Exclusion refers to the act of deliberately or unintentionally leaving someone or something out from a group, activity, or consideration, which can lead to feelings of isolation and marginalization. Understanding the causes and effects of exclusion is essential for fostering inclusivity and ensuring that everyone's rights and needs are respected. Explore the rest of this article to learn how exclusion impacts various aspects of life and discover strategies to promote inclusion in your community.
Table of Comparison
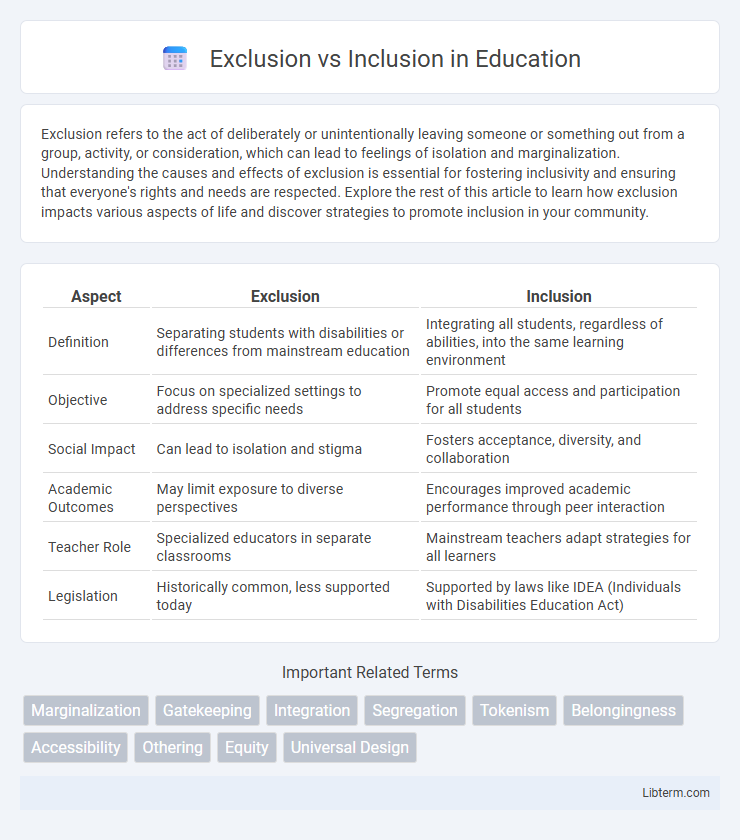
| Aspect | Exclusion | Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separating students with disabilities or differences from mainstream education | Integrating all students, regardless of abilities, into the same learning environment |
| Objective | Focus on specialized settings to address specific needs | Promote equal access and participation for all students |
| Social Impact | Can lead to isolation and stigma | Fosters acceptance, diversity, and collaboration |
| Academic Outcomes | May limit exposure to diverse perspectives | Encourages improved academic performance through peer interaction |
| Teacher Role | Specialized educators in separate classrooms | Mainstream teachers adapt strategies for all learners |
| Legislation | Historically common, less supported today | Supported by laws like IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) |
Understanding Exclusion and Inclusion
Understanding exclusion involves recognizing the barriers and social dynamics that prevent individuals or groups from accessing opportunities, resources, or participation in a community or system. Inclusion emphasizes creating environments where diversity is valued, and all members feel respected, supported, and able to contribute fully. Effective inclusion strategies address systemic inequalities by promoting equity, accessibility, and active engagement across social, educational, and organizational contexts.
Historical Perspectives on Exclusion
Historical perspectives on exclusion reveal systemic barriers faced by marginalized groups in various societies, often rooted in colonialism, slavery, and institutionalized racism. Exclusion has manifested through laws, social norms, and economic policies that marginalized ethnic minorities, women, and lower socio-economic classes, limiting their access to resources and opportunities. Understanding these historical patterns is essential for addressing entrenched inequalities and promoting inclusive policies in modern governance and social frameworks.
The Benefits of Inclusive Practices
Inclusive practices foster diverse perspectives that drive innovation and improve problem-solving within organizations. They enhance employee engagement by creating a sense of belonging, leading to higher retention rates and productivity. Research shows companies embracing inclusion experience up to 30% better financial performance compared to those practicing exclusion.
Social Impacts of Exclusion
Social exclusion generates significant negative impacts on mental health, economic opportunities, and community cohesion, often leading to increased poverty and social isolation. Marginalized groups experiencing exclusion face restricted access to education, healthcare, and employment, perpetuating cycles of disadvantage and systemic inequality. These consequences hinder social mobility and exacerbate disparities, emphasizing the critical need for inclusive policies and practices to foster equitable participation in society.
Psychological Effects of Inclusion
Inclusion promotes psychological well-being by fostering a sense of belonging and acceptance, which reduces feelings of isolation and anxiety. Social inclusion enhances self-esteem, encouraging positive interpersonal relationships and collaboration. Studies show inclusive environments improve mental health outcomes by boosting motivation and reducing stress.
Barriers to Achieving Inclusion
Barriers to achieving inclusion often stem from systemic exclusion rooted in social, economic, and institutional biases that limit access to opportunities for marginalized groups. Structural obstacles such as discriminatory policies, lack of accessible infrastructure, and insufficient representation in decision-making processes hinder equitable participation. Overcoming these barriers requires targeted interventions addressing underlying prejudices and promoting inclusive practices across all levels of society.
Strategies for Promoting Inclusion
Strategies for promoting inclusion emphasize creating accessible environments, implementing diverse hiring practices, and fostering cultural competence through ongoing training programs. Utilizing employee resource groups and inclusive leadership development contributes to higher engagement and retention of diverse talent. Leveraging technology for accommodation and encouraging open communication channels further supports an inclusive organizational culture.
Real-World Examples: Exclusion vs Inclusion
Workplaces that practice inclusion demonstrate higher employee engagement and innovation compared to those with exclusionary policies, as seen in companies like Microsoft and Salesforce that actively promote diverse hiring and inclusive cultures. Schools adopting inclusive education, such as those in Finland, report improved academic outcomes and social integration for students with disabilities versus exclusionary institutions. Urban planning projects, like Barcelona's superblocks, prioritize inclusive public spaces that foster community interaction, contrasting with exclusionary designs that segregate populations and reduce accessibility.
Inclusion in the Workplace and Education
Promoting inclusion in the workplace and education enhances collaboration, innovation, and employee or student engagement by valuing diverse perspectives and experiences. Inclusive environments reduce biases, improve retention rates, and foster a culture of belonging that drives productivity and academic success. Strategies such as equitable policies, accessibility accommodations, and diversity training are essential for building sustainable inclusion frameworks.
The Future of Exclusion and Inclusion
The future of exclusion and inclusion hinges on advancing equitable policies that leverage AI-driven analytics to identify and mitigate systemic biases in education, employment, and healthcare. Emerging technologies like machine learning and blockchain provide transparent frameworks for enhancing diversity while safeguarding privacy and fairness. Organizations prioritizing inclusive innovation are positioned to drive social cohesion, economic growth, and sustainable development globally.
Exclusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com