Direct Instruction is an evidence-based teaching method focusing on explicit, systematic, and structured guidance to help students grasp new concepts efficiently. Techniques include clear explanations, step-by-step demonstrations, and continuous assessment to ensure mastery at each learning stage. Discover how implementing Direct Instruction can transform Your teaching approach by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
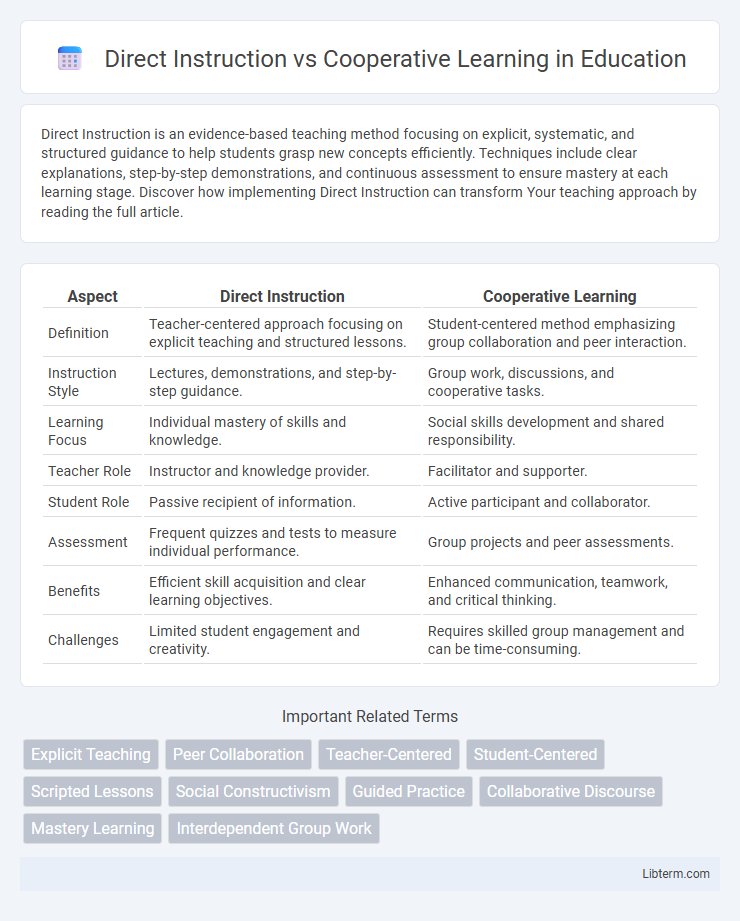
| Aspect | Direct Instruction | Cooperative Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered approach focusing on explicit teaching and structured lessons. | Student-centered method emphasizing group collaboration and peer interaction. |
| Instruction Style | Lectures, demonstrations, and step-by-step guidance. | Group work, discussions, and cooperative tasks. |
| Learning Focus | Individual mastery of skills and knowledge. | Social skills development and shared responsibility. |
| Teacher Role | Instructor and knowledge provider. | Facilitator and supporter. |
| Student Role | Passive recipient of information. | Active participant and collaborator. |
| Assessment | Frequent quizzes and tests to measure individual performance. | Group projects and peer assessments. |
| Benefits | Efficient skill acquisition and clear learning objectives. | Enhanced communication, teamwork, and critical thinking. |
| Challenges | Limited student engagement and creativity. | Requires skilled group management and can be time-consuming. |
Introduction to Direct Instruction and Cooperative Learning
Direct Instruction emphasizes explicit, structured teaching methods designed to deliver clear, concise lessons with immediate feedback to maximize student understanding and retention. Cooperative Learning involves students working in small groups to achieve shared learning goals, fostering collaboration, communication skills, and critical thinking. These two instructional strategies offer distinct approaches: Direct Instruction prioritizes teacher-led clarity and efficiency, while Cooperative Learning enhances peer interaction and active engagement.
Historical Background and Theoretical Foundations
Direct Instruction, developed in the 1960s by Siegfried Engelmann, is rooted in behaviorist theories emphasizing explicit, teacher-led training and measurable outcomes. Cooperative Learning, influenced by Vygotsky's social constructivism in the early 20th century, highlights interactive group work and peer collaboration as critical for cognitive development. Both methods reflect distinct philosophical foundations: Direct Instruction prioritizes structured skill acquisition, while Cooperative Learning fosters social interaction and shared knowledge construction.
Key Principles of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction emphasizes explicit teaching through scripted lessons, clear objectives, and immediate feedback to ensure mastery of content. It relies on systematic teacher-led demonstrations, frequent student practice, and ongoing assessment to monitor progress and correct errors promptly. This approach prioritizes structured, teacher-directed learning to maximize efficiency and student achievement.
Core Elements of Cooperative Learning
Core elements of cooperative learning include positive interdependence, individual accountability, and face-to-face promotive interaction, which foster deeper understanding through group collaboration. Structured group processing and heterogeneous group composition enhance social skills and ensure equitable participation. These elements contrast with Direct Instruction's teacher-centered approach by promoting active student engagement and shared responsibility for learning outcomes.
Comparison of Teaching Styles
Direct Instruction emphasizes structured, teacher-led lessons focusing on clear objectives and immediate feedback, promoting efficient skill acquisition and knowledge retention. Cooperative Learning centers on student collaboration, fostering critical thinking, communication, and social skills through group tasks and peer interaction. While Direct Instruction ensures content mastery with precise guidance, Cooperative Learning enhances interpersonal competencies and active engagement by encouraging shared responsibility and diverse perspectives.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Direct Instruction provides structured, teacher-led lessons that enhance clarity and focus, resulting in increased student engagement through clear expectations and immediate feedback. Cooperative Learning fosters collaboration and peer interaction, boosting motivation by promoting social skills and a sense of community among students. Research shows Cooperative Learning often leads to higher intrinsic motivation, while Direct Instruction excels in maintaining disciplined engagement and measurable academic progress.
Effectiveness in Academic Achievement
Direct Instruction consistently demonstrates higher effectiveness in academic achievement through its structured, explicit teaching methods and clear learning goals. Cooperative Learning promotes better development of social skills and engagement but often results in variable academic outcomes depending on group dynamics and individual participation. Research meta-analyses reveal that Direct Instruction yields stronger gains in standardized test scores and foundational skills compared to Cooperative Learning models.
Classroom Management and Implementation Challenges
Direct Instruction emphasizes structured, teacher-led lessons that facilitate strong classroom management through clear expectations and controlled pacing, minimizing disruptions and ensuring efficient content delivery. Cooperative Learning fosters student collaboration and active participation but often faces implementation challenges such as managing group dynamics, ensuring equal participation, and maintaining focus, which can complicate classroom control. Effective implementation of both strategies requires balancing the level of teacher control with student autonomy to optimize engagement while mitigating behavioral issues.
Suitability for Different Student Populations
Direct Instruction is highly effective for students requiring structured guidance and clear, explicit teaching methods, including learners with special needs or those struggling academically. Cooperative Learning suits diverse classrooms by promoting peer interaction, social skills, and collaborative problem-solving, benefiting students who thrive in interactive and communicative environments. Both approaches can be tailored to individual learner profiles, ensuring inclusive education across varied student populations.
Integrating Both Approaches for Optimal Learning
Integrating Direct Instruction and Cooperative Learning leverages structured, teacher-led guidance with collaborative, student-centered activities to enhance comprehension and retention. Combining explicit teaching of core concepts through Direct Instruction with cooperative peer interactions promotes deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. This blended approach addresses diverse learning needs, fosters engagement, and maximizes educational outcomes in diverse classroom settings.
Direct Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com