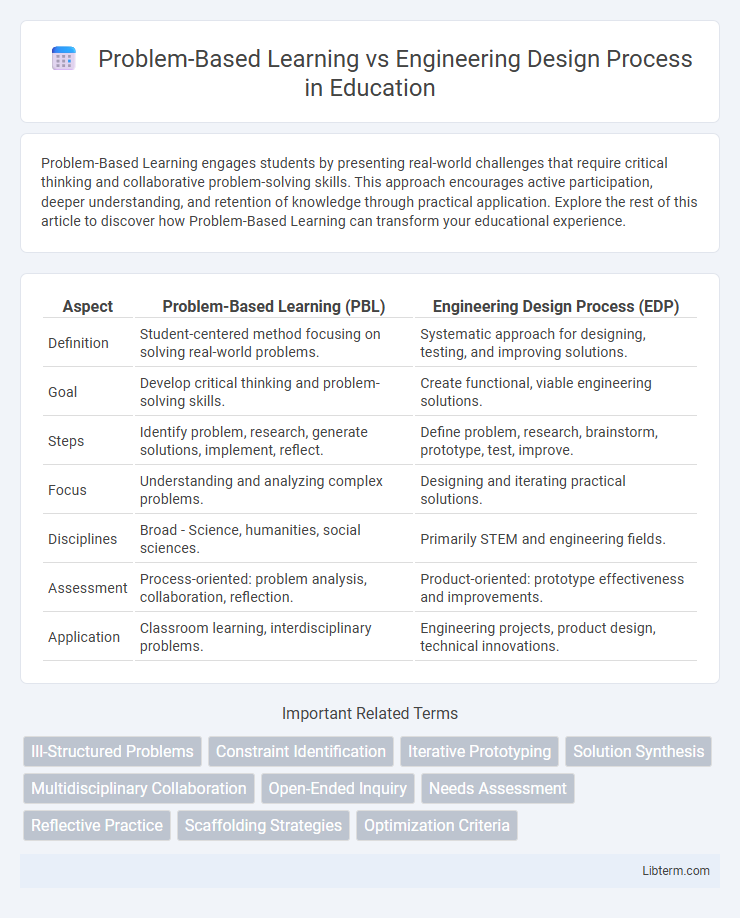
| Aspect | Problem-Based Learning (PBL) | Engineering Design Process (EDP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered method focusing on solving real-world problems. | Systematic approach for designing, testing, and improving solutions. |
| Goal | Develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. | Create functional, viable engineering solutions. |
| Steps | Identify problem, research, generate solutions, implement, reflect. | Define problem, research, brainstorm, prototype, test, improve. |
| Focus | Understanding and analyzing complex problems. | Designing and iterating practical solutions. |
| Disciplines | Broad - Science, humanities, social sciences. | Primarily STEM and engineering fields. |
| Assessment | Process-oriented: problem analysis, collaboration, reflection. | Product-oriented: prototype effectiveness and improvements. |
| Application | Classroom learning, interdisciplinary problems. | Engineering projects, product design, technical innovations. |
Introduction to Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional approach where students engage in solving complex, real-world problems to acquire new knowledge and skills. Unlike traditional methods, PBL emphasizes student-centered inquiry, critical thinking, and collaborative learning, fostering deeper understanding through active problem-solving. PBL frameworks often involve identifying problems, researching solutions, and reflecting on outcomes, which enhances skills essential for engineering and other disciplines.
Overview of the Engineering Design Process (EDP)
The Engineering Design Process (EDP) is a systematic, iterative series of steps engineers use to develop functional solutions to complex problems, typically involving defining the problem, researching, brainstorming, prototyping, testing, and refining. This approach emphasizes creating tangible, practical outcomes through continuous feedback and optimization, differentiating it from Problem-Based Learning which centers more on student-driven inquiry and knowledge construction. EDP's structured methodology enhances innovation by integrating technical criteria, constraints, and real-world applications throughout the design cycle.
Core Principles of Problem-Based Learning
Core principles of Problem-Based Learning (PBL) emphasize student-centered inquiry, where learners engage deeply with real-world problems to develop critical thinking and self-directed research skills. Unlike the linear, solution-focused Engineering Design Process, PBL encourages iterative exploration, collaboration, and reflective assessment to build knowledge through problem-solving. Key elements include defining authentic problems, facilitating active learning, and promoting metacognitive awareness to enhance understanding and application of concepts.
Essential Stages of the Engineering Design Process
The Engineering Design Process consists of essential stages including defining the problem, conducting research, brainstorming solutions, creating prototypes, testing, and refining designs to meet specific criteria and constraints. Problem-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven inquiry and real-world problem solving but lacks the structured iterative steps found in the Engineering Design Process. Understanding these stages enhances the application of engineering principles by promoting systematic analysis and continuous improvement within technical projects.
Key Similarities Between PBL and EDP
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) and the Engineering Design Process (EDP) both emphasize iterative problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Both approaches engage learners in real-world challenges, requiring research, ideation, prototyping, and testing to develop effective solutions. Collaboration, reflection, and continuous refinement are central elements that drive deeper understanding and innovation in both PBL and EDP.
Major Differences Between PBL and EDP
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes student-driven inquiry where learners identify problems and research solutions independently, fostering critical thinking and self-directed learning. The Engineering Design Process (EDP) follows a structured sequence of steps--defining a problem, brainstorming, prototyping, testing, and iterating--aimed specifically at creating functional engineering solutions. PBL is broader and applies to various disciplines with fluid problem definitions, while EDP is methodical and focused on producing tangible, optimized designs through iterative refinement.
Benefits of Implementing Problem-Based Learning
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and collaboration by engaging students in real-world problems that require interdisciplinary solutions. Unlike the linear steps of the Engineering Design Process, PBL encourages iterative inquiry and adaptability, fostering deeper conceptual understanding. Implementing PBL improves communication skills and prepares learners for complex, dynamic challenges in engineering and other STEM fields.
Advantages of Using the Engineering Design Process
The Engineering Design Process offers a structured, iterative framework that enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by emphasizing research, prototype development, and testing. It promotes collaboration and communication among team members, fostering innovation through continual refinement based on feedback. This method's clear stages align well with real-world engineering challenges, making it highly effective for developing practical, efficient solutions.
Choosing Between PBL and EDP in STEM Education
Choosing between Problem-Based Learning (PBL) and the Engineering Design Process (EDP) in STEM education depends on the instructional goals and desired skill development; PBL emphasizes critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving through real-world scenarios, while EDP focuses on iterative design, prototyping, and testing to develop engineering solutions. PBL fosters broader inquiry and exploration across disciplines, making it ideal for multidisciplinary STEM projects, whereas EDP provides a structured framework to address technical challenges with step-by-step refinement. Aligning the choice to curriculum outcomes ensures effective student engagement and mastery of both theoretical concepts and practical engineering skills.
Integrating PBL and EDP for Effective Learning
Integrating Problem-Based Learning (PBL) and the Engineering Design Process (EDP) fosters deeper understanding by combining real-world problem solving with systematic design steps. This approach enhances critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration, enabling learners to apply theoretical concepts through iterative prototyping and testing. Effective integration leverages PBL's emphasis on student-driven inquiry alongside EDP's structured methodology to produce impactful educational outcomes in STEM fields.
Problem-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com