Disciplinary actions maintain order and uphold standards within organizations by addressing violations of rules or policies promptly and fairly. Effective disciplinary measures promote a respectful and productive environment, ensuring that employees understand the consequences of their behavior. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to implement disciplinary procedures that protect your workplace culture.
Table of Comparison
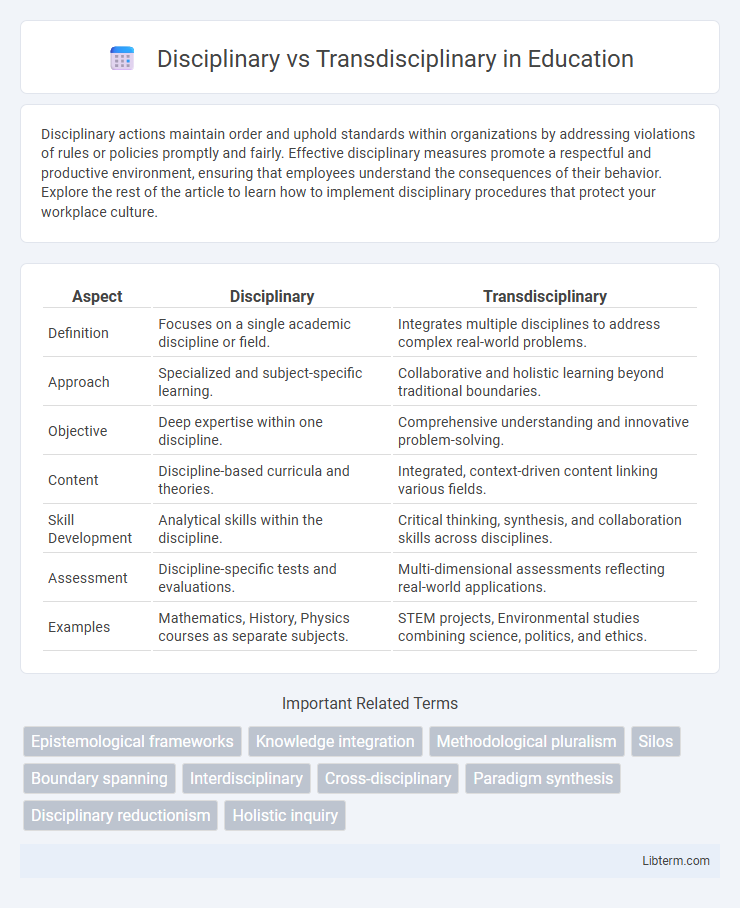
| Aspect | Disciplinary | Transdisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on a single academic discipline or field. | Integrates multiple disciplines to address complex real-world problems. |
| Approach | Specialized and subject-specific learning. | Collaborative and holistic learning beyond traditional boundaries. |
| Objective | Deep expertise within one discipline. | Comprehensive understanding and innovative problem-solving. |
| Content | Discipline-based curricula and theories. | Integrated, context-driven content linking various fields. |
| Skill Development | Analytical skills within the discipline. | Critical thinking, synthesis, and collaboration skills across disciplines. |
| Assessment | Discipline-specific tests and evaluations. | Multi-dimensional assessments reflecting real-world applications. |
| Examples | Mathematics, History, Physics courses as separate subjects. | STEM projects, Environmental studies combining science, politics, and ethics. |
Introduction to Disciplinary and Transdisciplinary Approaches
Disciplinary approaches concentrate on specialized knowledge within distinct academic fields, fostering deep expertise and methodological rigor. Transdisciplinary approaches integrate insights across multiple disciplines, transcending traditional boundaries to address complex, real-world problems through collaborative innovation. Understanding the contrast highlights the shift from isolated expertise to holistic, interconnected problem-solving frameworks in contemporary research and practice.
Defining Disciplinary Research
Disciplinary research entails in-depth exploration within a specific academic field, emphasizing specialized theories, methods, and knowledge unique to that discipline. It focuses on refining expertise and advancing understanding by operating within established boundaries and frameworks. This approach contrasts with transdisciplinary research, which integrates perspectives across multiple disciplines to address complex, real-world problems beyond traditional academic confines.
What is Transdisciplinary Research?
Transdisciplinary research transcends traditional disciplinary boundaries, integrating knowledge from diverse fields to address complex real-world problems holistically. Unlike disciplinary approaches that focus narrowly within specific fields, transdisciplinary research fosters collaboration among academics, practitioners, and stakeholders, producing innovative solutions grounded in multiple perspectives. This approach enhances problem-solving capacity by blending theoretical frameworks, methodologies, and empirical data from various disciplines into a unified, actionable strategy.
Core Principles of Disciplinary Methods
Disciplinary methods emphasize specialized knowledge, rigorous adherence to established theories, and systematic investigation within distinct academic boundaries. Core principles include precise terminology, methodological consistency, and validation through peer review, ensuring depth and reliability in research outcomes. This approach fosters expert understanding but often limits integration across diverse fields.
Fundamental Characteristics of Transdisciplinary Methods
Transdisciplinary methods integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines to address complex problems by transcending traditional academic boundaries, emphasizing collaboration and co-creation with non-academic stakeholders. These approaches prioritize holistic understanding, adaptive learning, and the synthesis of diverse perspectives to generate innovative solutions that are socially relevant and context-specific. Key characteristics include problem-centric frameworks, iterative processes, and the inclusion of both scientific and experiential knowledge.
Key Differences: Disciplinary vs Transdisciplinary
Disciplinary approaches focus on deep expertise within a single field, emphasizing specialized knowledge and methodologies unique to that discipline. Transdisciplinary methods integrate insights, theories, and techniques across multiple disciplines to address complex problems holistically. Key differences include the scope of collaboration, with disciplinary work confined to one area versus transdisciplinary efforts that transcend boundaries to co-create new frameworks and solutions.
Advantages and Limitations of Disciplinary Approaches
Disciplinary approaches offer deep expertise and specialized knowledge within a specific field, ensuring rigorous methodologies and established frameworks for problem-solving. However, their limitations include narrow perspectives that may overlook complex, multifaceted issues requiring integration across various fields. This specialization can hinder innovation and adaptability when addressing global challenges that demand collaborative, cross-disciplinary insights.
Benefits and Challenges of Transdisciplinary Approaches
Transdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge from multiple disciplines and non-academic sources, fostering innovative solutions for complex societal challenges through holistic understanding. Benefits include enhanced creativity, improved problem-solving capacity, and stronger stakeholder engagement, leading to practical and sustainable outcomes. Challenges involve managing diverse perspectives, overcoming communication barriers, and coordinating collaboration across varied expertise and organizational structures.
Practical Applications in Academia and Industry
Disciplinary approaches in academia and industry focus on deep expertise within a single field, facilitating specialized problem-solving and targeted innovation. Transdisciplinary methods integrate knowledge across multiple disciplines and stakeholders, promoting holistic solutions to complex real-world issues such as sustainability and healthcare. In practical applications, transdisciplinary collaboration enhances adaptability and creativity, driving breakthroughs beyond the scope of traditional disciplinary boundaries.
Future Trends: Integrating Disciplinary and Transdisciplinary Perspectives
Future trends emphasize the integration of disciplinary expertise with transdisciplinary collaboration to address complex global challenges effectively. This approach leverages deep domain knowledge while fostering holistic problem-solving through stakeholder engagement and knowledge co-creation. Advancements in digital platforms and data sharing accelerate the convergence of disciplinary and transdisciplinary methodologies for innovative research and policy development.
Disciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com